Abstract
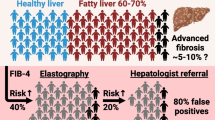
According to World Health Organization, an estimated 3 % of the global population is suffering from chronic hepatitis C. Furthermore, 60–70 % of chronically-infected patients develop liver diseases, of which 5–20 % of all cases advance to cirrhosis, and 1–5 % die from hepatitis C related hepatocellular carcinoma. This high incidence might be ascribed to the poor performance of the currently available diagnostic, treatment, and vaccination protocols, together with the lack of knowledge of the underlying disease mechanisms. In this review, we discuss the role that the relatively new research field termed metabolomics, alone or as part of an integrated ‘omics’ approach, has played in the investigation of hepatitis C and associated clinical manifestations. We also consider future research possibilities in this field, and the impact that these results might have on the fight against this global health predicament.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr, J., Alonso, C., Vázquez-Chantada, M., Pérez-Cormenzana, M., Mayo, R., Galán, A., et al. (2010). Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC/MS)-based parallel metabolic profiling of human and mouse model serum reveals putative biomarkers associated with the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 4501–4512.
Broeckling, C. D., Reddy, I. R., Duran, A. L., Zhao, X., & Sumner, L. W. (2006). MET-IDEA: Data extraction tool for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 4334–4341.
Castera, L., Vergniol, J., Foucher, J., Le Bail, B., Chanteloup, E., Haaser, M., et al. (2005). Prospective comparison of transient elastography, Fibrotest, APRI, and liver biopsy for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology, 128, 343–350.
Chen, S. (2011). An ‘‘Omics’’ approach to determine the mechanisms of acquired aromatase inhibitor resistance. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 15, 347–352.
Chen, S. L., & Morgan, T. R. (2006). The natural history of hepatitis C virus (HCV). International Journal of Medical Sciences, 3, 47–52.
Choo, Q. L., Kuo, G., Weiner, A. J., Overby, L. R., Bradley, D. W., & Houghton, M. (1989). Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science, 244, 359–362.
Cobbold, J. F. L., Patel, J. H., Goldin, R. D., North, B. V., Crossey, M. M. E., Fitzpatrick, J., et al. (2010). Hepatic lipid profiling in chronic hepatitis C: An in vitro and in vivo protonmagnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Journal of Hepatology, 52, 16–24.
Colin, C., Lanoir, D., Touzet, S., Meyaud-Kraemer, L., Bailly, F., Trepo, C., et al. (2001). Sensitivity and specificity of third-generation hepatitis C virus antibody detection assays: An analysis of the literature. Journal of Viral Hepatitis, 8, 87–95.
Debnath, M., Pandey, M., & Bisen, P. S. (2011). An omics approach to understand the plant abiotic stress. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 15, 739–762.
Diamond, D. L., Krasnoselsky, A. L., Burnum, K. E., Monroe, M. E., Webb-Robertson, B., McDermott, J. E., et al. (2012). Proteome and computational analyses reveal new insights into the mechanisms of hepatitis C virus-mediated liver disease posttransplantation. Hepatology, 56, 28–38.
Diamond, D. L., Syder, A. J., Jacobs, J. M., Sorensen, C. M., Walters, K.-A., Proll, S. C., et al. (2010). Temporal proteome and lipidome profiles reveal hepatitis C virus-associated reprogramming of hepatocellular metabolism and bioenergetics. Plos Pathogens, 6(1), e1000719. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000719.
Dienstag, J. L. (2002). The role of liver biopsy in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology, 36, S152–S160.
Dunn, W. B., Bailey, N. J. C., & Johnson, H. E. (2005). Measuring the metabolome: Current analytical technologies. Analyst, 130, 606–625.
Fiehn, O., Kopka, J., Dörmann, P., Altmann, T., Trethewey, R. N., & Willmitzer, L. (2000). Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nature Biotechnology, 18, 1157–1161.
Gao, H. C., Lu, Q., Liu, X., Cong, H., Zhao, L. C., Wang, H. M., et al. (2009). Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Science, 100, 782–785.
Ghany, M. G., Strader, D. B., Thomas, D. L., & Seeff, L. B. (2009). Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: An update. Hepatology, 49, 1335–1374.
Gomaa, A. I., Khan, S. A., Leen, E. L. S., Waked, I., & Taylor-Robinson, S. D. (2009). Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 15, 1301–1314.
Halket, J. M., Waterman, D., Przyborowska, A. M., Patel, R. K. P., Fraser, P. D., & Bramley, P. M. (2005). Journal of Experimental Botany, 56, 219–243.
Hao, S., Xin, J., Lian, J., Xie, Q., Chen, D., Guo, Y., et al. (2011). Establishing a metabolomic model for the prognosis of hepatitis B virus-induced acute-on-chronic liver failure treated with different liver support systems. Metabolomics, 7, 400–412.
He, Y., Duan, W., & Tan, S. L. (2007). Emerging host cell targets for hepatitis C therapy. Drug Discovery Today, 12, 209–217.
Hendricks, D. A., Friesenhahn, M., Tanimoto, L., Goergen, B., Dodge, D., & Comanor, L. (2003). Multicenter evaluation of the VERSANT HCV RNA qualitative assay for detection of hepatitis C virus RNA. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41, 651–656.
Ikeda, M., & Kato, N. (2007). Modulation of host metabolism as a target of new antivirals. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 59, 1277–1289.
Imbert-Bismut, F., Ratziu, V., Pieroni, L., Charlotte, F., Benhamou, Y., Poynard, T., et al. (2001). Biochemical markers of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C virus infection: A prospective study. Lancet, 357, 1069–1075.
Irving, W. L. (2002). The role of the virology laboratory in the management of hepatitis C virus infection. Journal of Clinical Virology, 25, 3–13.
Jang, J. Y., & Chung, R. T. (2011). Chronic hepatitis C. Gut and Liver, 5, 117–132.
Lavanchy, D. (2011). Evolving epidemiology of hepatitis C virus. Clinical Microbiology and Infection, 17, 107–115.
Lawton, K. A., Berger, A., Mitchell, M., Millgram, K. E., Evans, A. M., Guo, L., et al. (2008). Analysis of the adult human plasma metabolome. Pharmacogenomics, 9, 383–397.
Liang, T. J., Rehermann, B., Seeff, L. B., & Hoofnagle, J. H. (2000). Pathogenesis, natural history, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis C. Annals of Internal Medicine, 132, 297–299.
Maheshwari, A., Ray, S., & Thuluvath, P. J. (2008). Acute hepatitis C. Lancet, 372, 321–332.
Meissner-Roloff, R. J., Koekemoer, G., Warren, R. M., & Loots, D. T. (2012). A metabolomics investigation of a hyper- and hypo-virulent phenotype of Beijing lineage M. tuberculosis. Metabolomics,. doi:10.1007/s11306-012-0424-6.
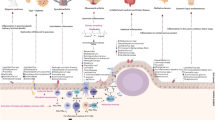
Mengshol, J. A., Golden-Mason, L., & Rosen, H. R. (2007). Mechanisms of Disease: HCV-induced liver injury. Nature Clinical Practice Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 4, 622–634.
Nagarajan, R., Sarma, M. K., Thames, A. D., Castellon, S. A., Hinkin, C. H., & Thomas, M. A. (2012). International Journal of Hepatology,. doi:10.1155/2012/179365.
Negro, F., & Sanyal, A. J. (2009). Hepatitis C virus, steatosis and lipid abnormalities: Clinical and pathogenic data. Liver International, S2, 26–37.
Nelson, P. K., Mathers, B. M., Cowie, B., Hagan, H., Jarlais, D. D., Horyniak, D., et al. (2011). Global epidemiology of hepatitis B and hepatitis C in people who inject drugs: Results of systematic reviews. Lancet, 378, 571–583.
Olivier, I., & Loots, D. T. (2011). An overview of tuberculosis treatments and diagnostics. What role could metabolomics play? Journal of Cell and Tissue Research, 11, 2655–2671.
Olivier, I., & Loots, D. T. (2012). A metabolomics approach to characterise and identify various Mycobacterium species. The Journal of Microbiological Methods, 88, 419–426.
Pondé, R. A. D. (2011). Hidden hazards of HCV transmission. Medical Microbiology and Immunology, 200, 7–11.
Raedle, J., Roth, W. K., Oremek, G., Caspary, W. F., & Zeuzem, S. (1995). Alpha-fetoprotein and p53 autoantibodies in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 40, 2587–2594.
Rasmussen, A. L., Tchitchek, N., Susnow, N. J., Krasnoselsky, A. L., Diamond, D. L., Yeh, M. M., et al. (2012). Early transcriptional programming links progression to hepatitis C virus—induced severe liver disease in transplant patients. Hepatology, 56, 17–27.
Rehermann, B. (2000). Immunopathogenesis of hepatitis C. In: Liang, T. J., moderator. pathogenesis, natural history, treatment, and prevention of hepatitis C. Annals of Internal Medicine, 132, 297–299.
Roe, B., Kensicki, E., Mohney, R., & Hall, W. W. (2011). Metabolomic profile of hepatitis C virus—infected hepatocytes. Plos One, 6(8), e23641. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023641.
Schnackenberg, L. K., Jones, R. C., Thyparambil, S., Taylor, J. T., Han, T., Tong, W., et al. (2006). An integrated study of acute effects of valproic acid in the liver using metabonomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics platforms. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology, 10, 1–14.
Schoeman, J. C., & Loots, D. T. (2011). Improved disease characterisation and diagnostics using metabolomics: A review. Journal of Cell and Tissue Research, 11, 2673–2683.
Shariff, M. I. F., Gomaa, A. I., Cox, I. J., Patel, M., Williams, H. R. T., Crossey, M. M. E., et al. (2011). Urinary metabolic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma in an Egyptian population: A validation study. Journal of Proteome Research, 10, 1828–1836.
Shariff, M. I. F., Ladep, N. G., Cox, I. J., Williams, H. R. T., Okeke, E., Malu, A., et al. (2010). Characterization of urinary biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma using magnetic resonance spectroscopy in a Nigerian population. Journal of Proteome Research, 9, 1096–1103.
Sithebe, N. P., Aspinall, S., & Smuts, H. (1996). Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection at Ga-Rankuwa Hospital. South African Medical Journal, 86, 1543–1545.
Soga, T., Sugimoto, M., Honma, M., Mori, M., Igarashi, K., Kashikura, K., et al. (2011). Serum metabolomics reveals γ-glutamyl dipeptides as biomarkers for discrimination among different forms of liver disease. Journal of Hepatology, 55, 896–905.
Strader, D. B., Wright, T., Thomas, D. L., & Seeff, L. B. (2004). Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology, 39, 1147–1171.
Torresi, J., Johnson, D., & Wedemeyer, H. (2011). Progress in the development of preventive and therapeutic vaccines for hepatitis C virus. Journal of Hepatology, 54, 1273–1285.
Van Ravenzwaay, B., Cunha, G. C., Leibold, E., Looser, R., Mellert, W., Prokoudine, A., et al. (2007). The use of metabolomics for the discovery of new biomarkers of effect. Toxicology Letters, 172, 21–28.
Vlaar, A. P. J., Rietdijk, S. T., Zeerleder, S. S., Boerman, T., & Beuers, U. (2011). Malignancies associated with chronic hepatitis C: Case report and review of the literature. The Netherlands journal of medicine, 69, 211–215.
Walters, K. A., Syder, A. J., Lederer, S. L., Diamond, D. L., Paeper, B., Rice, C. M., et al. (2009). Genomic analysis reveals a potential role for cell cycle perturbation in HCVmediated apoptosis of cultured hepatocytes. Plos Pathogens, 5, e1000269. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000269.
WHO. (2011). Hepatitis C: Factsheet no. 164. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs164/en/. Accessed 30 May 2012.
Woodhouse, S. D., Narayan, R., Latham, S., Lee, S., Antrobus, R., Gangadharan, B., et al. (2010). Transcriptome sequencing, microarray, and proteomic analyses reveal cellular and metabolic impact of hepatitis C virus infection in vitro. Hepatology, 52, 443–453.
Wu, H., Xue, R., Dong, L., Liu, T., Deng, C., Zeng, H., et al. (2009). Metabolomic profiling of human urine in hepatocellular carcinoma patients using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 648, 98–104.
Xia, J., Psychogios, N., Young, N., & Wishart, D. S. (2009). MetaboAnalyst: A web server for metabolomic data analysis and interpretation. Nucleic Acids Research, 37, W652–W660.
Xue, R., Lin, Z., Deng, C., Dong, L., Liu, T., Wang, J., et al. (2008). A serum metabolomic investigation on hepatocellular carcinoma patients by chemical derivatization followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 22, 3061–3068.
Yang, Y., Li, C., Nie, X., Feng, X., Chen, W., Yue, Y., et al. (2007). Metabonomic studies of human hepatocellular carcinoma using high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy in conjunction with multivariate data analysis. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2605–2614.
Yang, J., Xu, G., Zheng, Y., Kong, H., Wang, C., Zhao, X., et al. (2005). Strategy for metabonomics research based on high-performance liquid chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography A, 1084, 214–221.
Yang, F., Yan, S., He, Y., Wang, F., Song, S., Guo, Y., et al. (2008). Expression of hepatitis B virus proteins in transgenic mice alters lipid metabolism and induces oxidative stress in the liver. Journal of Hepatology, 48, 12–19.
Yin, P. Y., Wan, D. F., Zhao, C. X., Chen, J., Zhao, X. J., Wang, W. Z., et al. (2009). A metabonomic study of hepatitis B induced liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by using RP-LC and HILIC coupled with mass spectrometry. Molecular Biosystems, 5, 868–876.
Yu, K., Sheng, G., Sheng, J., Chen, Y., Xu, W., Liu, X., et al. (2007). A metabonomic investigation on the biochemical perturbation in liver failure patients caused by hepatitis B virus. Journal of Proteome Research, 6, 2413–2419.
Zhang, Q., Takahashi, M., Noguchi, Y., Sugimoto, T., Kimura, T., Okumura, A., et al. (2006). Plasma amino acid profiles applied for diagnosis of advanced liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Hepatology Research, 34, 170–177.
Zhou, L., Wang, Q., Yin, P., Xing, W., Wu, Z., Chen, S., et al. (2012). Serum metabolomics reveals the deregulation of fatty acids metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver diseases. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 403, 203–213.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
du Preez, I., Sithebe, N.P. The use of metabolomics as a tool to investigate hepatitis C. Metabolomics 9, 497–505 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0467-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-012-0467-8