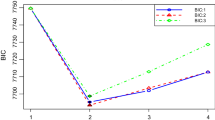
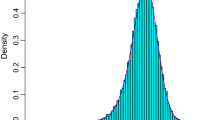
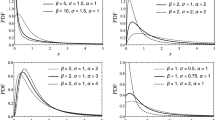
Abstract
Two-parameter gamma distributions are widely used in liability theory, lifetime data analysis, financial statistics, and other areas. Finite mixtures of gamma distributions are their natural extensions, and they are particularly useful when the population is suspected of heterogeneity. These distributions are successfully employed in various applications, but many researchers falsely believe that the maximum likelihood estimator of the mixing distribution is consistent. Similarly to finite mixtures of normal distributions, the likelihood function under finite gamma mixtures is unbounded. Because of this, each observed value leads to a global maximum that is irrelevant to the true distribution. We apply a seemingly negligible penalty to the likelihood according to the shape parameters in the fitted model. We show that this penalty restores the consistency of the likelihoodbased estimator of the mixing distribution under finite gamma mixture models. We present simulation results to validate the consistency conclusion, and we give an example to illustrate the key points.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batir N. Inequalities for the gamma function. J Inequal Pure Appl Math, 2007, 8: 554–563
Bechtel Y C, Bonaiti-Pellie C, Poisson N, et al. A population and family study N-acetyltransferase using caffeine urinary metabolites. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 1993, 54: 134–141
Birnbaum Z W, Saunders S C. A statistical model for life-length of materials. J Amer Statist Assoc, 1958, 53: 151–160
Böhning D. Computer-Assisted Analysis of Mixture and Applications: Meta—Analysis, Disease Mapping, and Others. New York: Chapman & Hall/CRC, 2000
Chen J. Optimal rate of convergence for finite mixture models. Ann Statist, 1995, 23: 221–233
Chen J. Penalized likelihood ratio test for finite mixture models with multinomial observations. Canad J Statist, 1998, 26: 583–599
Chen J. Consistency of the MLE under mixture models. ArXiv:1607.01251, 2016
Chen J, Tan X. Inference for multivariate normal mixtures. J Multivariate Anal, 2009, 100: 1367–1383
Chen J, Tan X, Zhang R. Inference for normal mixtures in mean and variance. Statist Sinica, 2008, 18: 443–465
Ciuperca G, Ridolfi A, Idier J. Penalized maximum likelihood estimator for normal mixtures. Scand J Statist, 2003, 30: 45–59
Craig B M, Strassels S A. Out-of-pocket prices of opioid analgesics in the United States, 1999–2004. Pain Med, 2010, 11: 240–247
Hathaway R J. A constrained formulation of maximum-likelihood estimation for normal mixture distributions. Ann Statist, 1985, 13: 795–800
Kiefer J, Wolfowitz J. Consistency of the maximum likelihood estimator in the presence of infinitely many nuisance parameters. Ann Math Statist, 1956, 27: 887–906
Lawless J F. Statistical Models and Methods for Lifetime Data, 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2003
Lee A H, Wang K, Yau K K, et al. Maternity length of stay modelling by gamma mixture regression with random effects. Biom J, 2007, 49: 750–764
Lee S C K, Lin X S. Modeling and evaluating insurance losses via mixtures of Erlang distributions. N Am Actuar J, 2010, 14: 107–130
Li S T, Chen J. Test for homogeneity under gamma mixture model. J Systems Sci Math Sci, 2015, 35: 1418–1435
Lindsay B G. Mixture Models: Theory, Geometry and Applications. Hayward: Institute for Mathematical Statistics, 1995
MacLachlan G J, Peel D. Finite Mixture Models. New York: Wiley, 2000
Nguyen X. Convergence of latent mixing measures in finite and infinite mixture models. Ann Statist, 2013, 4: 370–400
Pfanzagl J. Consistency of maximum likelihood estimators for certain nonparametric families, in particular: Mixtures. J Statist Plann Inference, 1988, 19: 137–158
Redner R. Note on the consistency of the maximum likelihood estimate for nonidentifiable distributions. Ann Math Statist, 1981, 9: 225–228
Ridolfi A, Idier J. Penalized maximum likelihood estimation for univariate normal mixture distributions. Actes Du E Colloque Gretsi, 2010, 568: 259–262
Tanaka K, Takemura A. Strong consistency of MLE for finite uniform mixtures when the scale parameters are exponentially small. Ann Inst Statist Math, 2005, 57: 1–19
Tanaka K, Takemura A. Strong consistency of MLE for finite mixtures of location-scale distributions when the scale parameters are exponentially small. Bernoulli, 2006, 12: 1003–1017
Titterington D M, Smith A F M, Makov U E. Statistical Analysis of Finite Mixture Distributions. Chichester: Wiley, 1985
Venturini S, Dominici F, Parmigiani G. Gamma shape mixtures for heavy-tailed distributions. Ann Appl Stat, 2008, 2: 756–776
Wald A. Note on the consistency of the maximum likelihood estimate. Ann Math Statist, 1949, 20: 595–601
Wiper M, Insua D R, Ruggeri F. Mixtures of gamma distributions with applications. J Comp Graph Statist, 2001, 10: 440–454
Wong S T, Li W K. Test for homogeneity in gamma mixture models using likelihood ratio. Comput Statist Data Anal, 2014, 70: 127–137
Wu C F J. On the convergence properties of the EM algorithm. Ann Statist, 1981, 11: 95–103
Ziou D, Bouguila N, Allili M S, et al. Finite gamma mixture modelling using minimum message length inference: Application to SAR image analysis. Int J Remote Sensing, 2009, 30: 771–792
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
In memory of Professor Xiru Chen (1934–2005)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Li, S. & Tan, X. Consistency of the penalized MLE for two-parameter gamma mixture models. Sci. China Math. 59, 2301–2318 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-016-0125-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11425-016-0125-0