Abstract
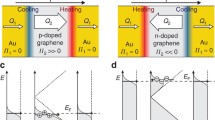
Based on the phenomenon of curvature-induced doping in graphene we propose a class of Peltier cooling devices, produced by geometrical effects, without gating. We show how a graphene nanoribbon laid on an array of curved nano cylinders can be used to create a targeted and tunable cooling device. Using two different approaches, the Nonequilibrium Green’s Function (NEGF) method and experimental inputs, we predict that the cooling power of such a device can approach the order of kW/cm2, on par with the best known techniques using standard superlattice structures. The structure proposed here helps pave the way toward designing graphene electronics which use geometry rather than gating to control devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. H. Zeng, X. F. Fan, C. LaBounty, E. Croke, Y. Zhang, J. Christofferson, D. Vashaee, A. Shakouri, and J. E. Bowers, Cooling power density of SiGe/Si superlattice micro refrigerators, Volume 793 of Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Materials Research Society, 2004
I. Chowdhury, R. Prasher, K. Lofgreen, G. Chrysler, S. Narasimhan, R. Mahajan, D. Koester, R. Alley, and R. Venkatasubramanian, On-chip cooling by superlattice-based thin-film thermoelectrics, Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4(4): 235
X. Fan, G. Zeng, E. Croke, C. LaBounty, C. C. Ahn, D. Vashaee, A. Shakouri, and J. E. Bowers, High cooling power density SiGe/Si micro-coolers, Electron. Lett., 2001, 37(2): 126
A. Shakouri and Yan Zhang, On-chip solid-state cooling for integrated circuits using thin-film microrefrigerators, IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Tech., 2005, 28(1): 65
J. Zhang, N. G. Anderson, and K. M. Lau, AlGaAs superlattice microcoolers, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2003, 83(2): 374
H. Y. Chiu, V. Perebeinos, Y. M. Lin, and P. Avouris, Controllable p-n junction formation in monolayer graphene using electrostatic substrate engineering, Nano Lett., 2010, 10(11): 4634
G. Liu, J. Velasco, and W. Bao, and C. N. Lau, Fabrication of graphene p-n-p junctions with contactless top gates., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92(20): 203103
S. G. Nam, D. K. Ki, J. W. Park, Y. Kim, J. S. Kim, and H. J. Lee, Ballistic transport of graphene p-n-p junctions with embedded local gates, Nanotechnology, 2011, 22(41): 415203
B. Öyilmaz, P. Jarillo-Herrero, D. Efetov, D. Abanin, L. Levitov, and P. Kim, Electronic transport and quantum Hall effect in bipolar graphene p-n-p junctions, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, 99(16): 166804
G. Rao, M. Freitag, H. Y. Chiu, R. S. Sundaram, and P. Avouris, Raman and photocurrent imaging of electrical stress-induced p-n junctions in graphene, ACS Nano, 2011, 5(7): 5848
J. R. Williams, L. DiCarlo, and C. M. Marcus, Quantum Hall effect in a gate-controlled p-n junction of graphene, Science, 2007, 317(5838): 638
T. Yu, C. W. Liang, C. Kim, and B. Yu, Local electrical stress-induced doping and formation of monolayer graphene P-N junction, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2011, 98(24): 243105
H. C. Cheng, R. J. Shiue, C. C. Tsai, W. H. Wang, and Y. T. Chen, High-quality graphene p-n junctions via resistfree fabrication and solution-based noncovalent functionalization, ACS Nano, 2011, 5(3): 2051
T. Lohmann, K. von Klitzing, and J. H. Smet, Four-terminal magneto-transport in graphene p-n junctions created by spatially selective doping, Nano Lett., 2009, 9(5): 1973
E. A. Kim and A. H. Castro Neto, Graphene as an electronic membrane, Europhys. Lett., 2008, 84(5): 57007
D. Rowe, Thermoelectrics Handbook: Macro to Nano, Boca Raton: CRC/Taylor and Francis, 2006
P. Wei, W. Z. Bao, Y. Pu, C. N. Lau, and J. Shi, Anomalous thermoelectric transport of Dirac particles in graphene, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 102(16): 166808
S. Datta, Quantum Transport: Atom to transistor, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005
Y. Ouyang and J. Guo, A theoretical study on thermoelectric properties of graphene nanoribbons, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94(26): 263107
K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva, and A. A. Firsov, Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films, Science, 2004, 306(5696): 666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, WJ., Yao, DX. & Carlson, E.W. Tunable nano Peltier cooling device from geometric effects using a single graphene nanoribbon. Front. Phys. 9, 472–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-014-0415-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11467-014-0415-3