Abstract
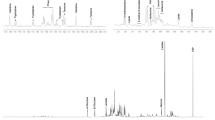
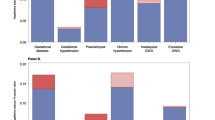
Obesity is currently an increasing public health problem. The intra-uterine environment plays a critical role in foetal development. The objective of this study is to investigate the association of obesity with modifications in the metabolic profiles of pregnant women, and their new-borns. Based on the PELAGIE cohort (Brittany, France), a sample of 321 pregnant women was divided into three groups according to their body mass index (BMI) (normal, over-weight and obese). Nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomics analyses were performed on maternal urine and cord-blood samples. Partial least squares regression-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA), polytomous and logistic regressions were used to differentiate the metabolic profiles of the three BMI groups after adjusting for potential confounders. Specific profiles were observed for the overweight and obese women (BMI > 25) compared to the normal-weight women: they had a decrease in urinary hippurate excretion associated with a decrease in phenylalanine and an increase in creatinine. We also showed an increase in the urinary excretion of lactate, citrate, acetate, creatine, and lysine only in obese women (BMI > 30) compared to the normal-weight women. The PLS-DA modelling did not reveal any significant difference between the cord-blood metabolic profiles of newborns according to maternal BMI—although infants born of obese women had a higher birth weight and a lower Apgar score. Our results confirmed the potential link between obesity and gut microbiota disruption (changes in urinary acids), as well as energy and amino-acid metabolism but did not reveal any disruption among newborns.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. H. (2011). Emerging perspectives on essential amino acid metabolism in obesity and the insulin-resistant state. Advances in Nutrition, 2, 445–456. doi:10.3945/an.111.000737.
Bonvallot, N., Tremblay-Franco, M., Chevrier, C., Canlet, C., Warembourg, C., Cravedi, J.-P., & Cordier, S. (2013). Metabolomics tools for describing complex pesticide exposure in pregnant women in Brittany (France). PLoS One, 8, e64433. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064433.
Bouanane, S., Merzouk, H., Benkalfat, N. B., Soulimane, N., Merzouk, S. A., Gresti, J., et al. (2010). Hepatic and very low-density lipoprotein fatty acids in obese offspring of overfed dams. Metabolism, 59, 1701–1709. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2010.04.003.
Bouchard, L., Hivert, M.-F., Guay, S.-P., St-Pierre, J., Perron, P., & Brisson, D. (2012). Placental adiponectin gene DNA methylation levels are associated with mothers’ blood glucose concentration. Diabetes, 61, 1272–1280. doi:10.2337/db11-1160.
Bouchard, L., Thibault, S., Guay, S.-P., Santure, M., Monpetit, A., St-Pierre, J., et al. (2010). Leptin gene epigenetic adaptation to impaired glucose metabolism during pregnancy. Diabetes Care, 33, 2436–2441. doi:10.2337/dc10-1024.
Breitling, R., Pitt, A. R., & Barrett, M. P. (2006). Precision mapping of the metabolome. Trends in Biotechnology, 24(12), 543–548.
Calvani, R., Miccheli, A., Capuani, G., Tomassini Miccheli, A., Puccetti, C., Delfini, M., et al. (2010). Gut microbiome-derived metabolites characterize a peculiar obese urinary metabotype. International Journal of Obesity, 2005(34), 1095–1098. doi:10.1038/ijo.2010.44.
Challier, J. C., Basu, S., Bintein, T., Minium, J., Hotmire, K., Catalano, P. M., & Hauguel-de Mouzon, S. (2008). Obesity in pregnancy stimulates macrophage accumulation and inflammation in the placenta. Placenta, 29, 274–281. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2007.12.010.
Chevrier, C., Limon, G., Monfort, C., Rouget, F., Garlantézec, R., Petit, C., et al. (2011). Urinary biomarkers of prenatal atrazine exposure and adverse birth outcomes in the PELAGIE birth cohort. Environmental Health Perspectives, 119, 1034–1041. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002775.
Dahlhoff, M., Pfister, S., Blutke, A., Rozman, J., Klingenspor, M., Deutsch, M. J., et al. (2014). Peri-conceptional obesogenic exposure induces sex-specific programming of disease susceptibilities in adult mouse offspring. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1842, 304–317. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.11.021.
Dewulf, E. M., Cani, P. D., Claus, S. P., Fuentes, S., Puylaert, P. G. B., Neyrinck, A. M., et al. (2013). Insight into the prebiotic concept: lessons from an exploratory, double blind intervention study with inulin-type fructans in obese women. Gut, 62, 1112–1121. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303304.
Dong, M., Zheng, Q., Ford, S. P., Nathanielsz, P. W., & Ren, J. (2013). Maternal obesity, lipotoxicity and cardiovascular diseases in offspring. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 55, 111–116. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.08.023.
Duggan, G. E., Hittel, D. S., Hughey, C. C., Weljie, A., Vogel, H. J., & Shearer, J. (2011). Differentiating short- and long-term effects of diet in the obese mouse using (1) H-nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomics. Diabetes Obesity and Metabolism, 13, 859–862. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2011.01410.x.
Dumas, M.-E., Maibaum, E. C., Teague, C., Ueshima, H., Zhou, B., Lindon, J. C., et al. (2006). Assessment of analytical reproducibility of 1H NMR spectroscopy based metabonomics for large-scale epidemiological research: the INTERMAP Study. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 2199–2208. doi:10.1021/ac0517085.
Farley, D. M., Choi, J., Dudley, D. J., Li, C., Jenkins, S. L., Myatt, L., & Nathanielsz, P. W. (2010). Placental amino acid transport and placental leptin resistance in pregnancies complicated by maternal obesity. Placenta, 31, 718–724. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2010.06.006.
Fiehn, O. (2002). Metabolomics–the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Molecular Biology, 48, 155–171.
Friedrich, N., Budde, K., Wolf, T., Jungnickel, A., Grotevendt, A., Dressler, M., et al. (2012). Short-term changes of the urine metabolome after bariatric surgery. Omics A Journal of Integrative Biology, 16, 612–620. doi:10.1089/omi.2012.0066.
Godfrey, K. M., & Barker, D. J. (2000). Fetal nutrition and adult disease. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 71, 1344S–1352S.
Gross, M. (2013). Does the gut microbiome hold clues to obesity and diabetes? Current Biology, 23, R359–R362.
Gudbrandsen, O. A., Wergedahl, H., Liaset, B., Espe, M., Mørk, S., & Berge, R. K. (2008). Dietary single cell protein reduces fatty liver in obese Zucker rats. British Journal of Nutrition, 100, 776–785. doi:10.1017/S0007114508960906.
Guzmán, C., Cabrera, R., Cárdenas, M., Larrea, F., Nathanielsz, P. W., & Zambrano, E. (2006). Protein restriction during fetal and neonatal development in the rat alters reproductive function and accelerates reproductive ageing in female progeny. Journal of Physiology, 572, 97–108. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.103903.
Hanzu, F. A., Vinaixa, M., Papageorgiou, A., Párrizas, M., Correig, X., Delgado, S., et al. (2013). Obesity rather than regional fat depots marks the metabolomic pattern of adipose tissue: An untargeted metabolomic approach. Obesity,. doi:10.1002/oby.20541.
Inadera, H. (2013). Developmental origins of obesity and type 2 diabetes: molecular aspects and role of chemicals. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine, 18, 185–197. doi:10.1007/s12199-013-0328-8.
Janesick, A., & Blumberg, B. (2011). Endocrine disrupting chemicals and the developmental programming of adipogenesis and obesity. Birth Defects Research Part C Embryo Today: Reviews, 93, 34–50. doi:10.1002/bdrc.20197.
Jones, H. N., Woollett, L. A., Barbour, N., Prasad, P. D., Powell, T. L., & Jansson, T. (2009). High-fat diet before and during pregnancy causes marked up-regulation of placental nutrient transport and fetal overgrowth in C57/BL6 mice. The FASEB Journal, 23, 271–278. doi:10.1096/fj.08-116889.
Karmaus, W., Osuch, J. R., Eneli, I., Mudd, L. M., Zhang, J., Mikucki, D., et al. (2009). Maternal levels of dichlorodiphenyl-dichloroethylene (DDE) may increase weight and body mass index in adult female offspring. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 66, 143–149. doi:10.1136/oem.2008.041921.
Kim, K. E., Onesti, G., Ramirez, O., Brest, A. N., & Swartz, C. (1969). Creatinine clearance in renal disease. A reappraisal. British Medical Journal, 4, 11–14.
Kim, M. J., Yang, H. J., Kim, J. H., Ahn, C.-W., Lee, J. H., Kim, K. S., & Kwon, D. Y. (2013). Obesity-related metabolomic analysis of human subjects in black soybean peptide intervention study by ultraperformance liquid chromatography and quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Obesity, 2013, 874981. doi:10.1155/2013/874981.
Kim, S.-H., Yang, S.-O., Kim, H.-S., Kim, Y., Park, T., & Choi, H.-K. (2009). 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy-based metabolic assessment in a rat model of obesity induced by a high-fat diet. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 395, 1117–1124. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-3054-8.
Kirk, S. L., Samuelsson, A.-M., Argenton, M., Dhonye, H., Kalamatianos, T., Poston, L., et al. (2009). Maternal obesity induced by diet in rats permanently influences central processes regulating food intake in offspring. PLoS One, 4, e5870. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005870.
Lee, J. V., Shah, S. A., & Wellen, K. E. (2013). Obesity, cancer, and acetyl-CoA metabolism. Drug Discovery Today Disease Mechanisms, 10, e55–e61. doi:10.1016/j.ddmec.2013.03.005.
Lees, H. J., Swann, J. R., Wilson, I. D., Nicholson, J. K., & Holmes, E. (2013). Hippurate: the natural history of a mammalian-microbial cometabolite. Journal of Proteome Research, 12, 1527–1546. doi:10.1021/pr300900b.
Li, H., Xie, Z., Lin, J., Song, H., Wang, Q., Wang, K., et al. (2008). Transcriptomic and metabonomic profiling of obesity-prone and obesity-resistant rats under high fat diet. Journal of Proteome Research, 7, 4775–4783. doi:10.1021/pr800352k.
Lowe, W. L., & Karban, J. (2014). Genetics, genomics and metabolomics: new insights into maternal metabolism during pregnancy. Diabetic Medicine, 31, 254–262. doi:10.1111/dme.12352.
Magyar, D. M., Fridshal, D., Elsner, C. W., Glatz, T., Eliot, J., Klein, A. H., et al. (1980). Time-trend analysis of plasma cortisol concentrations in the fetal sheep in relation to parturition. Endocrinology, 107, 155–159. doi:10.1210/endo-107-1-155.
Muhlhausler, B. S., Gugusheff, J. R., Ong, Z. Y., & Vithayathil, M. A. (2013). Nutritional approaches to breaking the intergenerational cycle of obesity. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 91, 421–428. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2012-0353.
Norman, J. D., Ferguson, M. M., & Danzmann, R. G. (2014). Transcriptomics of salinity tolerance capacity in Arctic charr (Salvelinus alpinus): A comparison of gene expression profiles between divergent QTL genotypes. Physiological Genomics, 46, 123–137. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00105.2013.
O’Reilly, J. R., & Reynolds, R. M. (2013). The risk of maternal obesity to the long-term health of the offspring. Clinical Endocrinology, 78, 9–16. doi:10.1111/cen.12055.
Orsi, C. M., Hale, D. E., & Lynch, J. L. (2011). Pediatric obesity epidemiology. Current opinion in Endocrinology Diabetes and Obesity, 18, 14–22. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3283423de1.
Phipps, A. N., Stewart, J., Wright, B., & Wilson, I. D. (1998). Effect of diet on the urinary excretion of hippuric acid and other dietary-derived aromatics in rat. A complex interaction between diet, gut microflora and substrate specificity. Xenobiotica, 28, 527–537. doi:10.1080/004982598239443.
Proczko, M., Kaska, Ł., Kobiela, J., Stefaniak, T., Zadrożny, D., & Śledziński, Z. (2013). Bariatric surgery in morbidly obese patients with chronic renal failure, prepared for kidney transplantation–case reports. Polski Przeglad Chirurgiczny, 85, 407–411. doi:10.2478/pjs-2013-0062.
Respondek, F., Gerard, P., Bossis, M., Boschat, L., Bruneau, A., Rabot, S., et al. (2013). Short-chain fructo-oligosaccharides modulate intestinal microbiota and metabolic parameters of humanized gnotobiotic diet induced obesity mice. PLoS One, 8, e71026. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071026.
Rull, A., Vinaixa, M., Angel Rodríguez, M., Beltrán, R., Brezmes, J., Cañellas, N., et al. (2009). Metabolic phenotyping of genetically modified mice: An NMR metabonomic approach. Biochimie, 91, 1053–1057. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2009.04.019.
Salek, R. M., Maguire, M. L., Bentley, E., Rubtsov, D. V., Hough, T., Cheeseman, M., et al. (2007). A metabolomic comparison of urinary changes in type 2 diabetes in mouse, rat, and human. Physiological Genomics, 29, 99–108. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00194.2006.
Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S., Silventoinen, K., Jousilahti, P., Hu, G., & Tuomilehto, J. (2004). The association between thinness and socio-economic disadvantage, health indicators, and adverse health behaviour: a study of 28 000 Finnish men and women. International Journal of Obesity, 28, 568–573. doi:10.1038/sj.ijo.0802596.
Schirra, H. J., Anderson, C. G., Wilson, W. J., Kerr, L., Craik, D. J., Waters, M. J., & Lichanska, A. M. (2008). Altered metabolism of growth hormone receptor mutant mice: a combined NMR metabonomics and microarray study. PLoS One, 3, e2764. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002764.
Serkova, N. J., Jackman, M., Brown, J. L., Liu, T., Hirose, R., Roberts, J. P., et al. (2006). Metabolic profiling of livers and blood from obese Zucker rats. Journal of Hepatology, 44, 956–962. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2005.07.009.
Shearer, J., Duggan, G., Weljie, A., Hittel, D. S., Wasserman, D. H., & Vogel, H. J. (2008). Metabolomic profiling of dietary-induced insulin resistance in the high fat-fed C57BL/6 J mouse. Diabetes Obesity and Metabolism, 10, 950–958. doi:10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00837.x.
Shelley, P., Martin-Gronert, M. S., Rowlerson, A., Poston, L., Heales, S. J. R., Hargreaves, I. P., et al. (2009). Altered skeletal muscle insulin signaling and mitochondrial complex II-III linked activity in adult offspring of obese mice. American Journal of Physiology: Regulatory Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 297, R675–R681. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00146.2009.
Simmons, R. A., Suponitsky-Kroyter, I., & Selak, M. A. (2005). Progressive accumulation of mitochondrial DNA mutations and decline in mitochondrial function lead to beta-cell failure. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 28785–28791. doi:10.1074/jbc.M505695200.
Smink, A., Ribas-Fito, N., Garcia, R., Torrent, M., Mendez, M. A., Grimalt, J. O., & Sunyer, J. (2008). Exposure to hexachlorobenzene during pregnancy increases the risk of overweight in children aged 6 years. Acta Paediatrica, 1992(97), 1465–1469. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2008.00937.x.
Smit, S., van Breemen, M. J., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Smilde, A. K., Aerts, J. M. F. G., & de Koster, C. G. (2007). Assessing the statistical validity of proteomics based biomarkers. Analytica Chimica Acta, 592, 210–217. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2007.04.043.
Smolinska, A., Blanchet, L., Buydens, L. M. C., & Wijmenga, S. S. (2012). NMR and pattern recognition methods in metabolomics: from data acquisition to biomarker discovery: a review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 750, 82–97. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2012.05.049.
Suter, M. A., Sangi-Haghpeykar, H., Showalter, L., Shope, C., Hu, M., Brown, K., et al. (2012). Maternal high-fat diet modulates the fetal thyroid axis and thyroid gene expression in a nonhuman primate model. Molecular Endocrinology, 26, 2071–2080. doi:10.1210/me.2012-1214.
Symonds, M. E., Mendez, M. A., Meltzer, H. M., Koletzko, B., Godfrey, K., Forsyth, S., & van der Beek, E. M. (2013). Early life nutritional programming of obesity: mother-child cohort studies. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism, 62, 137–145. doi:10.1159/000345598.
Szymańska, E., Saccenti, E., Smilde, A. K., & Westerhuis, J. A. (2012). Double-check: validation of diagnostic statistics for PLS-DA models in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics, 8, 3–16. doi:10.1007/s11306-011-0330-3.
Tuersunjiang, N., Odhiambo, J. F., Long, N. M., Shasa, D. R., Nathanielsz, P. W., & Ford, S. P. (2013). Diet reduction to requirements in obese/overfed ewes from early gestation prevents glucose/insulin dysregulation and returns fetal adiposity and organ development to control levels. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism, 305(7), E868–E878. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00117.2013.
Vinayavekhin, N., Homan, E. A., & Saghatelian, A. (2010). Exploring disease through metabolomics. ACS Chemical Biology, 5, 91–103. doi:10.1021/cb900271r.
Waldram, A., Holmes, E., Wang, Y., Rantalainen, M., Wilson, I. D., Tuohy, K. M., et al. (2009). Top-down systems biology modeling of host metabotype-microbiome associations in obese rodents. Journal of Proteome Research, 8, 2361–2375. doi:10.1021/pr8009885.
Wang, C., Feng, R., Sun, D., Li, Y., Bi, X., & Sun, C. (2011). Metabolic profiling of urine in young obese men using ultra performance liquid chromatography and Q-TOF mass spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF MS). Journal of Chromatography, 879, 2871–2876. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.08.014.
Waterman, D. S., Bonner, F. W., & Lindon, J. C. (2009). Review: Spectroscopic and statistical methods in metabonomics. Bioanalysis, 1(9), 1559–1578. doi:10.4155/bio.09.143.
Wen, X., Triche, E. W., Hogan, J. W., Shenassa, E. D., & Buka, S. L. (2011). Prenatal factors for childhood blood pressure mediated by intrauterine and/or childhood growth? Pediatrics, 127, e713–e721. doi:10.1542/peds.2010-2000.
Werner, E., Heilier, J.-F., Ducruix, C., Ezan, E., Junot, C., & Tabet, J.-C. (2008). Mass Spectrometry for the Identification of the Discriminating Signals from Metabolomics: Current Status and Future Trends. Journal of Chromatography B, 871(2), 143–163.
Whitehead, T. L., Holley, A. W., Korourian, S., Shaaf, S., Kieber-Emmons, T., & Hakkak, R. (2007). (1)H nuclear magnetic resonance metabolomic analysis of mammary tumors from lean and obese Zucker rats exposed to 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 20, 573–580.
WHO Expert Consultation. (2004). Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet, 363, 157–163. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3.
Williams, R. E., Eyton-Jones, H. W., Farnworth, M. J., Gallagher, R., & Provan, W. M. (2002). Effect of intestinal microflora on the urinary metabolic profile of rats: a (1)H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Xenobiotica, 32, 783–794. doi:10.1080/00498250210143047.
Williams, R. E., Lenz, E. M., Evans, J. A., Wilson, I. D., Granger, J. H., Plumb, R. S., & Stumpf, C. L. (2005). A combined (1)H NMR and HPLC-MS-based metabonomic study of urine from obese (fa/fa) Zucker and normal Wistar-derived rats. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 38, 465–471. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2005.01.013.
Won, E.-Y., Yoon, M.-K., Kim, S.-W., Jung, Y., Bae, H.-W., Lee, D., et al. (2013). Gender-specific metabolomic profiling of obesity in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice by 1H NMR spectroscopy. PLoS One, 8, e75998. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075998.
Worley, B., & Powers, R. (2013). Multivariate analysis in metabolomics. Current Metabolomics, 1, 92–107. doi:10.2174/2213235X11301010092.
Xie, B., Waters, M. J., & Schirra, H. J. (2012). Investigating potential mechanisms of obesity by metabolomics. BioMed Research International, 2012, 805683. doi:10.1155/2012/805683.
Yan, X., Huang, Y., Zhao, J.-X., Rogers, C. J., Zhu, M.-J., Ford, S. P., et al. (2013). Maternal obesity downregulates microRNA let-7 g expression, a possible mechanism for enhanced adipogenesis during ovine fetal skeletal muscle development. International Journal of Obesity, 2005(37), 568–575. doi:10.1038/ijo.2012.69.
Zambrano, E., & Nathanielsz, P. W. (2013). Mechanisms by which maternal obesity programs offspring for obesity: evidence from animal studies. Nutrition Reviews, 71(Suppl 1), S42–S54. doi:10.1111/nure.12068.
Zhang, A., Sun, H., & Wang, X. (2013). Power of metabolomics in biomarker discovery and mining mechanisms of obesity. Obesity Reviews, 14, 344–349. doi:10.1111/obr.12011.
Zhao, L.-C., Zhang, X.-D., Liao, S.-X., Gao, H.-C., Wang, H.-Y., & Lin, D.-H. (2010). A metabonomic comparison of urinary changes in Zucker and GK rats. BioMed Research International, 2010, 431894. doi:10.1155/2010/431894.
Zhou, Y., Qiu, L., Xiao, Q., Wang, Y., Meng, X., Xu, R., et al. (2013). Obesity and diabetes related plasma amino acid alterations. Clinical Biochemistry, 46, 1447–1452. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2013.05.045.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the EHESP School of Public Health, France. We gratefully acknowledge Marie Tremblay-Franco for helpful advice on statistics, and Sven Delaye for advice on English translation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
Gynaecologists informed the women of the nature of the study and asked them to participate, after providing written consent. This consent was accompanied by a letter of information describing the goal of the study, the consortium, data collection procedures and follow-up after birth (via questionnaires and medical examinations). Explicit mention was made of the right to refuse to participate, and the fact that such a refusal would not have any effect on the woman's relationship with her doctor. Both the INSERM (French National Institute of Health and Medical Research) ethics committee and the National Commission in charge of Data Protection (CNIL) approved the study procedures. Reference (N°902076; 31 may 2002).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desert, R., Canlet, C., Costet, N. et al. Impact of maternal obesity on the metabolic profiles of pregnant women and their offspring at birth. Metabolomics 11, 1896–1907 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0836-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-015-0836-1