Abstract
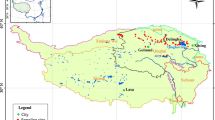
Black soils in Northeast China are characteristic of high soil organic carbon (SOC) density and were strongly influenced by human activities. Therefore, any change in SOC pool of these soils would not only impact the regional and global carbon cycle, but also affect the release and immobilization of nutrients. In this study, we reviewed the research progress on SOC storage, budget, variation, and fertility under different scenarios. The results showed that the organic carbon storage of black soils was 646.2 TgC and the most potential sequestration was 2887.8 g m−2. According to the SOC budget, the net carbon emission of black soils was 1.3 TgC year−1 under present soil management system. The simulation of CENTURY model showed that future climate change and elevated CO2 concentration, especially the increase of precipitation, would increase SOC content. Furthermore, fertilization and cropping sequence obviously influenced SOC content, composition, and allocation among different soil particles. Long-term input of organic materials such as manure and straw renewed original SOC, improved soil structure and increased SOC accumulation. Besides, soil erosion preferred to transport soil particles with low density and fine size, decreased recalcitrant SOC fractions at erosion sites and increased activities of soil microorganism at deposition sites. After natural grasslands were converted into croplands, obvious variation of soil chemical nutrients, physical structure, and microbial activities had taken place in surface and subsurface soils, and represented a degrading trend to a certain degree. Our studies suggested that adopting optimal management such as conservation tillage in black soil region is an important approach to sequester atmospheric CO2 and to slow greenhouse effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruce JP, Frome M, Haites E, Janzen H, Lal R, Paustian K (1999) Carbon sequestration in soils. J Soil Water Conserv 54:382–389
Burke IC, Laurenroth WK, Coffin DP (1995) Recovery of soil organic matter and N mineralization in semiarid grasslands: implications for the conservation reserve program. Ecol Appl 5:793–801
Buyanoysky GA, Wagner GH (1986) Post harvest residue input to cropland. Plant Soil 93:57–65
Cao MK, Woodward FI (1998) Dynamic responses of terrestrial ecosystem carbon cycling to global climate change. Nature 393:249–252
Carter MR, Angers DA, Gregorich EG, Bolinder MA (2003) Characterizing organic matter retention for surface soils in eastern Canada using density and particle size fractions. Can J Soil Sci 83:1–23
Cheng EF, Zhou LK, Wu GY (1994) Performances of soil micro-aggregates in storing and supplying moisture and nutrients and role of their compositional proportion in judging fertility level. Acta Pedol Sin 31:18–25
Cole CV, Cerri C, Minami K, Mosier A, Rosenberg N, Sauerbeck D, Dumanski J (1996) Agricultural options for mitigation of greenhouse gas emissions. In: Watson RT, Zinyowera MC, Moss RH (eds) Climate change 1995—impacts, adaptations and mitigation of climate change: scientific–technical analyses. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 745–771
Coughenour MB, Chen DX (1997) Assessment of grassland ecosystem responses to atmospheric change using linked plant–soil process models. Ecol Appl 7:802–827
Ding H, Wang YS, Wang DL (2003) Emission of CO2 and CH4 from black soil in Northeast China. J Agro Environ Sci 22:720–723
Fan HM, Cai QG, Wang HS (2004) Condition of soil erosion in phaeozem region of Northeast China. J Soil Water Conserv 18:66–70
Fang HJ, Yang XM, Zhang XP (2003) Organic carbon stock of black soils in Northeast China and its contribution to atmospheric CO2. J Soil Water Conserv 17:9–12
Fang HJ, Yang XM, Zhang XP, Liang AZ (2005a) Study on soil erosion and deposition of black soils on a sloping cultivated land using 137Cs tracer method. Acta Ecol Sin 25:141–147
Fang HJ, Yang XM, Zhang XP, Liang AZ (2005b) Profile distribution of organic carbon and δ13C in a black soil at a sloping field. Acta Pedol Sin 42:81–90
Fang HJ, Yang XM, Zhang XP, Liang AZ (2006) Soil organic carbon redistribution and budget of erosion and deposition in a sloping field. Land Degrad Dev 17:89–96
Gao LP, Liang WJ, Zhao J, Wen DZ (2005) Simulation of climate impact on soil organic carbon pool in black soil. J Liaoning Techl Univ 24:288–291
Gregorich EG, Greer KJ, Anderson DW, Liang BC (1998) Carbon distribution and losses: erosion and deposition effects. Soil Tillage Res 47:291–302
Guo ZM, Miao QL, Li X (2005) Change characteristics of temperature in North China since recent 50 years. Arid Land Geogr 28:176–182
Hassink J (1997) The capacity of soils to preserve organic C and N by their association with clay and silt particles. Plant Soil 191:77–87
Heilongjiang Land Management Bureau, Soil Survey Office (HLMB-SSO) (1992) Soils in Heilongjian. Agricultural Science Press, Beijing
Hunt HW, Trlica MJ, Redente EF, Moore JC, Detling JK, Kittel TGF, Walter DE, Fowler MC, Klein DA, Elliott ET (1991) Simulation model for the effects of climate change on temperate grassland ecosystems. Ecol Modell 53:205–246
Jilin General Station of Soil, Fertilizer (JGSSF) (1998) Soils in Jilin. Agricultural Science Press, Beijing
Li ZP, Lin XX, Che YP (2002) Analysis for the balance of organic carbon pools and their tendency in typical arable soils of Eastern China. Acta Pedol Sin 39:351–360
Liu SX (2002) The analysis of the regularity and influence factors of the turnover of organic carbon in Phaeozem. Doctoral Dissertation of Northeast Institute of Geography and Agricultural Eulogy, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Chinese Science Press, Changchun
Liu S, Bliss N, Sundquist E, Huntington TG (2003) Modeling carbon dynamics in vegetation and soil under the impact of soil erosion and deposition. Global Biogeochem Cycles 17:1074–1098
Lu RK (1999) Methods of soil and agriculture chemical analysis. Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Ma Q, Yu WT, Zhao SH, Zhang L, Shen SM, Wang YB (2004) Comprehensive evaluation of cultivated black soil fertility. Chin J Appl Ecol 15:1916–1920
Meng K, Zhang XY (1998) Mechanism of degradation of black soils in Songneng plain and ecological recover. Chin J Soil Sci 29:100–102
Parton WJ, Scurlock JMO, Ojima DS, Schimel DS, Hall DO (1995) Impact of climate change on grassland production and soil carbon worldwide. Global Change Biol 1:13–22
Riedo M, Gyalistras D, Fuhrer J (2000) Net primary production and carbon stocks in differently managed grasslands: simulation of site-specific sensitivity to an increase in atmospheric CO2 and to climate change. Ecol Modell 134:207–227
Ritchie JC, McCarty GW (2003) 137Cs and soil carbon in a small agricultural watershed. Soil Tillage Res 69:45–51
Soil Survey Staff (1999) Soil taxonomy—a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys, 2nd edn. Agricultural Handbook 436 United State Department of Agriculture, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Somebroek WG, Nachtergaele FO, Hebel A (1993) Amounts, dynamics and sequestration of carbon in tropic and subtropical soils. Ambio 22:417–426
Stallard RF (1998) Terrestrial sedimentation and the carbon cycle: coupling weathering and erosion to carbon burial. Global Biogeochem Cycles 12:231–257
Vanden Bygaart AJ (2001) Erosion and deposition history derived by depth-stratigraphy of 137Cs and soil organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res 61:187–192
Wang SQ, Zhou CH, Li KR, Zhu SL, Huang FH (2000) Analysis on spatial distribution characteristics of soil organic carbon reservoir in China. Acta Geogr Sin 55:533–544
Wang JK, Wang TY, Zhang XD, Guan LZ, Wang QB, Hu HX, Zhao YC (2002a) An approach to the changes of black soil quality (I)—changes of the indices of black soil with the years of reclamation. J Shenyang Agri Univ 33:43–47
Wang JK, Wang TY, Zhang XD, Zhao YC, Wang QB (2002b) An approach to the changes of black soil quality (II)—the status and changes of organic matter, total N, total S and total P in black soils (Isohumosols) in different areas. J Shenyang Agri Univ 33:270–273
Wang SQ, Zhou CH, Liu JY, Tian HQ, Li KR, Yang XM (2002c) Carbon storage in Northeast China as estimated from vegetation and soil inventories. Environ Pollut 116:S157–S165
Wang TY, Yan L, Guan LZ, Wang JK, Lü YL (2004a) Variation of organic matter with long-term location monitoring in black soil. J Agro Environ Sci 23:76–79
Wang ZY, Ding YH, He JH (2004b) An updating analysis of the climate change in China in recent 50 years. Acta Meteorol Sin 62:228–236
Xiong Y, Li QK (1987) Soils in China. Science press, Beijing
Yakovchenko VP, Sikora LJ, Millner PD (1998) Carbon and nitrogen mineralization of added particulate and macroorganic matter. Soil Biol Biochem 30:2139–2146
Yang XM, Zhang XP, Fang HJ, Zhu P, Ren J, Wang LC (2003) Long-term effects of fertilization on soil organic carbon changes in Northeast China: Roth-C model simulations. Environ Manage 32:459–465
Yang XM, Zhang XP, Fang HJ, Liang AZ (2004) Changes in organic matter and total nitrogen of black soils in Jilin province over the past two decades. Sci Geogr Sin 24:710–714
Zhang HW, Zhou QX, Zhang QR, Zhang CG (2004) Toxic effects of acetochlor, methamidophos and their combination on bacterial amount and population richness at molecular levels in agricultural black soils. Environ Sci 25:144–148
Zhou QX, Sun FH, Guo GL, Sun TH (2004) Influence of acetochlor on Pb forms and their bioavailability in Phaiozem of Northeast China. Chin J Appl Ecol 15:1883–1886
Zu HC, Lü SH, Hu YQ (2004) Variations trend of yearly mean air temperature and precipitation in China in the last 50 years. Plateau Meteor 23:238–244
Acknowledgments
We would like to express appreciation to Dr. Ma Qiang and Dr. Liu Shuxia for supplying the data. We wish to express our appreciation to Wang Shaoqiang for reviewing the manuscript. This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30225012) and Chinese Academy of Sciences (2002CB412501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, G., Fang, H., Gao, L. et al. Soil organic carbon budget and fertility variation of black soils in Northeast China. Ecol Res 21, 855–867 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-006-0033-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11284-006-0033-9