Abstract
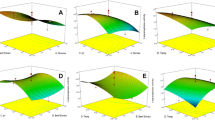
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a cytokine widely used in cancer patients receiving high doses of chemotherapeutic drugs to prevent the chemotherapy-induced suppression of white blood cells. The production of recombinant G-CSF should be increased to meet the increasing market demand. This study aims to model and optimize the carbon source of auto-induction medium to enhance G-CSF production using artificial neural networks coupled with genetic algorithm. In this approach, artificial neural networks served as bioprocess modeling tools, and genetic algorithm (GA) was applied to optimize the established artificial neural network models. Two artificial neural network models were constructed: the back-propagation (BP) network and the radial basis function (RBF) network. The root mean square error, coefficient of determination, and standard error of prediction of the BP model were 0.0375, 0.959, and 8.49 %, respectively, whereas those of the RBF model were 0.0257, 0.980, and 5.82 %, respectively. These values indicated that the RBF model possessed higher fitness and prediction accuracy than the BP model. Under the optimized auto-induction medium, the predicted maximum G-CSF yield by the BP-GA approach was 71.66 %, whereas that by the RBF-GA approach was 75.17 %. These predicted values are in agreement with the experimental results, with 72.4 and 76.014 % for the BP-GA and RBF-GA models, respectively. These results suggest that RBF-GA is superior to BP-GA. The developed approach in this study may be helpful in modeling and optimizing other multivariable, non-linear, and time-variant bioprocesses.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson M, Adlercreutz P (1999) Evaluation of simple enzyme kinetics by response surface modelling. Biotechnol Tech 13(12):903–907
Baş D, Boyacı İH (2007) Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78(3):836–845
Basri M, Rahman RN, Ebrahimpour A, Salleh AB, Gunawan ER, Rahman MB (2007) Comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology (RSM) with artificial neural network (ANN) in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of palm-based wax ester. BMC Biotechnol 7:53
Bertho JM, Frick J, Prat M, Demarquay C, Dudoignon N, Trompier F, Gorin NC, Thierry D, Gourmelon P (2005) Comparison of autologous cell therapy and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) injection vs. G-CSF injection alone for the treatment of acute radiation syndrome in a non-human primate model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 63(3):911–920
Bishop B, Koay DC, Sartorelli AC, Regan L (2001) Reengineering granulocyte colony-stimulating factor for enhanced stability. J Biol Chem 276(36):33465–33470
Blommel PG, Becker KJ, Duvnjak P, Fox BG (2007) Enhanced bacterial protein expression during auto-induction obtained by alteration of lac repressor dosage and medium composition. Biotechnol Prog 23(3):585–598
Chi L, Fan DD, Ma XX, Mi Y, Luo YE, Zhu CH, Zhu XL, Xue WJ (2011) A genetic algorithm for the optimization of the thermoinduction protocol for high-level production of recombinant human-like collagen from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 58(3):175–184
Chua CG, Goh ATC (2003) A hybrid Bayesian back-propagation neural network approach to multivariate modelling. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 27(8):651–667
Dale DC (2002) Colony-stimulating factors for the management of neutropenia in cancer patients. Drugs 62(Suppl 1):1–15
Fine TL (1999) Algorithms for designing feedforward networks feedforward neural network methodology. In: Information science and statistics. Springer, New York, pp 129–202
Franco-Lara E, Link H, Weuster-Botz D (2006) Evaluation of artificial neural networks for modelling and optimization of medium composition with a genetic algorithm. Proc Biochem 41(10):2200–2206
Galushkin AI (2007) Qualitative characteristics of neural network architectures neural networks theory. Springer, Berlin, pp 43–52
Giordano PC, Martinez HD, Iglesias AA, Beccaria AJ, Goicoechea HC (2010) Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural networks for optimization of recombinant Oryza sativa non-symbiotic hemoglobin 1 production by Escherichia coli in medium containing byproduct glycerol. Bioresour Technol 101(19):7537–7544
Gomes FR, Maluenda AC, Tapias JO, Oliveira FL, Sa-Rocha LC, Carvalho E, Ho PL (2012) Expression of recombinant human mutant granulocyte colony stimulating factor (Nartograstim) in Escherichia coli. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28(7):2593–2600
Haider MA, Pakshirajan K, Singh A, Chaudhry S (2008) Artificial neural network-genetic algorithm approach to optimize media constituents for enhancing lipase production by a soil microorganism. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 144(3):225–235
He L, Xu YQ, Zhang XH (2008) Medium factor optimization and fermentation kinetics for phenazine-1-carboxylic acid production by Pseudomonas sp. M18G. Biotechnol Bioeng 100(2):250–259
Huang Y, Kangas LJ, Rasco BA (2007) Applications of artificial neural networks (ANNs) in food science. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47(2):113–126
Jacob F, Monod J (1961) Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol 3:318–356
Lee TY, Chen SA, Hung HY, Ou YY (2011) Incorporating distant sequence features and radial basis function networks to identify ubiquitin conjugation sites. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17331
Li Z, Kessler W, van den Heuvel J, Rinas U (2011) Simple defined autoinduction medium for high-level recombinant protein production using T7-based Escherichia coli expression systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(4):1203–1213
Mahadevan R, Edwards JS, Doyle FJ III (2002) Dynamic flux balance analysis of diauxic growth in Escherichia coli. Biophys J 83(3):1331–1340
Milano M, Koumoutsakos P, Schmidhuber J (2004) Self-organizing nets for optimization. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 15(3):758–765
Moody J, Darken CJ (1989) Fast learning in networks of locally-tuned processing units. Neural Comput 1(2):281–294
Neerathilingam M, Markley JL (2010) Auto-induction medium containing glyphosate for high-level incorporation of unusual aromatic amino acids into proteins. Biotechniques 49(3):659–661
Nelofer R, Ramanan RN, Rahman RN, Basri M, Ariff AB (2011) Comparison of the estimation capabilities of response surface methodology and artificial neural network for the optimization of recombinant lipase production by E. coli BL21. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39(2):243–254
Patel VL, Shortliffe EH, Stefanelli M, Szolovits P, Berthold MR, Bellazzi R, Abu-Hanna A (2009) The coming of age of artificial intelligence in medicine. Artif Intell Med 46(1):5–17
Patnaik PR (2006) Synthesizing cellular intelligence and artificial intelligence for bioprocesses. Biotechnol Adv 24(2):129–133
Reznikoff WS (1992) The lactose operon-controlling elements: a complex paradigm. Mol Microbiol 6(17):2419–2422
Rumelhart DE, Hinton GE, Williams RJ (1986) Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 323(6088):533–536
Schubert M, Mourad S, Schwarze F (2010) Radial basis function neural networks for modeling growth rates of the basidiomycetes Physisporinus vitreus and Neolentinus lepideus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(3):703–712
Silva R, Ferreira S, Bonifacio MJ, Dias JM, Queiroz JA, Passarinha LA (2012) Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of human soluble catechol-O-methyltransferase by Escherichia coli using artificial neural network. J Biotechnol 160(3–4):161–168
Singh V, Khan M, Khan S, Tripathi CK (2009) Optimization of actinomycin V production by Streptomyces triostinicus using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82(2):379–385
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):207–234
Sung L, Dror Y (2007) Clinical applications of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Front Biosci 12:1988–2002
Tripathi CK, Khan M, Praveen V, Khan S, Srivastava A (2012) Enhanced antibiotic production by Streptomyces sindenensis using artificial neural networks coupled with genetic algorithm and Nelder-Mead downhill simplex. J Microbiol Biotechnol 22(7):939–946
Tyler RC, Sreenath HK, Singh S, Aceti DJ, Bingman CA, Markley JL, Fox BG (2005) Auto-induction medium for the production of [U-15 N]- and [U-13C, U-15 N]-labeled proteins for NMR screening and structure determination. Protein Expr Purif 40(2):268–278
Vanz AL, Renard G, Palma MS, Chies JM, Dalmora SL, Basso LA, Santos DS (2008) Human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (hG-CSF): cloning, overexpression, purification and characterization. Microb Cell Fact 7:13
Wong P, Gladney S, Keasling JD (1997) Mathematical model of the lac operon: inducer exclusion, catabolite repression, and diauxic growth on glucose and lactose. Biotechnol Prog 13(2):132–143
Xiong AS, Yao QH, Peng RH, Duan H, Li X, Fan HQ, Cheng ZM, Li Y (2006) PCR-based accurate synthesis of long DNA sequences. Nat Protoc 1(2):791–797
Yang M, Yu MY, Shi XF, Teng YP (2008) Back-propagation neural network and genetic algorithm for multi-objective optimization of extraction technology of cortex fraxini. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 33(22):2622–2626
Zhang Y, Xu J, Yuan Z, Xu H, Yu Q (2010) Artificial neural network-genetic algorithm based optimization for the immobilization of cellulase on the smart polymer Eudragit L-100. Bioresour Technol 101(9):3153–3158
Zong H, He Y, Zhan Y, Du J, Feng F, Li D (2010) Optimization of medium constituents for epsilon-poly-l-lysine fermentation with response surface methodology. J Food Sci 75(9):M552–M556
Zupan J, Noviča M, Gasteiger J (1995) Neural networks with counter-propagation learning strategy used for modelling. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 27(2):175–187
Zurera-Cosanoa G, García-Gimenoa RM, Rodríguez-Péreza R, Hervás-Martínez C (2006) Performance of response surface model for prediction of Leuconostoc mesenteroides growth parameters under different experimental conditions. Food Control 17(6):429–438
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Program No. JKQ2011043), Jiangsu 333 High-level Talents Cultivating Program and Qing Lan Projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
H. Tian, and C. Liu contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Liu, C., Gao, X.D. et al. Optimization of auto-induction medium for G-CSF production by Escherichia coli using artificial neural networks coupled with genetic algorithm. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 505–513 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1204-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1204-1