Abstract
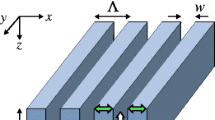
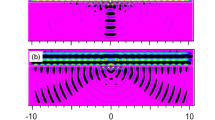
A modified transmission line model with the equivalent capacitors is proposed to describe extraordinary optical transmission (EOT) of the sub-wavelength slit with different inner walls. The equivalent capacitors can effectively explain the discontinuity of the interface at which the surface wave propagates. The transmittance calculated with this model is in accordance with finite difference time domain (FDTD) calculations. This modified analytical model provides a methodology to analyze the transmission properties of sub-wavelength slits with different inner walls. The results show that if well-designed and manufactured, sub-wavelength curved slits have the ability to enhance the optical transmission in the visible region or the infrared region.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebbesen TW, Lezec HJ, Ghaemi HF, Thio T, Wolff PA (1998) Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays. Nature 391(6668):667–669
Porto J, Garcia-Vidal F, Pendry J (1999) Transmission resonances on metallic gratings with very narrow slits. Phys Rev Lett 83(14):2845–2848
Gordon R, Sinton D, Kavanagh KL, Brolo AG (2008) A new generation of sensors based on extraordinary optical transmission. Accounts Chem Res 41(8):1049–1057
Brolo AG, Gordon R, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL (2004) Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 20(12):4813–4815
Yoon Y-T, Park C-H, Lee S-S (2012) Highly efficient color filter incorporating a thin metal-dielectric resonant structure. Appl Phys Express 5(2):022501
Park C-H, Yoon Y-T, Lee S-S (2012) Polarization-independent visible wavelength filter incorporating a symmetric metal-dielectric resonant structure. Opt Express 20(21):23769–23777
Verslegers L, Catrysse PB, Yu Z, White JS, Barnard ES, Brongersma ML, Fan S (2008) Planar lenses based on nanoscale slit arrays in a metallic film. Nano Lett 9(1):235–238
Xie Z, Yu W, Wang T, Zhang H, Fu Y, Liu H, Li F, Lu Z, Sun Q (2011) Plasmonic nanolithography: a review. Plasmonics 6(3):565–580
Cetnar JS, Middendorf JR, Brown ER (2012) Extraordinary optical transmission and extinction in a Terahertz wire-grid polarizer. Appl Phys Lett 100(23):231912
Zhai YS, Wang QL, Li XH, Chen XQ, Huang QQ, Zhao J, Liu J, Xia J (2014) Broadband extraordinary optical transmission of sub-wavelength metallic grating with parabolic wall. J Mod Opt 61(6):530–535
Shen HH, Maes B (2012) Enhanced optical transmission through tapered metallic gratings. Appl Phys Lett 100(24):241104
Sondergaard T, Bozhevolnyi SI, Beermann J, Novikov SM, Devaux E, Ebbesen TW (2012) Extraordinary optical transmission with tapered slits: effect of higher diffraction and slit resonance orders. J Opt Soc Am B-Opt Phys 29(1):130–137
Liang Y, Peng W, Hu R, Zou H (2013) Extraordinary optical transmission based on subwavelength metallic grating with ellipse walls. Opt Express 21(5):6139–6152
Martín-Moreno L, García-Vidal FJ, Lezec HJ, Pellerin KM, Thio T, Pendry JB, Ebbesen TW (2001) Theory of extraordinary optical transmission through subwavelength hole arrays. Phys Rev Lett 86(6):1114–1117
Hibbins AP, Sambles JR, Lawrence CR (2002) Gratingless enhanced microwave transmission through a subwavelength aperture in a thick metal plate. Appl Phys Lett 81(24):4661–4663
Beruete M, Sorolla M, Campillo I, Dolado J, Martín-Moreno L, Bravo-Abad J, García-Vidal F (2004) Enhanced millimeter-wave transmission through subwavelength hole arrays. Opt Lett 29(21):2500–2502
Pendry JB, Martín-Moreno L, Garcia-Vidal FJ (2004) Mimicking surface plasmons with structured surfaces. Science 305(5685):847–848
Medina F, Mesa F, Marques R (2008) Extraordinary transmission through arrays of electrically small holes from a circuit theory perspective. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techniques 56(12):3108–3120
Medina F, Mesa F, Skigin DC (2010) Extraordinary transmission through arrays of slits: a circuit theory model. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techniques 58(1):105–115
Alù A, D’Aguanno G, Mattiucci N, Bloemer MJ (2011) Plasmonic brewster angle: broadband extraordinary transmission through optical gratings. Phys Rev Lett 106(12):123902
Rakic AD, Djurisic AB, Elazar JM, Majewski ML (1998) Optical properties of metallic films for vertical-cavity optoelectronic devices. Appl Opt 37(22):5271–5283
Medina F, Rodriguez-Berral R, Mesa F (2012) Circuit model for metallic gratings with tapered and stepped slits, in Microwave Conference (EuMC), 42nd European (IEEE, 2012), p. 1225–8
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the financial supports by the National Science Foundation of China (61007036, 61203192,51477028), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2012326), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University, and Graduate Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYLX_0124).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Zhai, Y., Wu, S. et al. A Modified Transmission Line Model for Extraordinary Optical Transmission Through Sub-wavelength Slits. Plasmonics 10, 1545–1549 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9952-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9952-z