Abstract
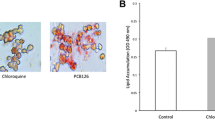
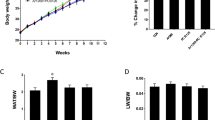
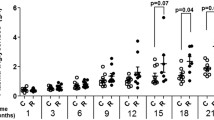
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) have been recognized as metabolic disruptors. The liver plays a pivotal role in detoxification of an organism. Fatty liver results from altered intra-, and extra-hepatic mediators and is associated with increased glucose-related protein 78 (GRP78), commonly used as a marker for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress signaling. This pilot study aimed to study the effects of a single exposure on fatty liver metabolic parameters. The objective of the study is to characterize the effects of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126) on ER stress protein chaperon GRP78 and CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) and intra-hepatic mediators such as microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c), and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), as well as extra-hepatic factors such as non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα). Hepatic GRP78 mRNA and protein levels, indicating the presence of ER stress, were significantly increased following a single PCB126 exposure in rats. Intra-hepatic mechanisms such as lipoprotein secretion pathway (i.e., MTP), lipogenesis de novo (i.e., SREBP1c), and oxidation (i.e., PPARα) were altered in PCB126-treated rats. In addition, a state of inflammation measured by higher TNFα plasma levels was present in contaminated rats. These data indicate that a single injection of PCB126-modulated expression of GRP78 associated with hepatic ER stress and systemic inflammation in rats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abenavoli L, Peta V (2014) Role of adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Recent Clin Trials 9(3):134–140
Agency, E. P. (2002). The foundation for global action onpersistent organic pollutants: a United States perspective. EPA/600/P-01/003F NCEA-I-1200
Arsov T, Silva DG, O'Bryan MK, Sainsbury A, Lee NJ, Kennedy C, Manji SS, Nelms K, Liu C, Vinuesa CG, de Kretser DM, Goodnow CC, Petrovsky N (2006) Fat aussie—a new Alstrom syndrome mouse showing a critical role for ALMS1 in obesity, diabetes, and spermatogenesis. Mol Endocrinol 20(7):1610–1622
Baker NA, Karounos M, English V, Fang J, Wei Y, Stromberg A, Sunkara M, Morris AJ, Swanson HI, Cassis LA (2013) Coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls impair glucose homeostasis in lean C57BL/6 mice and mitigate beneficial effects of weight loss on glucose homeostasis in obese mice. Environ Health Perspect 121(1):105–110
Boucher MP, Lefebvre C, Chapados NA (2015) The effects of PCB126 on intra-hepatic mechanisms associated with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Diabetes Metab Disord 14:88
Carter-Kent C, Zein NN, Feldstein AE (2008) Cytokines in the pathogenesis of fatty liver and disease progression to steatohepatitis: implications for treatment. Am J Gastroenterol 103(4):1036–1042
Chen Y, Gao H, Yin Q, Chen L, Dong P, Zhang X, Kang J (2013) ER stress activating ATF4/CHOP-TNF-alpha signaling pathway contributes to alcohol-induced disruption of osteogenic lineage of multipotential mesenchymal stem cell. Cell Physiol Biochem 32(3):743–754
Cuchel M, Bloedon LT, Szapary PO, Kolansky DM, Wolfe ML, Sarkis A, Millar JS, Ikewaki K, Siegelman ES, Gregg RE, Rader DJ (2007) Inhibition of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 356(2):148–156
Eberle D, Hegarty B, Bossard P, Ferre P, Foufelle F (2004) SREBP transcription factors: master regulators of lipid homeostasis. Biochimie 86(11):839–848
Ellgaard L, Molinari M, Helenius A (1999) Setting the standards: quality control in the secretory pathway. Science 286(5446):1882–1888
Endo M, Masaki T, Seike M, Yoshimatsu H (2007) TNF-alpha induces hepatic steatosis in mice by enhancing gene expression of sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c). Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 232(5):614–621
Gadupudi G, Gourronc FA, Ludewig G, Robertson LW, Klingelhutz AJ (2015) PCB126 inhibits adipogenesis of human preadipocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 29(1):132–141
Gibbons GF, Burnham FJ (1991) Effect of nutritional state on the utilization of fatty acids for hepatitic triacylglycerol synthesis and secretion as very-low-density lipoprotein. Biochem J 275(Pt 1):87–92
Grygiel-Gorniak B (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their ligands: nutritional and clinical implications—a review. Nutr J 13:17
Gu X, Li K, Laybutt DR, He ML, Zhao HL, Chan JC, Xu G (2010) Bip overexpression, but not CHOP inhibition, attenuates fatty-acid-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in HepG2 liver cells. Life Sci 87(23–26):724–732
Guth S, Volzing C, Muller A, Jung M, Zimmermann R (2004) Protein transport into canine pancreatic microsomes: a quantitative approach. Eur J Biochem 271(15):3200–3207
King IA, Tabiowo A (1981) Effect of tunicamycin on epidermal glycoprotein and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in vitro. Biochem J 198(2):331–338
Lai I, Chai Y, Simmons D, Luthe G, Coleman MC, Spitz D, Haschek WM, Ludewig G, Robertson LW (2010) Acute toxicity of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126) in male Sprague-Dawley rats: effects on hepatic oxidative stress, glutathione and metals status. Environ Int 36(8):918–923
Lee HG, Yang JH (2012) PCB126 induces apoptosis of chondrocytes via ROS-dependent pathways. Osteoarthr Cartil 20(10):1179–1185
Lee JS, Zheng Z, Mendez R, Ha SW, Xie Y, Zhang K (2012) Pharmacologic ER stress induces non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in an animal model. Toxicol Lett 211(1):29–38
Linden D, Lindberg K, Oscarsson J, Claesson C, Asp L, Li L, Gustafsson M, Boren J, Olofsson SO (2002) Influence of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha agonists on the intracellular turnover and secretion of apolipoprotein (Apo) B-100 and ApoB-48. J Biol Chem 277(25):23044–23053
Liu H, F. H. Nie, H. Y. Lin, Y. Ma, X. H. Ju, J. J. Chen and R. Gooneratne (2016) Developmental toxicity, oxidative stress, and related gene expression induced by dioxin-like PCB 126 in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ Toxicol 31(3):295–303
Loiola RA, Dos Anjos FM, Shimada AL, Cruz WS, Drewes CC, Rodrigues SF, Cardozo KH, Carvalho VM, Pinto E, Farsky SH (2016) Long-term in vivo polychlorinated biphenyl 126 exposure induces oxidative stress and alters proteomic profile on islets of Langerhans. Sci Rep 6:27882
Malhotra JD, Kaufman RJ (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: a vicious cycle or a double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal 9(12):2277–2293
Munro S, Pelham HR (1986) An Hsp70-like protein in the ER: identity with the 78 kd glucose-regulated protein and immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein. Cell 46(2):291–300
Nakamura MT, Yudell BE, Loor JJ (2014) Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids. Prog Lipid Res 53:124–144
Newberry EP, Xie Y, Kennedy SM, Luo J, Davidson NO (2006) Protection against western diet-induced obesity and hepatic steatosis in liver fatty acid-binding protein knockout mice. Hepatology 44(5):1191–1205
Ota T, Gayet C, Ginsberg HN (2008) Inhibition of apolipoprotein B100 secretion by lipid-induced hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress in rodents. J Clin Invest 118(1):316–332
Oyadomari S, Mori M (2004) Roles of CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ 11(4):381–389
Raabe M, Veniant MM, Sullivan MA, Zlot CH, Bjorkegren J, Nielsen LB, Wong JS, Hamilton RL, Young SG (1999) Analysis of the role of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in the liver of tissue-specific knockout mice. J Clin Invest 103(9):1287–1298
Ruzzin J, Petersen R, Meugnier E, Madsen L, Lock E-J, Lillefosse H, Ma T, Pesenti S, Sonne SB, Marstrand TT (2010) Persistent organic pollutant exposure leads to insulin resistance syndrome. Environ Health Perspect 118(4):465
Sandberg PO, Glaumann H (1980) Studies on the cellular toxicity of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) partial block and alteration of intracellular migration of lipoprotein particles in rat liver. Exp Mol Pathol 32(1):1–22
Staels B, Rubenstrunk A, Noel B, Rigou G, Delataille P, Millatt LJ, Baron M, Lucas A, Tailleux A, Hum DW, Ratziu V, Cariou B, Hanf R (2013) Hepatoprotective effects of the dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha/delta agonist, GFT505, in rodent models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 58(6):1941–1952
Tang WX, Wang LK, Wang YQ, Zong ZJ, Gao ZX, Liu XS, Shen YJ, Shen YX, Li YH (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha activation protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced HepG2 cell apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 385(1–2):179–190
Van den Berg, M., L. S. Birnbaum, M. Denison, M. De Vito, W. Farland, M. Feeley, H. Fiedler, H. Hakansson, A. Hanberg, L. Haws, M. Rose, S. Safe, D. Schrenk, C. Tohyama, A. Tritscher, J. Tuomisto, M. Tysklind, N. Walker and R. E. Peterson (2006) "The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and Mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds." Toxicol Sci 93(2): 223–241
van Ede KI, van Duursen MB, van den Berg M (2016) Evaluation of relative effect potencies (REPs) for dioxin-like compounds to derive systemic or human-specific TEFs to improve human risk assessment. Arch Toxicol 90(6):1293–1305
Werstuck GH, Lentz SR, Dayal S, Hossain GS, Sood SK, Shi YY, Zhou J, Maeda N, Krisans SK, Malinow MR, Austin RC (2001) Homocysteine-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes dysregulation of the cholesterol and triglyceride biosynthetic pathways. J Clin Invest 107(10):1263–1273
Xu J, Xiao G, Trujillo C, Chang V, Blanco L, Joseph SB, Bassilian S, Saad MF, Tontonoz P, Lee WN, Kurland IJ (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) influences substrate utilization for hepatic glucose production. J Biol Chem 277(52):50237–50244
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC 418312-2012) (to NAC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures were approved by the Animal Care Committee of the University of Ottawa and adhered to the guidelines established by the Canadian Council on Animal Care.
Funding
This project was funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC 418312-2012) (to NAC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Authors contribution
MPB carried out the molecular studies on rats and helped drafted the manuscript. NAC conceived the study and its design, as well ascoordinated and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Markus Hecker
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapados, N.A., Boucher, MP. Liver metabolic disruption induced after a single exposure to PCB126 in rats. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 1854–1861 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7939-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7939-8