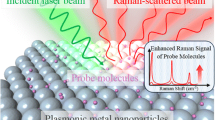
Abstract
In this paper, we report on an improved enhancement of the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect. Such improvement is obtained by using a continuous gold film (underlayer), which is added below an array of gold nanostructures. Two types of nanostructures were studied to validate our results: regular disk arrays with two diameters (110 and 210 nm) and lines with a width of 110 nm, all on a gold film of 30 nm thick. A supplementary gain of one order of magnitude on the SERS enhancement factor (EF) was experimentally demonstrated for several excitation wavelengths: 633, 660, and 785 nm. With such SERS substrates, EFs of 107 are observed for thiophenol detection. This opens the way towards routine and reliable detection of molecules at low concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raman CV (1928) A new radiation. Indian J Phys 2:387–398
Fleischmann M, Hendra P, McQuillan A (1974) Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem Phys Lett 26(2):163–166. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(74)85388-1
Le Ru EC, Etchegoin PG (2012) Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu Rev Phys Chem 63(1):65–87. doi:10.1146/annurev-physchem-032511-143757
Sharma B, Frontiera RR, Henry A-I, Ringe E, Van Duyne RP (2012) SERS: materials, applications, and the future. Materials Today 15(1–2):16–25. doi:10.1016/S1369-7021(12)70017-2
Guillot N, de la Chapelle ML (2012) Lithographied nanostructures as nanosensors. NANOP 6 (1):064506-064501-064506-064528. doi:10.1117/1.JNP.6.064506
Vo-Dinh T, Wang H-N, Scaffidi J (2010) Plasmonic nanoprobes for SERS biosensing and bioimaging. J Biophotonics 3(1–2):89–102. doi:10.1002/jbio.200910015
Tian ZQ, Ren B, Wu DY (2002) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: from noble to transition metals and from rough surfaces to ordered nanostructures. J Phys Chem B 106(37):9463–9483. doi:10.1021/jp0257449
Baia M, Baia L, Astilean S, Popp J (2006) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering efficiency of truncated tetrahedral Ag nanoparticle arrays mediated by electromagnetic couplings. Appl Phys Lett 88(14), 143121. doi:10.1063/1.2193778
Yuan H, Fales AM, Khoury CG, Liu J, Vo-Dinh T (2013) Spectral characterization and intracellular detection of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-encoded plasmonic gold nanostars. J Raman Spectrosc 44(2):234–239. doi:10.1002/jrs.4172
Vo-Dinh T, Dhawan A, Norton SJ, Khoury CG, Wang H-N, Misra V, Gerhold MD (2010) Plasmonic nanoparticles and nanowires: design, fabrication and application in sensing. J Phys Chem C 114(16):7480–7488. doi:10.1021/jp911355q
Guillot N, de la Chapelle ML (2012) The electromagnetic effect in surface enhanced Raman scattering: enhancement optimization using precisely controlled nanostructures. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transf 113(18):2321–2333. doi:10.1016/j.jqsrt.2012.04.025
Brown RJC, Milton MJT (2008) Nanostructures and nanostructured substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). J Raman Spectrosc 39(10):1313–1326. doi:10.1002/jrs.2030
Cialla D, Marz A, Bohme R, Theil F, Weber K, Schmitt M, Popp J (2012) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): progress and trends. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(1):27–54. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5631-x
Fan M, Andrade GFS, Brolo AG (2011) A review on the fabrication of substrates for surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and their applications in analytical chemistry. Anal Chim Acta 693(1–2):7–25. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.03.002
Yu QM, Braswell S, Christin B, Xu JJ, Wallace PM, Gong H, Kaminsky D (2010) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold quasi-3D nanostructure and 2D nanohole arrays. Nanotechnology 21(35):9. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/35/355301
Yue WS, Yang Y, Wang ZH, Han JG, Syed A, Chen LQ, Wong K, Wang XB (2012) Improved surface-enhanced Raman scattering on arrays of gold quasi-3D nanoholes. J Phys D-Appl Phys 45(42):7. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/45/42/425401
Yu Q, Guan P, Qin D, Golden G, Wallace PM (2008) Inverted size-dependence of surface-enhanced Raman scattering on gold nanohole and nanodisk arrays. Nano Lett 8(7):1923–1928. doi:10.1021/nl0806163
Lin YY, Liao JD, Ju YH, Chang CW, Shiau AL (2011) Focused ion beam-fabricated Au micro/nanostructures used as a surface enhanced Raman scattering-active substrate for trace detection of molecules and influenza virus. Nanotechnology 22(18):8. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/18/185308
Hamouda F, Sahaf H, Held S, Barbillon G, Gogol P, Moyen E, Aassime A, Moreau J, Canva M, Lourtioz JM, Hanbucken M, Bartenlian B (2011) Large area nanopatterning by combined anodic aluminum oxide and soft UV-NIL technologies for applications in biology. Microelectron Eng 88(8):2444–2446. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2011.02.013
Lee SY, Jeon HC, Yang SM (2012) Unconventional methods for fabricating nanostructures toward high-fidelity sensors. J Mater Chem 22(13):5900–5913. doi:10.1039/c2jm16568f
Barbillon G, Hamouda F, Held S, Gogol P, Bartenlian B (2010) Gold nanoparticles by soft UV nanoimprint lithography coupled to a lift-off process for plasmonic sensing of antibodies. Microelectron Eng 87(5–8):1001–1004. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2009.11.114
Masson J-F, Gibson KF, Provencher-Girard A (2010) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy amplification with film over etched nanospheres. J Phys Chem C 114(51):22406–22412. doi:10.1021/jp106450y
Fang C, Frontiera RR, Tran R, Mathies RA (2009) Mapping GFP structure evolution during proton transfer with femtosecond Raman spectroscopy. Nature 462 (7270):200–204. doi:10.1038/nature08527
Klingsporn JM, Sonntag MD, Seideman T, Van Duyne RP (2014) Tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with picosecond pulses. J Phys Chem Lett 5(1):106–110. doi:10.1021/jz4024404
Barchiesi D, Kessentini S, Guillot N, de la Chapelle ML, Grosges T (2013) Localized surface plasmon resonance in arrays of nano-gold cylinders: inverse problem and propagation of uncertainties. Opt Express 21(2):2245–2262. doi:10.1364/OE.21.002245
Caldwell JD, Glembocki O, Bezares FJ, Bassim ND, Rendell RW, Feygelson M, Ukaegbu M, Kasica R, Shirey L, Hosten C (2011) Plasmonic nanopillar arrays for large-area, high-enhancement surface-enhanced Raman scattering sensors. ACS Nano 5(5):4046–4055. doi:10.1021/nn200636t
Hohenau A, Krenn JR, Garcia-Vidal FJ, Rodrigo SG, Martin-Moreno L, Beermann J, Bozhevolnyi SI (2007) Spectroscopy and nonlinear microscopy of gold nanoparticle arrays on gold films. Phys Rev B 75(8):085104. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.75.085104
Hohenau A, Krenn JR, Beermann J, Bozhevolnyi SI, Rodrigo SG, Martin-Moreno L, Garcia-Vidal F (2006) Spectroscopy and nonlinear microscopy of Au nanoparticle arrays: experiment and theory. Phys Rev B 73(15):155404. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.73.155404
Hohenau A, Krenn JR, Garcia-Vidal FJ, Rodrigo SG, Martin-Moreno L, Beermann J, Bozhevolnyi SI (2007) Comparison of finite-difference time-domain simulations and experiments on the optical properties of gold nanoparticle arrays on gold film. J Opt A Pure Appl Opt 9(9):S366. doi:10.1088/1464-4258/9/9/S14
Aassime A, Hamouda F, Richardt I, Bayle F, Pillard V, Lecoeur P, Aubert P, Bouchier D (2013) Anti-charging process for electron beam observation and lithography. Microelectron Eng 110:320–323. doi:10.1016/j.mee.2013.02.036
Wang Y, Abb M, Boden SA, Aizpurua J, de Groot CH, Muskens OL (2013) Ultrafast nonlinear control of progressively loaded, single plasmonic nanoantennas fabricated using helium ion milling. Nano Lett 13(11):5647–5653. doi:10.1021/nl403316z
Iriarte GF, Rodriguez-Madrid JG, Calle F (2012) Fabrication of sub-100 nm IDT SAW devices on insulating, semiconducting and conductive substrates. J Mater Process Technol 212(3):707–712. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.08.007
Zhou Q, Liu Y, He Y, Zhang Z, Zhao Y (2010) The effect of underlayer thin films on the surface-enhanced Raman scattering response of Ag nanorod substrates. Appl Phys Lett 97(12), 121902. doi:10.1063/1.3489973
Cottat M, Lidgi-Guigui N, Tijunelyte I, Barbillon G, Hamouda F, Gogol P, Aassime A, Lourtioz J-M, Bartenlian B, de la Chapelle M (2014) Soft UV nanoimprint lithography-designed highly sensitive substrates for SERS detection. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):623. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-9-623
Chu Y, Banaee MG, Crozier KB (2010) Double-resonance plasmon substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering with enhancement at excitation and stokes frequencies. ACS Nano 4(5):2804–2810. doi:10.1021/nn901826q
Mandal P, Ramakrishna SA (2011) Dependence of surface enhanced Raman scattering on the plasmonic template periodicity. Opt Lett 36(18):3705–3707. doi:10.1364/OL.36.003705
Mandal P, Nandi A, Ramakrishna SA (2012) Propagating surface plasmon resonances in two-dimensional patterned gold-grating templates and surface enhanced Raman scattering. J Appl Phys 112(4), 044314. doi:10.1063/1.4748180
Willets KA, Van Duyne RP (2007) Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu Rev Phys Chem 58:267–297. doi:10.1146/annurev.physchem.58.032806.104607
Aroca R (2006) Surface enhanced vibrational spectroscopy, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, Ltd. doi:10.1002/9780470035641
Le Ru EC, Grand J, Félidj N, Aubard J, Lévi G, Hohenau A, Krenn JR, Blackie E, Etchegoin PG (2008) Experimental verification of the SERS electromagnetic model beyond the |E|4 approximation: polarization effects. J Phys Chem C 112(22):8117–8121. doi:10.1021/jp802219c
Sarkar M, Besbes M, Moreau J, Bryche J-F, Olivéro A, Barbillon G, Coutrot A-L, Bartenlian B, Canva M (2015) Hybrid plasmonic mode by resonant coupling of localized plasmons to propagating plasmons in a Kretschmann configuration. ACS Photonics 2(2):237–245. doi:10.1021/ph500351b
Chu Y, Crozier KB (2009) Experimental study of the interaction between localized and propagating surface plasmons. Opt Lett 34(3):244–246. doi:10.1364/OL.34.000244
Live LS, Dhawan A, Gibson KF, Poirier-Richard H-P, Graham D, Canva M, Vo-Dinh T, Masson J-F (2012) Angle-dependent resonance of localized and propagating surface plasmons in microhole arrays for enhanced biosensing. Anal Bioanal Chem 404(10):2859–2868. doi:10.1007/s00216-012-6195-0
Guillot N, Shen H, Fremaux B, Peron O, Rinnert E, Toury T, de la Chapelle ML (2010) Surface enhanced Raman scattering optimization of gold nanocylinder arrays: influence of the localized surface plasmon resonance and excitation wavelength. Appl Phys Lett 97(2), 023113. doi:10.1063/1.3462068
Shen H, Guillot N, Rouxel J, Lamy de la Chapelle M, Toury T (2012) Optimized plasmonic nanostructures for improved sensing activities. Opt Express 20(19):21278–21290. doi:10.1364/OE.20.021278
Bryche JF, Gillibert R, Barbillon G, Sarkar M, Coutrot AL, Hamouda F, Aassime A, Moreau J, de la Chapelle ML, Bartenlian B, Canva M (2015) Density effect of gold nanodisks on the SERS intensity for a highly sensitive detection of chemical molecules. J Mater Sci 50(20):6601–6607. doi:10.1007/s10853-015-9203-x
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge ANR P2N (ANR-12-NANO-0016) and the support of the French Government for partial funding of the project in which this work takes place. This work was partly supported by the French RENATECH network. IOGS/CNRS is also part of the European Network of Excellence in BioPhotonics, Photonics for Life, P4L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bryche, JF., Gillibert, R., Barbillon, G. et al. Plasmonic Enhancement by a Continuous Gold Underlayer: Application to SERS Sensing. Plasmonics 11, 601–608 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0088-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0088-y