Abstract
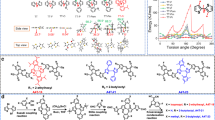
Organic electron acceptor materials play an important role in organic electronics. Recently, many organic electron acceptors have been developed, in which aromatic fused-imides have proved to be a promising family of excellent electron acceptors. We report the first synthesis of a novel aromatic fused-imide, acenaphtho[1, 2-k]fluoranthene diimide derivative (AFI), using lithium-halogen exchange and Diels-Alder reactions. The construction of a large conjugated plane and the introduction of electron-withdrawing imide groups endow AFI with a low lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) level of −3.80 eV. AFI exhibits a regular molecular arrangement and strong π-π interactions in the single-crystal structure, which indicates its potential application in organic electronic devices. Solar cell devices that were fabricated using AFI as the electron acceptor and P3HT as the electron donor achieved an energy conversion efficiency of 0.33%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Usta H, Facchetti A, Marks, TJ. n-Channel semiconductor materials design for organic complementary circuits. Acc Chem Res, 2011, 44: 501–510
Zhan X, Facchetti A, Barlow S, Marks TJ, Ratner MA, Wasielewski MR, Marder SR. Rylene and related diimides for organic electronics. Adv Mater, 2011, 23: 268–284
Tang Q, Li H, Liu Y, Hu WP. High-performance air-stable n-type transistors with an asymmetrical device configuration based on organic single-crystalline submicrometer/nanometer ribbons. J Am Chem Soc, 2006, 128: 14634–14639
Streetman BG. Solid State Electronic Devices, 4th ed. Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, 1995
Zaumseil J, Sirringhaus H. Electron and ambipolar transport in organic field-effect transistors. Chem Rev, 2007, 107: 1296–1323
Dhar BM, Kini GS, Xia GQ, Jung BJ, Markovic N, Katz HE. Field-effect-tuned lateral organic diodes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2010, 107: 3972–3976
Singh TB, Marjanovic N, Stadler P, Auinger M, Matt GJ, Günes S, Sariciftci NS, Schwödiauer R, Bauer S. Correlation between morphology and ambipolar transport in organic field-effect transistors. J Appl Phys, 2005, 97: 083714–1-5
He YJ, Chen HY, Hou JH, Li YF. Indene-C-60 bisadduct: a new acceptor for high-performance polymer solar cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 1377–1382
Pei C, Li YF, Zhan XW. Efficient ternary blend polymer solar cells with indene-C60 bisadduct as an electron-cascade acceptor. Energy Environ Sci, 2014, 7: 2005–2011
Gsaenger M, Oh JH, Koenemann M, Hoeffken HW, Krause AM, Bao Z, Würthner F. A crystal-engineered hydrogen-bonded octachloroperylene diimide with a twisted core: an n-Channel organic semiconductor. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2010, 49: 740–743
Gao J, Li Y, Wang ZH. Synthesis and properties of naphthobisbenzothiophene diimides. Org Lett, 2013, 15: 1366–1369
Wen YG, Liu YL, Di CA, Wang Y, Sun XN, Guo YL, Zheng J, Wu WP, Ye SH, Yu G. Improvements in stability and performance of N,N′-dialkyl perylene diimide-based n-Type thin-film transistors. Adv Mater, 2009, 21: 1631–1635
Zhou E, Cong J, Wei Q, Tajima K, Yang C, Hashimoto K. All-polymer solar cells from perylene diimide based copolymers: material design and phase separation control. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2011, 50: 2799–2803
Kamm V, Battagliarin G, Howard IA, Pisula W, Mavrinskiy A, Li C, Müllen K, Laquai F. Polythiophene:perylene diimide solar cells — the impact of alkyl-substitution on the photovoltaic performance. Adv Energy Mater, 2011, 1: 297–302
Ahmed E, Ren G, Kim FS, Hollenbeck EC, Jenekhe SA. Design of new electron acceptor materials for organic photovoltaics: synthesis, electron transport, photophysics, and photovoltaic properties of oligothiophene-functionalized naphthalene diimides. Chem Mater, 2011, 23: 4563–4577
Earmme T, Hwang YJ, Murari NM, Subramaniyan S, Jenekhe SA. All-polymer solar cells with 3.3% efficiency based on naphthalene diimide-selenophene copolymer acceptor. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135: 14960–14963
Handa S, Miyazaki E, Takimiya K, Kunugi Y. Solution-processible n-channel organic field-effect transistors based on dicyanomethylene-substituted terthienoquinoid derivative. J Am Chem Soc, 2007, 129: 11684–11685
Liang Z, Tang Q, Liu J, Li J, Yan F, Miao Q. n-Type organic semi conductors based on pi-deficient pentacenequinones: synthesis, electronic structures, molecular packing, and thin film transistors. Chem Mater, 2010, 22: 6438–6443
Ando S, Murakami R, Nishida JI, Tada H, ji Inoue Y, Tokito S, Yamashita Y. n-Type organic field-effect transistors with very high electron mobility based on thiazole oligomers with trifluoromethylphenyl groups. J Am Chem Soc, 2005, 127: 14996–14997
Ding L, Ying HZ, Zhou Y, Lei T, Pei J. Polycyclic imide derivatives: synthesis and effective tuning of lowest unoccupied molecular orbital levels through molecular engineering. Org Lett, 2010, 12: 5522–5525
Tesmer M, Vahrenkamp H. Sterically fixed dithiolate ligands and their zinc complexes: derivatives of 1,8-dimercaptonaphthalene. Eur J Inorg Chem, 2001, 1183–1188
Bhandari S, Ray S. A novel synthesis of bisbenzyl ketones by DCC induced condensation of phenylacetic acid. Synth Commun, 1998, 28: 765–771
Sheldrick GM, SHELXS-97. A program for automatic solution of crystal structure. University of Goettingen, Germany, 1997
Sheldrick GM, SHELXL-97. A program for crystal structure refinement. University of Goettingen, Germany, 1997
Zhou Y, Ding L, Shi K, Dai YZ, Ai N, Wang J, Pei J. A non-fullerene small molecule as efficient electron acceptor in organic bulk heterojunction solar cells. Adv Mater, 2012, 24: 957–961
Podzorov V, Pudalov VM, Gershenson ME, Field-effect transistors on rubrene single crystals with parylene gate insulator. App Phys Lett, 2003, 82: 1739–1741
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, L., Yang, C., Su, Z. et al. Synthesis, crystal structure, and application of an acenaphtho[1,2-k] fluoranthene diimide derivative. Sci. China Chem. 58, 364–369 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-014-5282-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-014-5282-9