Abstract
Purpose
Tumor resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs is one of the major obstacles in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). In this study, we attempted to modulate tumor response to chemotherapy by combination treatment that included experimental (small interference RNA (siRNA), chlorotoxin) and conventional (temozolomide, TMZ) therapeutics.
Procedures
siRNA therapy was used to silence O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT), a key factor in brain tumor resistance to TMZ. For targeting of tumor cells, we used chlorotoxin (CTX), a peptide with antitumoral properties. siRNA and CTX were conjugated to iron oxide nanoparticles (NP) that served as the drug carrier and allowed the means to monitor the changes in tumor volume by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Results
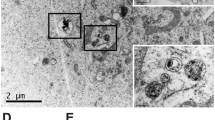
Theranostic nanoparticles (termed CTX-NP-siMGMT) were internalized by T98G glioblastoma cells in vitro leading to enhancement of TMZ toxicity. Combination treatment of mice bearing orthotopic tumors with CTX-NP-siMGMT and TMZ led to significant retardation of tumor growth, which was monitored by MRI.
Conclusions
While our results demonstrate that siRNA delivery by targeted nanoparticles resulted in modulating tumor response to chemotherapy in GBM, they also point to a significant contribution of CTX to tumor cell death.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD et al (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Friedman HS, Kerby T, Calvert H (2000) Temozolomide and treatment of malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 6:2585–2597
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Godard S et al (2004) Clinical trial substantiates the predictive value of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase promoter methylation in glioblastoma patients treated with temozolomide. Clin Cancer Res 10:1871–1874
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T et al (2005) MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:997–1003
Pegg AE (1990) Mammalian O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase: regulation and importance in response to alkylating carcinogenic and therapeutic agents. Cancer Res 50:6119–6129
Dumenco LL, Allay E, Norton K, Gerson SL (1993) The prevention of thymic lymphomas in transgenic mice by human O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase. Science 259:219–222
Kaina B, Fritz G, Mitra S, Coquerelle T (1991) Transfection and expression of human O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) cDNA in Chinese hamster cells: the role of MGMT in protection against the genotoxic effects of alkylating agents. Carcinogenesis 12:1857–1867
Pistollato F, Abbadi S, Rampazzo E et al (2010) Intratumoral hypoxic gradient drives stem cells distribution and MGMT expression in glioblastoma. Stem Cells 28:851–862
Hegi ME, Liu L, Herman JG et al (2008) Correlation of O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylation with clinical outcomes in glioblastoma and clinical strategies to modulate MGMT activity. J Clin Oncol 26:4189–4199
Paz MF, Yaya-Tur R, Rojas-Marcos I et al (2004) CpG island hypermethylation of the DNA repair enzyme methyltransferase predicts response to temozolomide in primary gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 10:4933–4938
Weller M, Stupp R, Reifenberger G et al (2010) MGMT promoter methylation in malignant gliomas: ready for personalized medicine? Nat Rev Neurol 6:39–51
Yoshino A, Ogino A, Yachi K et al (2010) Gene expression profiling predicts response to temozolomide in malignant gliomas. Int J Oncol 36:1367–1377
Chinnasamy N, Rafferty JA, Hickson I et al (1997) O6-benzylguanine potentiates the in vivo toxicity and clastogenicity of temozolomide and BCNU in mouse bone marrow. Blood 89:1566–1573
Fairbairn LJ, Watson AJ, Rafferty JA et al (1995) O6-benzylguanine increases the sensitivity of human primary bone marrow cells to the cytotoxic effects of temozolomide. Exp Hematol 23:112–116
Kato T, Natsume A, Toda H et al (2010) Efficient delivery of liposome-mediated MGMT-siRNA reinforces the cytotoxity of temozolomide in GBM-initiating cells. Gene Ther 17:1363–1371
Kumar M, Yigit M, Dai G et al (2010) Image-guided breast tumor therapy using a small interfering RNA nanodrug. Cancer Res 70:7553–7561
Medarova Z, Pham W, Farrar C et al (2007) In vivo imaging of siRNA delivery and silencing in tumors. Nat Med 13:372–377
Kumar M, Medarova Z, Pantazopoulos P et al (2010) Novel membrane-permeable contrast agent for brain tumor detection by MRI. Magn Reson Med 63:617–624
DeBin JA, Strichartz GR (1991) Chloride channel inhibition by the venom of the scorpion Leiurus quinquestriatus. Toxicon 29:1403–1408
Lyons SA, O'Neal J, Sontheimer H (2002) Chlorotoxin, a scorpion-derived peptide, specifically binds to gliomas and tumors of neuroectodermal origin. Glia 39:162–173
Deshane J, Garner CC, Sontheimer H (2003) Chlorotoxin inhibits glioma cell invasion via matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem 278:4135–4144
Veiseh M, Gabikian P, Bahrami SB et al (2007) Tumor paint: a chlorotoxin:Cy5.5 bioconjugate for intraoperative visualization of cancer foci. Cancer Res 67:6882–6888
Mamelak AN, Rosenfeld S, Bucholz R et al (2006) Phase I single-dose study of intracavitary-administered iodine-131-TM-601 in adults with recurrent high-grade glioma. J Clin Oncol 24:3644–3650
Shen S, Khazaeli MB, Gillespie GY, Alvarez VL (2005) Radiation dosimetry of 131I-chlorotoxin for targeted radiotherapy in glioma-bearing mice. J Neurooncol 71:113–119
Soroceanu L, Gillespie Y, Khazaeli MB, Sontheimer H (1998) Use of chlorotoxin for targeting of primary brain tumors. Cancer Res 58:4871–4879
Kievit FM, Veiseh O, Fang C et al (2010) Chlorotoxin labeled magnetic nanovectors for targeted gene delivery to glioma. ACS Nano 4:4587–4594
Lee MJ, Veiseh O, Bhattarai N et al (2010) Rapid pharmacokinetic and biodistribution studies using cholorotoxin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles: a novel non-radioactive method. PLoS One 5:e9536
Sun C, Fang C, Stephen Z et al (2008) Tumor-targeted drug delivery and MRI contrast enhancement by chlorotoxin-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 3:495–505
Veiseh O, Kievit FM, Fang C et al (2010) Chlorotoxin bound magnetic nanovector tailored for cancer cell targeting, imaging, and siRNA delivery. Biomaterials 31:8032–8042
Veiseh O, Sun C, Fang C et al (2009) Specific targeting of brain tumors with an optical/magnetic resonance imaging nanoprobe across the blood–brain barrier. Cancer Res 69:6200–6207
Veiseh O, Sun C, Gunn J et al (2005) Optical and MRI multifunctional nanoprobe for targeting gliomas. Nano Lett 5:1003–1008
Fu YJ, Yin LT, Liang AH et al (2007) Therapeutic potential of chlorotoxin-like neurotoxin from the Chinese scorpion for human gliomas. Neurosci Lett 412:62–67
McFerrin MB, Sontheimer H (2006) A role for ion channels in glioma cell invasion. Neuron Glia Biol 2:39–49
Watson AJ, Margison GP (1999) O (6)-Alkylguanine-DNA Alkyltransferase Assay. Methods Mol Med 28:167–178
Carlson BL, Pokorny JL, Schroeder MA, Sarkaria JN (2011) Establishment, maintenance and in vitro and in vivo applications of primary human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) xenograft models for translational biology studies and drug discovery. Curr Protoc Pharmacol Chapter 14:Unit 14 16.
Akinc A, Thomas M, Klibanov A, Lanfer R (2005) Exploring polyethylenimine-mediated DNA transfection and the proton sponge hypothesis. J Gene Med 7:657–663
Wang P, Yigit MV, Ran C et al (2012) A theranostic small interfering RNA nanoprobe protects pancreatic islet grafts from adoptively transferred immune rejection. Diabetes 61:3247–3254
Wang P, Yigit M, Medarova Z et al (2011) Combined small interfering RNA therapy and in vivo magnetic resonance imaging in islet transplantation. Diabetes 60:565–571
Hobbs SK, Monsky WL, Yuan F et al (1998) Regulation of transport pathways in tumor vessels: role of tumor type and microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4607–4612
Chahal M, Xu Y, Lesniak D et al (2010) MGMT modulates glioblastoma angiogenesis and response to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib. Neuro Oncol 12:822–833
Cordier D, Forrer F, Kneifel S et al (2010) Neoadjuvant targeting of glioblastoma multiforme with radiolabeled DOTAGA-substance P—results from a phase I study. J Neurooncol 100:129–136
Jenkinson MD, Smith TS, Haylock B et al (2010) Phase II trial of intratumoral BCNU injection and radiotherapy on untreated adult malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 99:103–113
Oshiro S, Tsugu H, Komatsu F et al (2006) Evaluation of intratumoral administration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in patients with malignant glioma. Anticancer Res 26:4027–4032
Moore A, Marecos E, Bogdanov A Jr, Weissleder R (2000) Tumoral distribution of long-circulating dextran-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in a rodent model. Radiology 214:568–574
Bartlett DW, Davis ME (2006) Insights into the kinetics of siRNA-mediated gene silencing from live-cell and live-animal bioluminescent imaging. Nucleic Acids Res 34:322–333
Stein GH (1979) T98G: an anchorage-independent human tumor cell line that exhibits stationary phase G1 arrest in vitro. J Cell Physiol 99:43–54
Yin D, Xie D, Hofmann WK et al (2003) DNA repair gene O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase: promoter hypermethylation associated with decreased expression and G:C to A:T mutations of p53 in brain tumors. Mol Carcinog 36:23–31
Kesavan K, Ratliff J, Johnson EW et al (2010) Annexin A2 is a molecular target for TM601, a peptide with tumor-targeting and anti-angiogenic effects. J Biol Chem 285:4366–4374
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by T32CA009502 (PI Anna Moore).
Conflict of Interest Statement
Authors declare no potential conflicts of interest relevant to this publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Byunghee Yoo and Marytheresa A. Ifediba contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 1,433 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, B., Ifediba, M.A., Ghosh, S. et al. Combination Treatment with Theranostic Nanoparticles for Glioblastoma Sensitization to TMZ. Mol Imaging Biol 16, 680–689 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0734-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-014-0734-3