Abstract
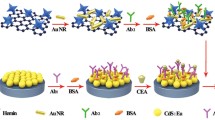
In this work, a double signal amplified immunosensor based on the enhanced CdSe@ZnS quantum dots (QDs) electrochemiluminescence (ECL) via TiO2 nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) and the outstanding quencher of polydopamine (PDA) decorated Au nanoparticles (Au@PDA NPs) for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) has been successfully achieved. The ECL of CdSe@ZnS QDs with different sizes has been investigated carefully, especially cooperation with TiO2 NPs. Au@PDA NPs have been synthesized and characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and UV–Vis spectrum, which acted as ECL quenchers to label the secondary antibody (Ab2) of CEA to form Ab2/Au@PDA NPs conjugates. The sandwich-structured immunosensor was formed between capture antibody (Ab1) on CdSe@ZnS QDs/TiO2 NPs/glassy carbon electrode, CEA and Ab2/Au@PDA NPs conjugates, resulting in a proportional ECL quenching signal relevant to the CEA concentration. Thus, CEA as a model biomarker has been detected in the linear range from 0.001 to 100 ng mL−1 with a limit of detection of 0.35 pg mL−1 (S/N = 3).
摘要
研究TiO2增强效应以及聚多巴胺(PDA)修饰的金纳米粒子(Au@PDA NPs)对CdSe@ZnS核壳结构量子点电化学发光信号的猝灭作用。基于此本文设计了一种双信号放大电化学发光(ECL)癌胚抗原(CEA)免疫传感器,测试TiO2对不同尺寸CdSe@ZnS量子点的增强效果。结果表明,TiO2对尺寸大的量子点ECL增强效果比尺寸小的量子点高。Au@PDA NPs表现出对电致化学发光高效的猝灭效应。通过TiO2增强及Au@PDA NPs猝灭效应的双信号放大,可得到CEA的检测线性范围为0.001~100 ng mL−1,检测线为0.35 pg mL−1(S/N = 3)。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Algar WR, Susumu K, Delehanty JB et al (2011) Semiconductor quantum dots in bioanalysis: crossing the valley of death. Anal Chem 83:8826–8837
Alivisatos AP (1996) Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 271:933–937
Bhattacharya P, Ghosh S, Stiff-Roberts AD (2004) Quantum dot opto-electronic devices. Annu Rev Mater Res 34:1–40
Guan W, Liu M, Zhang C (2016) Electrochemiluminescence detection in microfluidic cloth-based analytical devices. Biosens Bioelectron 75:247–253
Cheng L, Liu X, Lei J et al (2010) Low-potential electrochemiluminescent sensing based on surface unpassivation of CdTe quantum dots and competition of analyte cation to stabilizer. Anal Chem 82:3359–3364
Cheng Y, Lei J, Chen Y et al (2014) Highly selective detection of microRNA based on distance-dependent electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer between CdTe nanocrystals and Au nanoclusters. Biosens Bioelectron 51:431–436
Xia H, Li LL, Yin ZY et al (2015) Biobar-coded gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme-based dual signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of protein by electrochemiluminescence. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:696–703
Zhang Y, Liu W, Ge S et al (2013) Multiplexed sandwich immunoassays using flow-injection electrochemiluminescence with designed substrate spatial-resolved technique for detection of tumor markers. Biosens Bioelectron 41:684–690
Jie GF, Li LL, Chen C et al (2009) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots composited with CNTs and PDDA for sensitive immunoassay. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3352–3358
Dong YP, Gao TT, Zhou Y et al (2015) Enhancement of electrogenerated chemiluminescence of luminol by ascorbic acid at gold nanoparticle/graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Spectrochim Acta A 134:225–232
Guo ZY, Hao TT, Duan J et al (2012) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on graphene-CdS quantum dots-agarose composite for the ultrasensitive detection of alpha fetoprotein. Talanta 89:27–32
Jang J, Lee WY (2015) Solid-state tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) electrogenerated chemiluminescence sensor based on ionic liquid/sol–gel titania/Nafion composite film. J Electroanal Chem 736:55–60
Roop J, Nothnagel M, Schnuriger M et al (2011) Ionic liquid adsorbate enhanced electrogenerated chemiluminescence of ruthenium, osmium, and iridium complexes in water. J Electroanal Chem 656:34–40
Jie GF, Yuan JX, Zhang J (2012) Quantum dots-based multifunctional dendritic superstructure for amplified electrochemiluminescence detection of ATP. Biosens Bioelectron 31:69–76
Wu MS, He LJ, Xu JJ et al (2014) RuSi@Ru(bpy) 2+3 /Au@Ag2S nanoparticles electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system for sensitive DNA detection. Anal Chem 86:4559–4565
Wang DF, Guo LH, Huang R et al (2014) Surface enhanced electrochemiluminescence for ultrasensitive detection of Hg2+. Electrochim Acta 150:123–128
Wang DF, Guo LH, Huang R et al (2015) Surface enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Ru(bpy) 2+3 . Sci Rep 5:7954
Wang DF, Li YY, Lin ZY et al (2015) Surface-enhanced electrochemiluminescence of Ru@SiO2 for ultrasensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Chem 87:5966–5972
Ding SN, Gao BH, Shan D et al (2012) Dramatically enhanced solid-state electrochemiluminescence of CdTe quantum dots composed with TiO2 nanoparticles. Chem Eur J 18:1595–1598
Lee H, Dellatore SM, Miller WM et al (2007) Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 318:426–430
Choi CKK, Li J, Wei K et al (2015) A gold@polydopamine core-shell nanoprobe for long-term intracellular detection of microRNAs in differentiating stem cells. J Am Chem Soc 137:7337–7346
Zhao Y, Zheng Y, Zhao C et al (2015) Hollow PDA-Au nanoparticles-enabled signal amplification for sensitive nonenzymatic colorimetric immunodetection of carbohydrate antigen 125. Biosens Bioelectron 71:200–206
Lu Z, Xiao J, Wang Y et al (2015) In situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles uniformly distributed on polydopamine-coated silk fibers for antibacterial application. J Colloid Interface Sci 452:8–14
Qu K, Zheng Y, Dai S et al (2015) Polydopamine–graphene oxide derived mesoporous carbon nanosheets for enhanced oxygen reduction. Nanoscale 7:12598–12605
Feng DX, Li LH, Zhao JQ et al (2015) Simultaneous electrochemical detection of multiple biomarkers using gold nanoparticles decorated multiwall carbon nanotubes as signal enhancers. Anal Biochem 482:48–54
Feng XB, Gan N, Zhang HR et al (2015) A novel strategy for multiplexed immunoassay of tumor markers based on electrochemiluminescence coupled with cyclic voltammetry using graphene-polymer nanotags. Electrochim Acta 170:292–299
Chen LL, Zhang ZJ, Zhang P et al (2011) An ultra-sensitive chemiluminescence immunosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen using HRP-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as labels. Sens Actuators B Chem 155:557–561
Dungchai W, Siangproh W, Lin JM et al (2007) Development of a sensitive micro-magnetic chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for the determination of carcinoembryonic antigen. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1965–1971
Yuan JL, Wang GL, Majima K et al (2001) Synthesis of a terbium fluorescent chelate and its application to time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay. Anal Chem 73:1869–1876
Yang XM, Zhuo Y, Zhu SS et al (2015) Selectively assaying CEA based on a creative strategy of gold nanoparticles enhancing silver nanoclusters’ fluorescence. Biosens Bioelectron 64:345–351
Liu WY, Yang HM, Ding YA et al (2014) Paper-based colorimetric immunosensor for visual detection of carcinoembryonic antigen based on the high peroxidase-like catalytic performance of ZnFe2O4-multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Analyst 139:251–258
Luo C, Wen W, Lin FG et al (2015) Simplified aptamer-based colorimetric method using unmodified gold nanoparticles for the detection of carcinoma embryonic antigen. RSC Adv 5:10994–10999
Liu R, Liu X, Tang YR et al (2011) Highly sensitive immunoassay based on immunogold-silver amplification and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chem 83:2330–2336
Terenghi M, Elviri L, Careri M et al (2009) Multiplexed determination of protein biomarkers using metal-tagged antibodies and size exclusion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 81:9440–9448
Li J, Wang W, Zhao L et al (2015) Hydroquinone-assisted synthesis of branched Au–Ag nanoparticles with polydopamine coating as highly efficient photothermal agents. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:11613–11623
Bastus NG, Comenge J, Puntes V et al (2011) Kinetically controlled seeded growth synthesis of citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles of up to 200 nm: size focusing versus Ostwald ripening. Langmuir 27:11098–11105
Shan Y, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2011) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence quenching of CdS: Mn nanocrystals by CdTe QDs-doped silica nanoparticles for ultrasensitive detection of thrombin. Nanoscale 3:2916–2923
Kim YP, Oh YH, Oh E et al (2008) Energy transfer-based multiplexed assay of proteases by using gold nanoparticle and quantum dot conjugates on a surface. Anal Chem 80:4634–4641
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21575022, 21535003), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2015AA020502), the Open Research Fund of Key Laboratory of Energy Thermal Conversion and Control of Ministry of Education, Southeast University, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (KYLX15-0127).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, QL., Ding, SN. Double signal amplification sandwich-structured immunosensor based on TiO2 nanoparticles enhanced CdSe@ZnS QDs electrochemiluminescence and the dramatic quenching effect of Au@polydopamine nanoparticles. Sci. Bull. 61, 931–938 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1097-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1097-8