Abstract
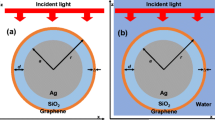
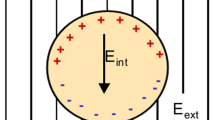
Graphene, new generation advance material of two dimensional hexagonal lattice having extraordinary optical signatures, is used as coating material to enhance the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect of core@shell metal nanospheres. In a core@shell nanosphere, we have chosen metal as a core and graphene monolayer (GML) as a shell. We have analysed optical signature of coated and non-coated nanospheres in terms of extinction efficiency (Q ext) and tunabilty of surface plasmon resonances using electrostatic model, where particle size is much smaller than the wavelength of incident light. We analysed this model over different metals (silver, gold and aluminium) core, coated with different thickness of GML (d = 0.1 to 0.5 nm). These core@shell nanospheres are embedded in refractive index media of air (n em = 1), SiO2 (n em = 1.47) and TiO2 (n em = 2.79). The Q ext has been calculated by varying both the core radii as well as the GML shell thickness. Graphene-coated metal nanosphere exhibits SPRs that have wide range tunability from 300 to 1500 nm. In the presenting work, we also analysed that extinction efficiency for metal@GML is higher in TiO2 than others. The optimum value of GML shell thickness is 0.4 nm for TiO2, the magnitude of extinction efficiency is maximum for the optimum thickness. The tunability of these plasmonic resonances is highly dependent on the core@shell material, thickness of Graphene shell and surrounding environment while non-coated metal nano-spheres do not show appropriate SPR tunability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kreibig U, Vollmer M (1995) Optical properties of metal clusters. Springer, Berlin
Noguez C (2007) Surface plasmons on metal nanoparticles: the influence of shape and physical environment. J Phys Chem C111(10):3806–3819
Maier S (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, Berlin
Jain PK, Lee KS, ElSayed IH, ElSayed MA (2006) Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B 110(14):7238
Wood V, Panzer MJ, Caruge JM, Halpert JE, Bawendi MG, Bulovic V (2010) Air-stable operation of transparent, colloidal quantum dot based LEDs with a unipolar device architecture. Nano Lett 10:24–29
Liang Z, Sun J, Jiang Y, Jiang L, Chen X (2014) Plasmonic enhanced optoelectronic devices. Plasmonics 9:859–866
McFarland AD, Van Duyne RP (2003) Single silver nanoparticles as real-time optical sensors with zeptomole sensitivity. Nano Lett 3(8):1057
Juan ML, Righini M, Quidant R (2011) Plasmon nano-optical tweezers. Nat Photonics 5:349–356
Dirix Y, Bastiaansen C, Caseri W, Smith P (1999) Oriented pearl‐necklace arrays of metallic nanoparticles in polymers: a new route toward polarization‐dependent color filters. Adv Mater 11(3):223–227
Moskovits M (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: a brief retrospective. J Raman Spectrosc 36:485–496
Inouye H, Tanaka K, Tanahashi I, Hattori T, Nakatsuka H (2000) Ultrafast optical switching in a silver nanoparticle system. Jpn J Appl Phys 39:5132
Spinelli P, Ferry VE, van de Groep J, van Lare M, Verschuuren MA, Schropp REI, Atwater HA, Polman A (2012) Plasmonic light trapping in thin-film Si solar cells. J Opt 14:024002 (11pp)
Amendola V, Bakr OM, Stellacci F (2010) A study of the surface Plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles by the discrete dipole approximation method: effect of shape, size, structure, and assembly. Plasmonics 5:85–97
Zhang W, Saliba M, Stranks SD, Sun Y, Shi X, Wiesner U, Snaith HJ (2013) Enhancement of perovskite-based solar cells employing core-shell metal nanoparticles. Nano Lett 13:4505–4510
Chen B, Deng J, Tong L, Yang W (2010) Optically active helical polyacetylene@silica hybrid organic–inorganic core/shell nanoparticles: preparation and application for enantioselective crystallization. Macromolecules 43:9613–9619
Das S, Chattopadhyay A (2012) Generation of inorganic–organic core-shell crystalline nanoparticles of silver and p-hydroxyacetanilide. RSC Adv 2:10245–10250
Yang Y, Shi J, Kawamurab G, Nogami M (2008) Preparation of Au-Ag, Ag-Au coreshellbimetallic nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Scr Mater 58:862–865
Tong Y, Bohm S, Song M (2013) Carbon based coating on steel with improved electrical conductivity. Austin J Nanomedicine Nanotechnol 1(1):1003, 16pp
Bian T, Chang R, Leung PT (2016) Förster resonance energy transfer between molecules in the vicinity of graphene-coated nanoparticles. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s11468-015-0167-0
Grigorenko AN, Polini M, Novoselov KS (2012) Grapheneplasmonics. Nat Photonics 6:749–758
Lv W, Phelan PE, Swaminathan R, Otanicar TP, Taylor RA (2013) Multifunctional coreshell nanoparticle suspensions for efficient absorption. J Sol Energy Eng 135:021005 (7 pp)
Lu H, Cumming BP, Gu M (2015) Highly efficient plasmonic enhancement of graphene absorption at telecommunication wavelengths. Opt Lett 40(15):3647–3650
Hwang EH, Sensarma R, Das Sarma S (2010) Plasmon-phonon coupling in grapheme. Phys Rev B 82:195406
Koppens FHL, Chang DE, García de Abajo FJ (2011) Graphene Plasmonics: a platform for strong light–matter interactions. Nano Lett 11:3370–3377
Zhou W, Lee J, Nanda J, Pantelides ST, Pennycook SJ, Idrobo JC (2012) Atomically localized plasmon enhancement in monolayer grapheme. Nat Nanotechnol 7:161–165
Kanade P, Yadav P, Kumar M, Tripathi B (2015) Plasmon-induced photon manipulation by Ag nanoparticle-coupled graphene thin-film: light trapping for photovoltaics. Plasmonics 10:157–164
Palik ED (ed) (1985) Handbook of optical constants of solids. Academic, Orlando
Bohren CF, Huffman DR (1998) Absorption and scattering of light by small particles. Wiley, New York
Bao Q, Zhang H, Wang B, Ni Z, Lim C, Wang Y, Tang D, Loh K (2011) Broadband graphene polarizer. Nat Photonics 5:411–415
Wang B, Zhang X, GarcíaVidal F, Yuan X, Teng J (2012) Strong coupling of surface plasmon polaritons in monolayer graphene sheet arrays. Phys Rev Lett 109:07390
Zhao B, Zhao JM, Zhang ZM (2014) Enhancement of near-infrared absorption in graphene with metal gratings. Appl Phys Lett 105:031905
Bhardwaj S, Pathak NK, Ji A, Uma R, Sharma RP (2016) Tunable properties of surface plasmon resonance of metal nanospheroid: graphene plasmon interaction. Plasmonics. doi:10.1007/s1146801602497
Chew WC (1999) Waves and fields in inhomogeneous media. Wiley IEEE Press, New York
Wang B, Zhang X, Yuan X, Teng J (2012) Optical coupling of surface plasmons between graphene sheets. Appl Phys Lett 100:131111
Acknowledgment
This research is financially supported by MNRE India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhardwaj, S., Uma, R. & Sharma, R.P. A Study of Metal@Graphene Core–Shell Spherical Nano-Geometry to Enhance the SPR Tunability: Influence of Graphene Monolayer Shell Thickness. Plasmonics 12, 961–969 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0347-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0347-6