Abstract
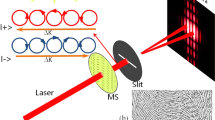
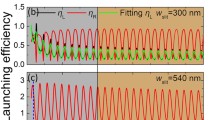
We proposed a scheme to tune the propagation direction of surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) by external control of the polarization and/or the inclination angle of the incident light. The phase of the SPPs generated by the laser beam through slits can be divided into two parts: the position-related phase which is affected by the position of slits and spin-related phase which is affected by the orientation of slits and spin of photons. Using theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, we studied the position-related phase and spin-related phase of the SPPs excited by an inclined and circularly polarized light through a column of slits and then designed symmetric V-type slit array. We found when the incident light is in the symmetry plane of symmetric V-type slit array, spin of the incident light would give directions of surface plasmon propagation and the inclination angle of the incident light would give the inclination angle of surface plasmon propagation. The result shows that we may tune the propagation of the SPPs with significant flexibility, by changing the polarization of the incident light and the inclination angle of the incident light. Our designed launcher, as a spin plasmonic device under control, is expected to be of interest for future applications in photonic integrated circuits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Sosnova MV, Mamykin SV, Korovin AV, Dmitruk NL (2016) Hybridization of surface plasmon polariton and photonic crystal modes in bragg mirror with periodically profiled metal film. Nanoscale Res Lett 144:1–7
Fang ZY, Qi H, Wang C, Zhu X (2010) Hybrid plasmonic waveguide based on tapered dielectric nanoribbon: excitation and focusing. Plasmonics 5:207–212
Lerman GM, Yama A, Levy U (2009) Demonstration of nanofocusing by the use of plasmonic lens illuminated with radially polarized light. Nano Lett 9:2139–2143
Lee B, Kim S, Kim H, Lim Y (2010) The use of plasmonics in light beaming and focusing. Prog Quantum Electron 34:47–87
Falk AL, Koppens FHL, CL Y, Kang K, Snapp ND, Akimov AV, Jo MH, Lukin MD, Park H (2009) Near-field electrical detection of optical plasmons and single plasmon sources. Nat Phys 5:475–479
Fang ZY, YW L, Fan LR, Lin CF, Zhu X (2010) Surface plasmon polariton enhancement in silver nanowire-nanoantenna structure. Plasmonics 5:57–62
Volkov VS, Bozhevolnyi SI, Leosson K, Boltasseva A (2003) Experimental studies of surface plasmon polariton band gap effect. J Microsc 210:324–329
Fang ZY, Zhang XJ, Liu D, Zhu X (2008) Excitation of dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton observed by using near-field optical microscopy. Appl Phys Lett 93:073306
Pyayt AL, Wiley B, Xia YN, Chen A, Dalton L (2008) Integration of photonic and silver nanowire plasmonic waveguides. Nat Nanotechnol 3:660–665
Kneipp K, Wang Y, Kneipp H, Perelman LT, Itzkan I, Dasari R, Feld MS (1997) Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS). Phys Rev Lett 78:1667–1670
Yang J, Xiao X, Hu C, Zhang WW, Zhou SX, Zhang JS (2014) Broadband surface plasmon polariton directional coupling via asymmetric optical slot nanoantenna pair. Nano Lett 14:704–709
Zhang YF, Wang HM, Liao HM, Li Z, Sun CW, Chen JJ, Gong QH (2014) Unidirectional launching of surface plasmons at the subwavelength scale. Appl Phys Lett 105:231101
Chen JJ, Sun CW, Li HY, Gong QH (2014) Ultra-broadband unidirectional launching of surface plasmon polaritons by a double-slit structure beyond the diffraction limit. Nanoscale 6:13487–13493
Baron A, Devaux E, Rodier JC, Hugonin JP, et al. (2011) Compact antenna for efficient and unidirectional launching and decoupling of surface plasmons. Nano Lett 11:4207–4212
Liu YM, Palomba S, Park Y, Zentgraf T, Yin XB, Zhang X (2012) Compact magnetic antennas for directional excitation of surface plasmons. Nano Lett 12:4853–4858
Lin J, Mueller JPB, Wang Q, Yuan GH, Antoniou N, Yuan XC, Capasso F (2013) Polarization-controlled tunable directional coupling of surface plasmon polaritons. Science 340:331–334
Li JM, Tang P, Liu W, Huang T, Wang JJ, Wang YQ, Lin F, Fang ZY, Zhu X (2015) Plasmonic circular polarization analyzer formed by unidirectionally controlling surface plasmon propagation. Appl Phys Lett 106:161106
Rodriguez-Fortuno FJ, Marino G, Ginzburg P, O’Connor D, Martinez A, Wurtz GA, Zayats AV (2013) Near-field interference for the unidirectional excitation of electromagnetic guided modes. Science 340:328–330
Bao YJ, Zu S, Zhang YF, Fang ZY (2015) Active control of graphene-based unidirectional surface plasmon launcher. ACS Photonics 2:1135–1140
Maier SA (2007) Plamonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer-Verlag, New York
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Nos. 61176120, 61378059, 60977015, and 11374023 and National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program), Grant No. 2012CB933004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, T., Wang, J., Liu, W. et al. Spin-Controlled Directional Launching of Surface Plasmons Under Oblique Illumination. Plasmonics 12, 729–734 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0319-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0319-x