Abstract
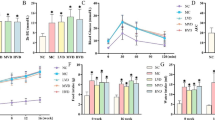
Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), the major protein component of serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL), exhibits its anti-inflammatory activity in inflammatory responses. As renal inflammation plays an important role in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury of the kidney, the aim of this study was to investigate the beneficial effect of ApoA-I on renal I/R injury in rats and the underlined mechanism. Using rats subjected to renal I/R by occlusion of bilateral renal pedicles, we found that administration of ApoA-I significantly reduced serum creatinine levels, serum TNF-α and IL-1β levels as well as tissue myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, compared with I/R controls. Moreover, ApoA-I treatment suppresses the expression of intercellular adhesion molecules-1 (ICAM-1) and P-selectin on endothelium, thus diminishing neutrophil adherence and the subsequent tissue injury. These results showed that ApoA-I reduced I/R-induced inflammatory responses, decreased renal microscopic damage and improved renal function. It seems likely that ApoA-I protects kidney from I/R injury by inhibiting inflammatory cytokines release and neutrophil infiltration and activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal M, Swartz R (2000) Acute renal failure. Am Fam Physician 61:2077–2088
Koo DD, Welsh KI, West NE, Channon KM, Penington AJ, Roake JA (2001) Endothelial cell protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury by lecithinized superoxide dismutase. Kidney Int 60:786–796
Williams P, Lopez H, Britt D, Chan C, Ezrin A, Hottendorf R (1997) Characterization of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 37:1–7
Thiemermann C, Patel NSA, Kvale EO, Cockerill GW, Brown PAJ, Stewart KN, Cuzzocrea S, Britti D, Mota-Filipe H, Chatterjee PK (2003) High density lipoprotein (HDL) reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1833–1843
Barter PJ, Nicholls S, Rye KA, Anantharamaiah GM, Navab M, Fogelman AM (2004) Antiinflammatory properties of HDL. Circ Res 95:764–772
Ma J, Liao XL, Lou B, Wu MP (2004) Role of apolipoproteinA-I in protecting against endotoxin toxicity. Acta Biochem Biophys Sin 36:419–424
Liao XL, Lou B, Ma J, Wu MP (2005) Neutrophils activation can be dimished by apolipoproteinA-I. Life Sci 77:325–335
Gu SS, Shi N, Wu MP (2007) The protective effect of apolipoproteinA-I on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Life Sci 81:702–709
Lerch PG, Förtsch V, Hodler G, Bolli R (1996) Production and characterization of a reconstituted high density lipoprotein for therapeutic applications. Vox Sang 71:155–164
Chatterjee PK, Zacharowski K, Cuzzocrea S, Otto M, Thiemermann C (2000) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase reduce renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in the anesthetized rat in vivo. FASEB J 14:641–651
Araki M, Schenk AD, Fairchild RL (2004) Cytokines and chemokines: roles in the pathophysiology and therapy of ischemia and reperfusion injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 9:139–144
Miltoris BA, Marrs J (1999) The role of cell adhesion molecules in ischemic acute renal failure. Am J Med 106:583–592
Chamoun F, Burne M, O’Donnell M, Rabb H (2000) Pathophysiologic role of selectins and their ligands in ischemia reperfusion injury. Front Biosci 5:e103–e109
Yan YJ, Li Y, Lou B, Wu MP (2006) Beneficial effects of ApoA-I on LPS-induced acute lung injury and endotoxemia in mice. Life Sci 79:210–215
Brewer HB, Ronan R, Meng MS, Bishop C (1986) Isolation and characterization of apolipoproteins A-I, A-II, and A-IV. Methods Enzymol 128:223–235
Schumaker VN, Puppione DL (1986) Sequential flotation ultracentrifugation. Methods Enzymol 128:155–170
Yokota N, O’Donnell M, Daniels F, Taney MB, Keane W, Kasiske B, Rabb H (2003) Protective effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor on experimental renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Nephrol 23:13–17
Patel NSA, Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Paola RD, Sautebin L, Britti D, Thiemermann C (2004) Reduction of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in 5-lipoxygenase knockout mice and by the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton. Mol Pharmacol 66:220–227
Bonventre JV, Zuk A (2004) Ischemic acute renal failure: an inflammatory disease? Kidney Int 66:480–485
Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, Cleveland JC, Cain BS, Shames BD, Meng X (1998) Hydrogen peroxide induces tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated cardiac injury by a P38 mitogen-activitied protein kinase-dependent mechanism. Surgery 124:291–297
Jiao YL, Wu MP (2008) Apolipoprotein A-I diminishes acute lung injury and sepsis in mice induced by lipoteichoic acid. Cytokine. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2008.04.002
McEver RP, Cummings RD (1997) Role of PSGL–1 binding to selectins in leukocyte recruitment. J Clin Invest 100:485–492
Moore KL, Patel KD, Bruehl RE (1995) P-selectin glycoprotein ligand–1 mediates rolling of human neytrophils on P-selectin. J Cell Biol 128:661–671
Donnahoo KK, Shames BD, Harken AH, Meldrum DR (1999) The role of tumor necrosis factor in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Urol 162:196–203
Kelly KJ (2003) Distant effects if experimental renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1549–1558
Jaeschke H, Smith CW (1997) Mechanisms of neutrophil-induced parenchymal cell injury. J Leukocyte Biol 61:647–653
Tall AR (1990) Plasma high density lipoprotein: metabolism and relationship to atherogenesis. J Clin Invest 86:379–384
Assmann G, Nofer JR (2003) Atheroprotective effects of high-density lipoproteins. Annu Rev Med 54:321–341
Tsujita M, Wu CA, Be-Dohmae S, Usui S, Okazaki M, Yokoyama S (2005) On the hepatic mechanism of HDL assembly by the ABCA1/apoA-I pathway. J Lipid Res 46:154–162
Krimbou L, Marcil M, Genest J (2006) New insights into the biogenesis of human high density lipoproteins. Curr Opin Lipidol 17:258–267
Rader DJ (2006) Molecular regulation of HDL metabolism and function: implications for novel therapies. J Clin Invest 116:3090–3100
Nanjee MN, Crouse JR, King JM, Hovorka R, Rees SE, Carson ER et al (1996) Effects of intravenous infusion of lipid-free ApoA-I in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 16:1203–1214
Kee P, Rye K-A, Taylor JL, Barrett P, Barter PJ (2002) Metabolism of ApoA-I as lipid-free protein or as component of discoidal and spherical reconstituted HDLs: studies in wild-type and hepatic lipase transgenic rabbits. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1912–1917
Tardif J-C, Gregoire J, L’Allier PL, Ibrahim R, Leaperance J, Heinonen TM et al (2007) Effects of reconstituted high-density lipoprotein infusions on coronary atherosclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 297:1675–1682
Hubsch AP, Casas AT, Doran JE (1995) Protective effects of reconstituted high density lipoproteins in rabbit gram negative bacteremia models. J Lab Clin Med 126:548–558
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, N., Wu, MP. Apolipoprotein A-I attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Biomed Sci 15, 577–583 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-008-9258-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11373-008-9258-7