Abstract
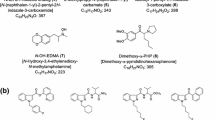
We identified two new-type designer drugs, piperazine derivative MT-45 [1-cyclohexyl-4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine, synonym: I-C6, 1] and synthetic peptide Noopept [ethyl 2-(1-(2-phenylacetyl)pyrrolidine-2-carboxamido)acetate, synonym: GVS-111, 2], in chemical and herbal products. MT-45 (1) was previously reported as an opiate-like analgesic substance, and Noopept (2) was reported to have nootropic (cognitive enhancer) activity. We also detected two synthetic cannabinoids, A-834735 (3) and QUPIC N-(5-fluoropentyl) analog (synonym: 5-fluoro-PB-22, 4), in the illegal products. A-834735 (3) was previously reported to act as an agonist at both cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. In addition, cathinone derivative 4-methoxy-α-pyrrolidinovalerophenone (4-methoxy-α-PVP, 5) and phenethylamine derivative 4-methylbuphedrine (6) were newly detected with known cathinone derivative 4-methylbuphedrone (7) in the products.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kikura-Hanajiri R, Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Goda Y (2013) Changes in the prevalence of synthetic cannabinoids and cathinone derivatives in Japan. Forensic Toxicol 31:44–53
EMCDDA (2012) 2012 Annual report on the state of the drugs problem in Europe. EMCDDA, Lisbon http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_190854_EN_TDAC12001ENC_.pdf. Accessed November 2012
Zuba D, Byrska B (2013) Analysis of the prevalence and coexistence of synthetic cannabinoids in “herbal high” products in Poland. Forensic Toxicol 31:21–30
Nakajima J, Takahashi M, Seto T, Yoshida M, Kanai C, Suzuki J, Hamano T (2012) Identification and quantitation of two new naphthoylindole drugs-of-abuse, (1-(5-hydroxypentyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)(naphthalen-1-yl)methanone (AM-2202) and (1-(4-pentenyl)-1H-indol-3-yl)(naphthalen-1-yl)methanone, with other synthetic cannabinoids in unregulated “herbal” products circulated in the Tokyo area. Forensic Toxicol 30:33–44
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2012) Identification of two new-type synthetic cannabinoids, N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indole-3-carboxamide (APICA) and N-(1-adamantyl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (APINACA), and detection of five synthetic cannabinoids, AM-1220, AM-2233, AM-1241, CB-13 (CRA-13), and AM-1248, as designer drugs in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 30:114–125
Kneisel S, Bisel P, Brecht V, Broecker S, Müller M, Auwärter V (2012) Identification of the cannabimimetic AM-1220 and its azepane isomer (N-methylazepan-3-yl)-3-(1-naphthoyl)indole in a research chemical and several herbal mixtures. Forensic Toxicol 30:126–134
Uchiyama N, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) URB-754: a new class of designer drug and 12 synthetic cannabinoids detected in illegal products. Forensic Sci Int 227:21–32
Shima N, Katagi M, Kamata H, Matsuta S, Nakanishi K, Zaitsu K, Kamata T, Nishioka H, Miki A, Tatsuno M, Sato T, Tsuchihashi H, Suzuki K (2013) Urinary excretion and metabolism of the newly encountered designer drug 3,4-dimethylmethcathinone in humans. Forensic Toxicol 31:101–112
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) Two new-type cannabimimetic quinolinyl carboxylates, QUPIC and QUCHIC, two new cannabimimetic carboxamide derivatives, ADB-FUBINACA and ADBICA, and five synthetic cannabinoids detected with a thiophene derivative α-PVT and an opioid receptor agonist AH-7921 identified in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 31:223–240
Uchiyama N, Matsuda S, Wakana D, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Goda Y (2013) New cannabimimetic indazole derivatives, N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-pentyl-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-PINACA) and N-(1-amino-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl)-1-(4-fluorobenzyl)-1H-indazole-3-carboxamide (AB-FUBINACA), identified as designer drugs. Forensic Toxicol 31:93–100
Kobayashi M (1991) Molecular pharmacological study on type selectivity of ligand for opioid receptor. Gifu Daigaku Igakubu Kiyo 39:541–558
Natsuka K, Nakamura H, Uno H, Umemoto S (1975) Studies on 1-substituted 4-(1,2-diphenylethyl)piperazine derivatives and their analgesic activities. 1. J Med Chem 18:1240–1244
Gudasheva TA, Voronina TA, Ostrovskaya RU, Rozantsev GG, Vasilevich NI, Trofimov SS, Kravchenko EV, Skoldinov AP, Seredenin SB (1996) Synthesis and antiamnesic activity of a series of N-acylprolyl-containing dipeptides. Eur J Med Chem 31:151–157
Chin CL, Tovcimak AE, Hradil VP, Seifert TR, Hollingsworth PR, Chandran P, Zhu CZ, Gauvin D, Pai M, Wetter J, Hsieh GC, Honore P, Frost JM, Dart MJ, Meyer MD, Yao BB, Cox BF, Fox GB (2008) Differential effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on regional brain activity using pharmacological MRI. Br J Pharmacol 153:367–379
Fraser DS, Park SB, Chong JM (2004) Diastereoselective reduction of α-aminoketones: synthesis of anti- and syn-β-aminoalcohols. Can J Chem 82:87–101
Acknowledgments
A portion of this work was supported by a Health and Labor Sciences Research Grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare, Japan.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchiyama, N., Matsuda, S., Kawamura, M. et al. Identification of two new-type designer drugs, piperazine derivative MT-45 (I-C6) and synthetic peptide Noopept (GVS-111), with synthetic cannabinoid A-834735, cathinone derivative 4-methoxy-α-PVP, and phenethylamine derivative 4-methylbuphedrine from illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 32, 9–18 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0194-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-013-0194-5