Abstract
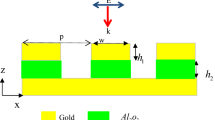
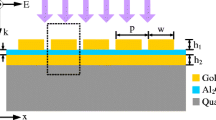
We propose a metal-dielectric-metal super absorber based on propagating and localized surface plasmons which exhibits a near perfect absorption in the visible and near-infrared spectrum. The absorber consists of Ag/Al2O3/Al triple layers in which the top Al layer is a periodic nano disk array. The absorption spectrum can be easily controlled by adjusting the structure parameters including the period and radius of the nano disk and the maximal absorption can reach 99.62 %. We completely analyze the PSPs and LSPs modes supported by the MDM structure and their relationship with the ultrahigh absorption. Moreover, we propose a novel idea to further enhance the absorption by exciting the PSPs and high-order LSPs modes simultaneously, which is different from the previous works. This kind of absorber using stable inexpensive Al instead of noble metal Au or Ag is an appropriate candidate for photovoltaics, spectroscopy, photodetectors, sensing, and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watts CM, Liu X, Padilla WJ (2012) Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers. Adv Mater 24:98–120
Cheng S, Jie S, Wang X (2015) A design of thin film silicon solar cells based on silver nanoparticle arrays. Plasmonics 10:633–641
Yen-Hsun S, Ke Y-F, Cai S-L, Yao QY (2014) Surface plasmon resonance of layer-by-layer gold nanoparticles induced photoelectric current in environmentally-friendly plasmon-sensitized solar cell. Light Sci Appl 3:e222
Chalabi H, Schoen D, Brongersma ML (2014) Hot-electron photodetection with a plasmonic nanostripe antenna. Nano Lett 14:1374–1380
Park B, Yun SH, Cho CY, Kim YC, Shin JC, Jeon HG, Huh YH, Hwang I, Baik KY, Lee YI, Uhm HS, Cho GS, Choi EH (2012) Surface plasmon excitation in semitransparent inverted polymer photovoltaic devices and their applications as label-free optical sensors. Light Sci Appl 1:e14
Argyropoulos C, Le KQ, Mattiucci N, D’Aguanno G, Alu A (2013) Broadband absorbers and selective emitters based on plasmonic Brewster metasurfaces. Phys Rev B 87:205112
W. W. Salisbury, (June 10, 1952) Absorbent body for electromagnetic waves. U S patent 2:599-944.
Lee W, Kinosita Y, Youngjin O, Mikami N, Yang H, Miyata M, Nishizaka T, Kim D (2015) Three-dimensional super localization imaging of gliding Mycoplasma mobile by extraordinary light transmission through arrayed nano holes. ACS Nano 9:10896–10908
Hu XL, Sun LB, Beibei Z, Wang LS, Yu ZG, Bai SA, Yang SM, Zhao LX, Li Q, Qiu M, Tai RZ, Fecht HJ, Jiang JZ, Zhang DX (2016) Polarization-independent plasmonic subtractive color filtering in ultrathin Ag nanodisks with high transmission. Appl Opt 55(1):148–152
Chu Y, Banaee MG, Crozier KB (2010) Double-resonance plasmon substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering with enhancement at excitation and stokes frequencies. ACS Nano 4:2804–2810
Dayal G, Anantha Ramakrishna S (2012) Design of highly absorbing metamaterials for infrared frequencies. Opt Express 20(16):17503–17508
Chen J, Hu J (2014) Strong coupling between localized and propagating surface plasmon modes in a noncentrosymmetric metallic photonic slab. J Opt Soc Am B 31(7):1600–1606
Wang BX, Zhai X, Wang GZ, Huang WQ, Wang LL (2015) A novel dual-band terahertz metamaterial absorber for a sensor application. J Appl Phys 117:014504–014501
Dong X, Tao K, Wang Q (2015) Ultrabroadband mid-infrared light absorption based on a multi-cavity plasmonic metamaterial Array. Plasmonics 10:1007
Lin C-H, Chern R-L, Lin H-Y (2011) Polarization-independent broad-band nearly perfect absorbers in the visible regime. Opt Express 19(2):415–424
Hao J, Wang J, Liu X, Padilla WJ, Zhou L, Qiu M (2010) High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl Phys Lett 96:251104
Li Y, An B, Jiang S, Gao J, Chen Y, Li SPY, An B, Jiang S, Gao J, Chen Y, Pan S (2015) Plasmonic induced triple-band absorber for sensor application. Opt Express 23(13):17607–17612
Knight MW, King NS, Liu L, Everitt HO, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2014) Aluminum for plasmonics. ACS Nano 8:834–840
Knight MW, Liu L, Wang Y, Brown L, Mukherjee S, King NS, Everitt HO, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2012) Aluminum plasmonic nanoantennas. Nano Lett 12:6000–6004
Palik ED (1998) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, New York
Zheng YB, Juluri BK, Mao X, Walker TR, Huang TJ (2008) Systematic investigation of localized surface plasmon resonance of long-range ordered Au nanodisk arrays. J Appl Phys 103:014308
Li G, Yang S, Xiao G, Jin C (2015) Double-layered metal grating for high performance refractive index sensing. Opt Express 23(7):8995–9003
Genet C, Ebbesen TW (2007) Light in tiny holes. Nature 445:39–46
Chen J, Wang P, Zhang ZM, Lu Y, Ming H (2011) Coupling between gap plasmon polariton and magnetic polariton in a metallic-dielectric multilayer structure. Phys Rev E 84:026603
Li W, Valentine J (2014) Metamaterial perfect absorber based hot electron photodetection. Nano Lett 14:3510–3514
Chu Y, Crozier KB (2009) Experimental study of the interaction between localized and propagating surface plasmons. Opt Lett 34(3):244–246
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61306125 and U1435210), the Science and Technology Innovation Project (Y3CX1SS143) of CIOMP, the Science and Technology Innovation Project of Jilin Province (Nos. Y3293UM130, 20130522147JH, and 20140101176JC), and the Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of CAS (CXJJ-15Q071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Gao, J., Yang, H. et al. Tunable Plasmonic Absorber Based on Propagating and Localized Surface Plasmons Using Metal-Dielectric-Metal Structure. Plasmonics 12, 1037–1043 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0356-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0356-5