Abstract
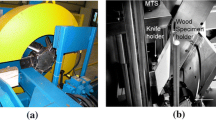
Wood chipping is a critical component part of many pulp and paper making processes. In order to study the damage mechanisms, when wood chips are created through the wood chipping process, it is crucial to have access to an experimental equipment in which chips can be produced under realistic conditions. In this paper, a laboratory chipper is presented, which has been developed to admit chipping at rates that can be varied in a large interval, i.e. at rates ranging from 0 to 50 m/s. The chipper also makes it possible to study e.g. the influence of different cutting angles on the chip geometry. The knife used to cut the chips is mounted on a knife holder, which is instrumented in such a way that forces in three orthogonal directions can be measured. One reason for measuring the forces acting on the knife during chipping is that the average force in the cutting direction will give information about the wear of the knife over time. Since the actual force and the measured force differ due to inertia effects, a simple mathematical model is developed and used to evaluate the force acting on the knife. The results from the force measurements are presented and it is concluded that the laboratory chipper is a versatile tool in the process of increasing the understanding of the chipping process.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kivimaa E, Murto JO (1949) Investigation on factors affecting chipping of pulpwood; Publ.9 Statens Tekniska Forskningsanstalt, Esboo, Finland
Twaddle A (1997) The influence of species, chip length, and ring orientation on chip thickness. Tappi J 80(6):123–131
Uhmeier A (1995) Some fundamental aspects of wood chipping. Tappi J 78(10):79–86
Buchanan JG, Duchnicki TS (1963) Some experiments in low-speed chipping. Pulp and Paper Magazine Can. May 1963, T235–T245
Hellström LM, Gradin PA, Carlberg T (2008) A method for experimental investigation of the wood chipping process. Nordic Pulp and Paper Res J 23(3):339–342
Hartler N (1962) The effect of spout angles as studied in an experimental chipper. Svensk Papperstidning 65(9):351–362
Krapivsky PL, Redner S (2007) Smoothing of a rock by chipping. Phys Rev E 75:031119
Carl de Boor (2001) A practical guide to splines; Springer (November 29, 2001); ISBN-10: 0387953663
http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/13812-fit-a-spline-to-noisy-data
Acknowledgements
The European Regional Development fund is acknowledged for financial support while Staffan Nyström at Mid Sweden University and GRW PRODUKTER AB are greatly acknowledged for the development and manufacture of the experimental equipment respectively. Iggesund Tools AB is also greatly acknowledged for their support in the development of the experimental equipment and for their help with the analysis of the wood chips. Jerry Larsson at SCA´s saw mill at Tunadal is greatly acknowledged for supplying us with fresh spruce.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hellström, L.M., Gradin, P.A., Gulliksson, M. et al. A Laboratory Wood Chipper for Chipping Under Realistic Conditions. Exp Mech 51, 1309–1316 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-010-9452-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-010-9452-1