Abstract
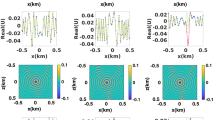
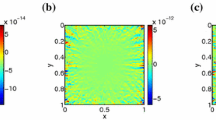
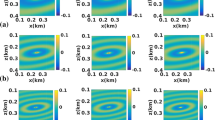
A lattice Boltzmann type pseudo-kineticmodel for a non-homogeneous Helmholtz equation is derived in this paper. Numerical results for some model problems show the robustness and efficiency of this lattice Boltzmann type pseudo-kinetic scheme. The computation at each site is determined only by local parameters, and can be easily adapted to solve multiple scattering problems with many scatterers or wave propagation in nonhomogeneous medium without increasing the computational cost.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayliss, A., Goldstein, C. I. and Turkel, E., An iterative method for the Helmholtz equation, J. Comput. Phys., 49, 1983, 443–457.
Benzi, R., Succi, S. and Vergassola, M., The lattice Boltzmann equations: theory and applications, Phys. Rep., 222, 1992, 147–197.
Chopard, B., Luthi, P. O. and Wagen, J. F., Lattice Boltzmann method for wave propagation in urban microcells, IEEE Proc. Microw. Antennas Propag., 144(4), 1997, 251–255.
Clayton, R. and Engquist, B., Absorbing boundary conditions for acoustic and elastic wave equations, Bull. Seis. Soc. America, 67(6), 1977, 1529–1540.
Clayton, R. and Engquist, B., Absorbing boundary conditions for wave-equation migration, Geophysics, 45(5), 1980, 895–904.
Collins, M. D. and Kuperman, W. A., Inverse problems in ocean acoustics, Inverse Problems, 10, 1994, 1023–1040.
Egorov, Y. V. and Shubin, M. A., Foundations of the Classical Theory of Partial Differential Equations (Translated by R. Cooke), Encyclopaedia of Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 30, Springer-Verlag, New York, 2001.
Engquist, B. and Majda, A., Absorbing boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves, Math. Comput., 31, 1977, 629–651.
Fries, T. P. and Belytschko, T., The extended/generalized finite element method: An overview of the method and its applications, Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng, 84, 2010, 253–304.
Giladi, E. and Keller, J. B., A hybrid numerical asymptotic method for scattering problems, J. Comput. Phys., 174, 2001, 226–247.
Givoli, D. and Patlashenko, I., Optimal local non-reflecting boundary conditions, Appl. Numer. Math., 27, 1998, 367–384.
He, X. and Luo, L. S., Theory of the lattice Boltzmann method: From the Boltzmann equation to the lattice Boltzmann equation, Phys. Rev. E, 56, 1997, 6811–6817.
Higdon, R. L., Numerical absorbing boundary conditions for the wave equation, Math. Comp., 49(179), 1987, 65–90.
Ishimaru, A., Theory and application of wave propagation and scattering in random media, Proceedings of the IEEE, 65, 1977, 1030–1061.
Ishimaru, A., Wave Propagation and Scattering in Random Media, Series on Electromagnetic Wave Theory, IEEE Press, New York, 1997.
Lindman, E. L., Free space boundary conditions for time dependent wave equation, J. Comput. Phys., 18, 1975, 66–78.
Luthi, P. O., Lattice Wave Automata: From Radio Waves to Fractures Propagation, Phd Thesis, Universite de Geneve, 1997.
Majda, A. and Osher, S., Reflection of singularities at the boundary, Comm. Pure Appl. Math., 28, 1975, 277–298.
Martin, P. A., Multiple Scattering: Interaction of Time-Harmonic Waves with N Obstacles, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, Vol. 107, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006.
Obrecht, C. and Kuznik, F., Tourancheau, B. and Roux, J., Multi-GPU implementation of the lattice Boltzmann method, Comp. Math. Appl., 65(2), 2013, 252–261.
Perthame, B., Vega, L., Energy concentration and Sommerfeld condition for Helmholtz and Liouville equations, C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris, Ser. I, 337, 2003, 587–592.
Perthame, B. and Vega, L., Morrey-Campanato estimates for Helmholtz equations, J. Funct. Anal., 164, 1999, 340–355.
Riegel, E., Indinger, T. and Adams, N. A., Implementation of a lattice Boltzmann method for numerical fluid mechanics using the nVIDIA CUDA technology, Computer Science-Research and Development, 23, 2009, 241–247.
Sommerfeld, A., Partial Differential Equations in Physics, Academic Press, New York, 1964.
Strouboulis, T., Babuskab, I. and Hidajat, R., The generalized finite element method for Helmholtz equation: Theory, computation, and open problems, Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 195, 2006, 4711–4731.
Succi, S., The Lattice Boltzmann Equation for Fluid Dynamics and Beyond, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2001.
Taylor, M. E., Partial differential equations II: Qualitative studies of linear equations, Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 116, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1996.
Tikhonov, A. N. and Samarskii, A. A., Equations of Mathematical Physics, Dover Publ., New York, 1990.
Tolke, J., Implementation of a lattice Boltzmann kernel using the compute unified device architecture developed by nVIDIA, Comput. Visual. Sci., 13, 2010, 29–39.
Tubbs, K. and Tsai, F., GPU accelerated lattice Boltzmann model for shallow water flow and mass transport, Int. J. Numer. Meth. Engng., 86, 2011, 316–334.
Yan, G., A lattice Boltzmann equation for waves, J. Comput. Phys., 161, 2000, 61–69.
Zhang, J., Yan, G. and Dong, Y., A new lattice Boltzmann model for the Laplace equation, Appl. Math. Comput., 215, 2009, 539–547.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandre, R., Liao, J. A pseudo-kinetic approach for Helmholtz equation. Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 34, 319–332 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11401-013-0775-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11401-013-0775-y