Abstract
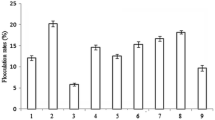
A bioflocculant with high flocculating activity, LC13-SF, produced by strain LC13T which was in a viable but nonculturable (VBNC) state, and which was woken up by Rpf (resuscitation promoting factor), was systematically investigated with regard to its fermentation conditions and flocculating activity. The key parameters influencing the bioflocculant LC13-SF were investigated through measuring the optical density at 660 (OD660) of the fermentation liquid and the optical density at 550 (OD550) of the centrifugal supernatant. The flocculating efficiency and the Zeta potentials were chosen as the response variables for the study of the flocculating activity. The results showed that the optimal conditions for bioflocculant LC13-SF production were a fermentation time of 72 h, an initial pH of 7.0, a fermentation temperature of 30°C and a shaking speed of 150 r/min. The optimized flocculating process was as follows: a final volume percentage of bioflocculant LC13-SF and 0.5% (w/w) CaCl2 were 1.5 and 5%, respectively in a 4 g/L Kaolin suspension, and the system pH was adjusted to 8.0. Under these conditions, the flocculating efficiency and the absolute value of the Zeta potential reached 94.83% and 4.37, respectively.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christopher E, Olga K, Deborah J, Stanisiav S, Anthony P, Peter C (2006) Non-invasive therapy to reduce the body burden of aluminium in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 10:17–24
Ding LX (2004) Studies on the isolation of viable but non-culturable bacteria and the phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aquaspirillum. PhD Thesis, The University of Tokyo
Ding LX, Yokota A (2010) Curvibacter fontana sp. nov., a microaerobic bacteria isolated from well water. J Gen Appl Microbiol 3:267–271
Ding LX, Hirose T, Yokota A (2007) Amycolatopsis echigonensis sp. nov. and Amycolatopsis niigatensis sp. nov., novel actinomycetes isolated from a filtration substrate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1747–1751
Ding LX, Hirose T, Yokota A (2009) Four novel Arthrobacter species isolated from filtration substrate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:856–862
Faegri A, Torsvik V, Goksoyr J (1997) Bacterial and fungal activities in soil: separation of bacteria and fungi by a rapid fractionated centrifugation technique. Soil Biol Biochem 9:105–112
Huang XW, Chen J (2004) Screening of flocculant-producing strains by NTG mutagenesis. J Environ Sci-China 17:494–498
Li B, Furihata K, Ding LX, Yokota A (2007) Rhodococcus kyotonensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1956–1959
Lian B, Chen Y, Yuan S, Zhu L, Liu CQ (2003) Study on the flocculability of metal ions by Bacillus mucilaginosus GY03 strain. Chin J Geochem 23:380–386
Lu WY, Zhang T, Zhang DY, Li CH, Wen JP, Du LX (2005) A novel bioflocculant produced by Enterobacter aerogenes and its use in defecating the trona suspension. Biochem Eng J 27:1–7
Mukamolova GV, Kaprelyants AS, Young DI, Young M, Kell DB (1998) A bacterial cytokine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:8916–8921
Olsen RA, Bakken LR (1987) Viability of soil bacteria: optimization of plate-counting technique and comparison between total counts and plate counts within different size groups. Microb Ecol 13:59–74
Prasertsan P, Dermlim W, Doelle H, Kennedy JF (2006) Screening, characterization and flocculating property of carbohydrate polymer from newly isolated Enterobacter cloacae WD7. Carbohyd Polym 66:289–297
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati SA (2001) Extracellular biopolymeric flocculants: recent trends and biotechnological importance. Biotechnol Adv 19:371–385
Salehizadeh H, Shojaosadati SA (2002) Isolation and characterization of a bioflocculant produced by Bacillus firmus. Biotechnol Lett 24:35–40
Shin IL, Van YT, Yeh LC, Lin HG, Chang YN (2001) Productiong of a biopolymer flocculant from Bacillus licheniformis and its flocculation properties. Bioresour Technol 78:267–272
Suh HH, Kwon GS, Lee CH, Kim HS, Oh HM, Yoon BD (1997) Characterization of bioflocculant produced by Bacillus sp. DP-152. J Ferment Bioeng 84:108–112
Tareke E, Rydberg P, Kalesson P, Eriksson S, Tornqvist M (2002) Analysis of acrylamide, a carcinogen formed in heated foodstuffs. J Agric Food Chem 50:4998–5006
Xia SQ, Zhang ZQ, Wang XJ, Yang A, Chen L, Zhao JF, Leonard D, Jaffrezic-Renault N (2008) Production and characterization of a bioflocculant by Proteus mirabilis TJ-1. Bioresour Technol 99:6520–6527
Yang ZH, Huang J, Zeng GM, Ruan M, Zhou CS, Li L, Rong ZG (2009) Optimization of flocculation conditions for Kaolin suspension using the composite flocculant of MBFGA1 and PAC by response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 100:4233–4239
Yokoi H, Natsuda O, Hirose J, Hayashi S, Takasaki Y (1995) Characteristics of a biopolymer flocculant produced by Bacillus sp. PY-90. J Ferment Bioeng 79:378–380
Yu GH, He PJ, Shao LM, He PP (2008) Statification structure of sludge flocs with implications to dewaterability. Environ Sci Technol 42:7944–7949
Zhang ZQ, Lin B, Xia SQ, Wang XJ, Yang AM (2007) Production and application of a novel bioflocculant by multiple-microorganism consortia using brewery wastewater as carbon source. J Environ Sci-China 19:667–673
Zhang ZQ, Xia SQ, Zhao JF, Zhang J (2010) Characterization and flocculation mechanism of high efficiency microbial flocculant TJ-F1 from Proteus mirabilis. Coll Surf B 75:247–251
Zhou X, Wang J, Zhou JT (2003) Studies on properties of a bioflocculant produced by Pseudomonas sp. GX4-1 in fish meal wastewater. J Environ Sci-China 16:31–34
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to HIROSE Co., Ltd., Japan for providing us the filter material as the source of isolated bacteria. We also thank Zhejiang Normal University for providing the “Professor Scientific Research Foundation, Grant No. ZC304009160”, so that this research could be conducted smoothly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, X., Shen, X., Ding, L. et al. Study on the flocculability of the Arthrobacter sp., an actinomycete resuscitated from the VBNC state. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28, 91–97 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0795-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0795-2