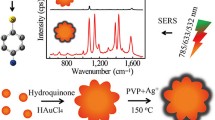
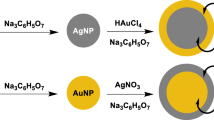
Abstract
The main objective of the present study is to investigate the shell thickness-dependent Raman enhancement activity of silver-coated gold nanoparticles (Au@Ag NPs) when bound to a model analyte 2-mercaptobenzoic acid (2-MBA). With an optimized Ag:Au ratio, dimeric and trimeric Au@Ag nanostructures were prepared in the presence of 2-MBA and are characterized by spectroscopic and microscopic techniques. These dimeric junctions act as hot spots and the molecules trapped at these junctions showed higher Raman signal enhancements due to the presence of amplified electric field.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tian ZQ, Ren B (2004) Adsorption and reaction at electrochemical interfaces as probed by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu Rev Phys Chem 55:197–229
Moskovits M (1985) Surface-enhanced spectroscopy. M ReV Mod Phys 57:783–826
Weitz DA, Garoff S, Gersten JI, Nitzan A (1983) The enhancement of Raman scattering, resonance Raman scattering and fluorescence from molecules adsorbed on a rough silver surface. J Phys Chem 78:5324
Creighton JA (1983) Surface Raman electromagnetic enhancement factors for molecules at the surface of small isolated metal spheres: the determination of adsorbate orientation from SERS relative intensities. Surf Sci 124:209–219
Hao E, Schatz GC (2004) Electromagnetic fields around silver nanoparticles and dimers. J Chem Phys 120:357–366
Guerrini L, Graham D (2012) Molecularly-mediated assemblies of plasmonic nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy applications. Chem Soc Rev 41:7085–7107
Lal S, Grady NK, Kundu J, Levin CS, Lassiterde JB, Halas NJ (2008) Tailoring plasmonic substrates for surface enhanced spectroscopy. Chem Soc Rev 37:898–911
Nabika H, Takase M, Nagasawa F, Murakoshi K (2010) Toward plasmon-induced photoexcitation of molecules. J Phys Chem Lett 1:2470–2487
Qin L, Zou S, Xue C, Atkinson A, Schatz GC, Mirkin CA (2006) Designing, fabricating, and imaging Raman hot spots. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:13300–13303
Talley CE, Jackson JB, Oubre C, Grady NK, Hollars CW, Lane SM, Huser TR, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2005) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering from individual Au nanoparticles and nanoparticle dimer substrates. Nano Lett 5:1569–1574
Kumar J, Thomas KG (2011) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: investigations at the nanorod edges and dimer junctions. J Phys Chem Lett 2:610–615
Li W, Camargo PHC, Au L, Zhang Q, Rycenga M, Xia Y (2010) Etching and dimerization: a simple and versatile route to dimers of silver nanospheres with a range of sizes. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:164–168
Cui Y, Ren B, Yao JL, Gu RA, Tian ZQ (2006) Synthesis of Ag core Au shell bimetallic nanoparticles for immunoassay based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B 110:4002–4006
Kumar GVP, Shruthi B, Vibha S, Reddy RBA, Kundu TK, Narayana C (2007) Hot spots in Ag core-Au shell nanoparticles potent for surface-enhanced Raman scattering studies of biomolecules. J Phys Chem C 111:4388–4392
Camden JP, Dieringer JA, Wang Y, Masiello DJ, Marks LD, Schatz GC, Van Duyne RP (2008) Probing the structure of single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman scattering hot spots. J Am Chem Soc 130:12616–12617
Li W, Camargo PHC, Lu X, Xia Y (2009) Dimers of silver nanospheres: facile synthesis and their use as hot spots for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Nano Lett 9:485–490
Kanjanawarut R, Su X (2009) Colorimetric detection of DNA using unmodified metallic nanoparticles and peptide nucleic acid probes. Anal Chem 81:6122–6129
Olson TY, Schwartzberg AM, Orme CA, Talley CEO, Connell B, Zhang JZ (2008) J Phys Chem C 118:6319–6329
Fenter P, Gustafsson T (1991) Structure and morphology of Au grown on Ag (110). Phys Rev B 43:12195–12204
Ma W, Fang Y, Hao G, Wang W (2010) Adsorption behaviors of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid on silver and gold films. Chin J Chem Phys 23:659–663
Shanthil M, Thomas R, Swathi RS, Thomas KG (2012) Ag@SiO2 core-shell nanostructures: distance-dependent plasmon coupling and SERS investigation. J Phys Chem Lett 3:1459–1464
Kneipp K, Kneipp H, Kneipp J (2006) Surface-enhanced Raman scattering in local optical fields of silver and gold nanoaggregates: from single-molecule Raman spectroscopy to ultrasensitive probing in live cells. Acc Chem Res 39:443–450
Jeanmaire DL, van Duyne RP (1977) Surface Raman electrochemistry part I. Heterocyclic, aromatic and aliphatic amines adsorbed on the anodized silver electrode. J Electroanal Chem 84:1–20
Wu YP, Nordlander P (2006) Plasmon hybridization in nanoshells with a nonconcentric core. J Chem Phys 125:124708–124718
Chen Y, Wu H, Li Z, Wang P, Yang L, Fang Y (2012) The study of surface plasmon in Au/Ag core/shell compound nanoparticles. Plasmonics 7:509–513
Prodan E, Radloff C, Halas NJ, Nordlander P (2003) A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 302:419–422
Rodríguez OP, Pal U (2011) Enhanced plasmonic behavior of bimetallic (Ag-Au) multilayered spheres. Nanoscale Res Lett 6:279–283
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the head of the Department of Chemistry, University of Kerala for proving the instrumental facilities and support. The authors greatly acknowledge the head of the Department of Optoelectronics, University of Kerala for providing the Raman Spectroscopy instrumental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aswathy, B., Sony, G. & Gopchandran, K.G. Shell Thickness-Dependent Plasmon Coupling and Creation of SERS Hot Spots in Au@Ag Core-Shell Nanostructures. Plasmonics 9, 1323–1331 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9745-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9745-9