Abstract
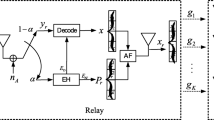
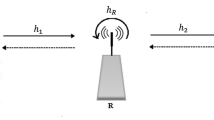
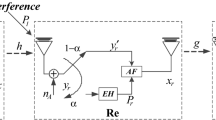
This paper considers optimal power control solutions in one-way and two-way relay system with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer (SWIPT). First, we develop SWIPT protocols for one-way and two-way relay systems, where two terminals exchange data assisted by an energy-harvesting relay node which gathers energy from the received signal by using a power splitting scheme and forwards the received signal by using the harvesting energy. For one-way relay system, the closed-form solution for optimal power splitting ratio is derived to maximize the system throughput. For asymmetric two-way relay system, we propose a novel power splitting strategy to maximize system throughput. Considering the total transmit power constraints, we develop a semi-closed form solution for power allocation among all nodes by exploiting convex optimization technology. It is shown that the optimal power allocation in two-way relay system would degrade into one-way relay mode if the relay node is close to one of the terminals. For symmetric two-way relay system, a closed-form solution for power allocation and power split ratio is derived. The performances of the three systems are compared numerically. It is revealed that the proposed power allocation algorithm can improve the transmission rate without consuming additional resource compared with non-cooperation relaying scheme.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi, Y., Xie, L., Hou, Y. T., & Sherali, H. D. (2011). On renewable sensor networks with wireless energy transfer. In Proceedings 2011 IEEE INFOCOM (pp. 1350–1358).
Fouladgar, A. M., & Simeone, O. (2012). On the transfer of information and energy in multi-user systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(11), 1733–1736.
Nasir, A. A., Zhou, X., Durrani, S., & Kennedy, R. A. (2013). Relaying protocols for wireless energy harvesting and information processing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(7), 3622–3636.
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. Wireless information and power transfer in multiuser OFDM systems. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications. arXiv:1308.2462
Varshney, L. R. (2008). Transporting information and energy simultaneously. In Proceedings 2008 IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 1612–1616).
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(11), 4754–4767.
Liu, L., Zhang, R., & Chua, K. C. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: A dynamic power splitting approach. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(9), 3990–4001.
Liu, L., Zhang, R., & Chua, K. C. (2013). Wireless information transfer with opportunistic energy harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(1), 288–300.
Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). MIMO broadcasting for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(5), 1989–2001.
Ding, Z., Perlaza, S. M., Esnaola, I., & Poor, H. V. (2013). Power allocation strategies in energy harvesting wireless cooperative networks. arXiv: 1307.1630
Ng, D. W. K., Lo, E. S., & Schober, R. (2013). Energy-efficient resource allocation in multiuser OFDM systems with wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(12), 6352–6370.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61340025, 61461029), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20114ACE00200, 20142BAB217005, and 20142BBE50046), Technology Foundation of Department of Education in Jiangxi Province (no. GJJ13062), and China/Jiangxi Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (nos. 2013MT541875, 2014MT561879, 2013KY007, and 2014KY044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D. Wireless Information and Power Transfer: Optimal Power Control in One-Way and Two-Way Relay System. Wireless Pers Commun 84, 1–14 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2874-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2874-4