Abstract
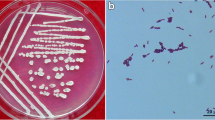
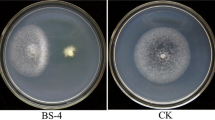
Present investigation is based on the isolation of Bacillus subtilis from cotton rhizosphere and their evaluation as biocontrol agent against Fusarium oxysporum. The production of extracellular hydrolytic enzyme was studied for determining the antagonism. 43% of 21 isolates were identified under the B. subtilis group on the basis of biochemical characterization. 38% isolates showed competitive activity against Fusarium oxysporum and exhibit more than 50% mycelial inhibition in dual culture bioassay. The pot assay of cotton by seed treatment and soil amendment technique under green house condition showed the competent activity of the isolates in preventing the wilting of cotton seedlings due to F. oxysporum infection. SVI values of 30 day old seedlings indicated that the soil inoculation with B. subtilis BP-2 and seed treatment with B. subtilis BP-9 significantly promoted the growth of cotton seedlings. RAPD profiling revealed the diversity in the Bacillus subtilis group, ranging from 10 to 32%. The discriminative pattern among the isolates belonging to the same species was validated by 16S rDNA partial sequencing which identified them into four different strains of B. subtilis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assigbetse KB, Fernandez D, Dubois MP, Geiger JP (1994) Differentiation of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum races on cotton by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis. Phytopathology 84:622–626
Bais HP, Fall R, Vianco JM (2004) Biocontrol of Bacillus subtilis against infection of Arabidopsis roots by Pseudomonas syringae is facilitated by biofilm formation and surfactin production. Plant Physiol 134:307–319
Bakker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas spp. mediated plant growth stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Bangera MG, Thomashow LS (1996) Characterization of a genomic locus required for synthesis of the antibiotic 2, 4-diacetylphloroglucinol by the biological control agent Pseudomonas fluorescens Q2–87. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 9:83–90
Bereswill S, Bugert P, Bruchmuller I, Geider K (1995) Identification of the fire blight pathogen, Erwinia amylovora, by PCR assays with chromosomal DNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2636–2642
Birch PRJ, Hyman LJ, Taylor R, Opio AF, Bragard C et al (1997) RAPD PCR-based differentiation of Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli and Xanthomonas campestris pv. phaseoli var. fuscans. Eur J Plant Pathol 103:809–814
Cappucino JG, Sherman N (2002) Biochemical activities of microorganisms. In: Microbiology, a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Pearson education, Singapore, pp 133–198
Cenci G, Trotta F, Caldini G (2006) Tolerance to challenges miming gastrointestinal transit by spores and vegetative cells of Bacillus clausii. J Appl Microbiol 101:1208–1215
Dautle MP, Ulrich RL, Hughes TA (2002) Typing and subtyping of 83 clinical isolates purified from surgically implanted silicone feeding tubes by random amplified polymorphic DNA amplification. J Clin Microbiol 40(2):414–421
Elizabeth AB, Emmert HJ (1999) Biocontrol of plant disease: a (Gram-)positive perspective. FEMS Microbiol Lett 171:1–9
Errampalli D, Leung K, Cassidy MB et al (1999) Applications of the green fluorescent protein as a molecular marker in environmental microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 35:187–199
Hermosa MR, Grondona I, Iturriaga EA, Diaz-Minguez JM, Castro C, Monte E et al (2000) Molecular characterization and identification of biocontrol isolates of Trichoderma spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(5):1890–1898
Islam MT, Hashidoko Y, Deora A, Ito T, Tahara S (2005) Suppression of damping-off disease in host plants by the rhizoplane bacterium Lysobacter sp. strain SB-K88 is linked to plant colonization and antibiosis against soilborne Peronosporomycetes. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(7):3786–3796
Jaccard P (1912) The distribution of the flora in the alpine zone. New Phytol 11:37–50
Jasra OP (2004) Preparation of genomic DNA from Bacteria. In: Techniques in microbiology, 1st edn. Sarup & Sons Publication, India, pp 25–26
Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G et al (1997) The complete genome sequence of the Grampositive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature 390(6657):249–256
Li D, Nie F, Wei L, Wei B, Chen Z (2007) Screening of high-yielding biocontrol bacterium Bs-916 mutant by ion implantation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(6):1401–1408
Liu YF, Chen ZY, Ng TB, Zhang J, Zhou MG, Song FP, Liu YZ (2006) Bacisubin, an antifungal protein with ribonuclease and hemagglutinating activities from Bacillus subtilis strain B-916. Peptides 28:553–559
Marten P, Smella K, Berge G (2000) Genotypic & phenotypic differentiation of an antifungal biocontrol strains belonging to Bacillus subtilis. J Appl Microbiol 89(3):463–471
Nagorska K, Bikowski M, Obuchowski M (2007) Multicellular behaviour and production of a wide variety of toxic substances support usage of Bacillus subtilis as a powerful biocontrol agent. Acta Biochim Pol 54(3):495–508
Nicholson WL (2002) Roles of Bacillus spores in the environment. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:410–416
Nielsen MN, Sorensen J, Fels J, Christian H (1998) Secondary metabolite and endochitinase dependent antagonism toward plant pathogenic microfungi of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolates from sugar beet rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 64(10):3563–3569
Ouoba LI, Diawara B, Amoa-Awua W, Traore AS, Moller PL (2004) Genotyping of starter cultures of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus pumilis for fermentation of African locust bean (Parkia biglobosa) to produce Soumbala. Int J Food Microbiol 90:197–205
Pimentel D, Levitan L (1986) Pesticides: amounts applied and amounts reaching pests. Bioscience 36:86–91
Quan CS, Wang JH, Xu HT, Fan SD (2006) Identification and characterization of a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens with high antifungal activity [Article in Chinese] Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 46(1):7–12
Reva ON, Dixelius C, Meijer J, Priest FG (2004) Taxonomic characterization and plant colonizing abilities of some bacteria related to Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:249–259
Rohlf FJ (1993) NTSYS-pc. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Exeter, New York
Ryu CM, Farag MA, Hu CH, Reddy MS, Kloepper JW, Pare PW (2004) Bacterial volatiles induce systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 134:1017–1026
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Shaver YJ, Nagpal ML, Fox KF, Rudner R, Fox A (2001) Variation in 16S–23S rRNA intergenic spacer regions among Bacillus subtilis 168 isolates. Mol Microbiol 42:101–109
Shoda M (2000) Bacterial control of plant diseases. J Biosci Bioeng 89:515–521
Siddiqui S, Siddiqui ZA, Ahmad I (2005) Evaluation of fluorescent Pseudomonads and Bacillus isolates for the biocontrol of a wilt disease complex of pigeonpea. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21(5):729–732
Sneath PHA (1986) In: Sneath PHA, Mair NS, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, vol 2, pp 1104–1139
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) The principle and practice of numerical classification. In: Kennedy D, Park RB (eds) Numerical taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA:DNA reassociation and 16s rRNA sequence analysis in the present species de ni-tion in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Stein T (2005) Bacillus subtilis antibiotics: structures, syntheses and specific functions. Mol Microbiol 56:845–857
Swofford DL, Olsen GJ (1990) Phylogenetic reconstruction. In: Hillis DM, Moritz C (eds) Molecular systematics. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, pp 411–501
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Veyrat A, Miralles MC, Pérez-Martinez G (1999) A fast method for monitoring the colonization rate of lactobacilli in a meat model system. J Appl Microbiol 87:49–61
Vurro M, Gressel J (2006) An ecological and societal approach to biological control: an integrated approach to biological control of plant diseases and weeds in Europe. Eilenberg J, Hokkane HMT (eds), Springer 2: 257–274
Walker R, Powell AA, Seddon B (1998) Bacillus isolates from the spermosphere of peas and dwarf French beans with antifungal activity against Botrytis cinerea and Pythium species. J Appl Microbiol 84:791–801
Xu D, Cote JC (2003) Phylogenetic relationships between Bacillus species and related genera inferred from comparison of 3′ end 16S rDNA and 5′ end 16S–23S ITS nucleotide sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:695–704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gajbhiye, A., Rai, A.R., Meshram, S.U. et al. Isolation, evaluation and characterization of Bacillus subtilis from cotton rhizospheric soil with biocontrol activity against Fusarium oxysporum . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26, 1187–1194 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0287-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0287-9