Abstract
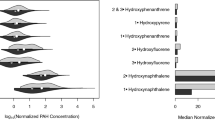
Links between environmental chemicals and human health have emerged, but the effects on self-rated health were less studied. Therefore, it was aimed to study the relationships of different sets of urinary environmental chemicals and the self-rated health in a national and population-based study in recent years. Data was retrieved from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys, 2011–2012, including demographics, serum measurements, lifestyle factors, self-rated health (with two grouping approaches) and urinary environmental chemical concentrations. T test and survey-weighted logistic regression modeling were performed. Among American adults aged 12–80 (n = 6833), 5892 people had reported their general health condition. Two thousand three hundred sixty-nine (40.2 %) people reported their general health condition as excellent or very good while 3523 (59.8 %) reported good, fair, or poor. People who reported their general health condition as good, fair, or poor had higher levels of urinary arsenic, heavy metals (including cadmium, cobalt, manganese, molybdenum, lead, antimony, strontium, tungsten and uranium), phthalates, pesticides and polyaromatic hydrocarbons but lower levels of benzophenone-3 and triclosan. There were no associations with urinary parabens, perchlorate, nitrate, thiocyanate or polyfluorinated compounds. However, only urinary cadmium, benzophenone-3, triclosan, and 2-hydroxynaphthalene remained significant when comparing between “good to excellent” and “poor to fair.” This is the first time observing risk associations of urinary arsenic, heavy metal, phthalate, pesticide, and hydrocarbon concentrations and self-rated health in people aged 12–80, although the causality cannot be established. Further elimination of these environmental chemicals in humans might need to be considered in health and environmental policies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2012) National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Hyattsville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, [http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes.htm]
Euteneuer F (2014) Subjective social status and health. Curr Opin Psychiatry 27:337–343
Mavaddat N, Parker RA, Sanderson S, Mant J, Kinmonth AL (2014) Relationship of self-rated health with fatal and non-fatal outcomes in cardiovascular disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e103509
Quon EC, McGrath JJ (2014) Subjective socioeconomic status and adolescent health: a meta-analysis. Health Psychol 33:433–447
Shiue I (2013a) Urine phthalate concentrations are higher in people with stroke: United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES), 2001–2004. Eur J Neurol 20:728–731
Shiue I (2013b) Association of urinary arsenic, heavy metal, and phthalate concentrations with food allergy in adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2005–2006. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 111:421–423
Shiue I (2013c) Urinary environmental chemical concentrations and vitamin D are associated with vision, hearing, and balance disorders in the elderly. Environ Int 53:41–46
Shiue I (2014a) Urinary thiocyanate concentrations are associated with adult cancer and lung problems: US NHANES, 2009–2012. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-014-3777-8
Shiue I (2014b) Higher urinary heavy metal, phthalate, and arsenic but not parabens concentrations in people with high blood pressure, U.S. NHANES, 2011–2012. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11:5989–5999
Shiue I (2015a) Arsenic, heavy metals, phthalates, pesticides, hydrocarbons and polyfluorinated compounds but not parabens or phenols are associated with adult remembering condition: US NHANES, 2011–2012. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22:6381–6386
Shiue I (2015b) Urinary parabens and polyaromatic hydrocarbons independent of health conditions are associated with adult emotional support needs: USA NHANES, 2005-2008. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4561-0
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiue, I. Urinary arsenic, heavy metals, phthalates, pesticides, polyaromatic hydrocarbons but not parabens, polyfluorinated compounds are associated with self-rated health: USA NHANES, 2011–2012. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9570–9574 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4604-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4604-6