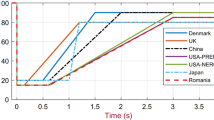
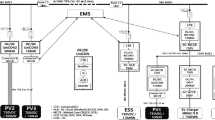
Abstract
In this paper, 5 investigations on the current states of power distribution grids in China have been introduced that cover the surveys of the practical distribution asset utilization, the simultaneity factor of feeder loading, the load compositions and characteristics, the urban reliability and the integration of distributed generations of renewable resources. Based on the survey results in the investigations, 12 Facts are clearly presented. It shows that the challenges to modernize the distribution grids in China are to improve the asset utilization rates, the electricity efficiencies and the reliability of distribution systems, as well as to integrate increasing amount of variable distributed renewable resources. Furthermore based on the challenges, 8 R&D opportunities have been identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu Y X. Smart Grid—a new strategy for global energy in the 21st century (Part I) (in Chinese). Power Elec Eng, 2013, 1: 8–13
Yu Y X. Smart Grid—a new strategy for global energy in the 21st century (Part II) (in Chinese). Power Elec Eng, 2013, 2: 3–7
Yu Y X, Luan W P. Smart grid and its implementations (in Chinese). Proc CSEE, 2009, 29: 1–8
Chinese Academy of Engineering. The development strategy of smart and flexible technology of Chinese grid (in Chinese). CAE Report, 2011
US DOE. Grid 2030 a national vision for electricity’s second 100 years. US DOE Report, 2003
State Electricity Regulatory Commission. Electricity Regulatory Annual Report (2011). SERC Report, 2012
IEEE Distribution Reliability Working Group. IEEE Distribution Reliability Benchmarking 2011 Results. IEEE Report, 2012
Koizumi S, Okumura M, Yanase T. Application and development of distribution automation system in TEPCO. In: IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. New York: IEEE PES, 2005
Kasajima T, Endo R, Wada Y, Kudo Y, et al. The development of the advanced distribution automation system with optical fiber network of Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. In: IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. Denver: IEEE PES, 2004
McGranaghan M, Goodman F. Technical and system requirements for advanced distribution automation. EPRI Report, 2005
Sullivan M, Mercurio M, Schellenberg J, et al. Estimated value of service reliability for electric utility customers in the United States. Ernest Orlando LBNL Report, 2009
Yu Y X, Zhou J H. Value-based evaluation of power system planning alternatives with large-scale wind power (in Chinese). J Tianjin Univ, 2011, 44: 941–946
McDonald J, McGranaghan M, Denton D, et al. Strategic R&D Opportunities for the Smart Grid. US NIST Report, 2013
Yu Y X, Ma S Q, Xu C. A research framework for the distribution fast simulation and modeling (in Chinese). Proc CSEE, 2014, 34: 1675–1681
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Y., Zeng, Y., Liu, H. et al. Challenges and R&D opportunities of smart distribution grids in China. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 57, 1588–1593 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5585-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-014-5585-2