Abstract
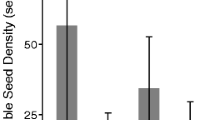
The sexual reproduction of annual and perennial Zostera marina was investigated in Moon Lake, Shandong, China. Based on the disturbance and stress regimes, the Z. marina beds were classified into five types: intertidal annual (IA) and perennial (IP) eelgrass patches, subtidal patch area (PA), meadow margin (MM) and meadow center (MC). Seed dispersal was investigated using artificial seagrass units in the five areas and another two areas [adjacent bare area and Zostera japonica meadow (Zj)]. Total and flowering shoot density and aboveground biomass of flowering shoots per unit area were higher in PA and MM, and lower in IA and IP, whereas the total biomass per unit area in MC showed the highest value. Reproductive effort (RE) in IA showed negative response to intertidal stress, while in perennial IP, PA and MM it showed significantly positive response to anthropogenic or natural disturbances. The density-based RE in perennial IP, PA and MM was 1.1-, 5.1- and 5.1-fold higher than that in MC, while in annual IA it was 0.46-fold lower. Additionally, the biomass-based RE in IP, PA and MM was 1.8-, 3.5- and 3.8-fold higher than that in MC, while the RE in IA was 0.84-fold lower. The estimated seed production per unit area was much greater in PA (60,793 ± 9,843 seeds m−2) and MM (43,414 ± 8,718 seeds m−2) than in IA (416 ± 83 seeds m−2), IP (3,820 ± 1,470 seeds m−2) and MC (9,779 ± 631 seeds m−2), while the seed density ranged from 24 ± 6 to 584 ± 56 seeds m−2. Results suggested that in response to disturbances and stress, Z. marina in subtidal areas increased their RE and seed production and thus seeds were available to be dispersed into areas where seed production was limited.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman JD (2006) Sexual reproduction of seagrasses: pollination in the marine context. In: Larkum AW, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 89–109
Alexandre A, Santos R, Serrão E (2005) Effects of clam harvesting on sexual reproduction of the seagrass Zostera noltii. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 298:115–122
Bell SS, Fonseca MS, Kenworthy WJ (2008) Dynamics of a subtropical seagrass landscape: links between disturbance and mobile seed banks. Landsc Ecol 23(1):67–74
Boese BL, Alayan KE, Gooch EF, Robbins BD (2003) Desiccation index: a measure of damage caused by adverse aerial exposure on intertidal eelgrass (Zostera marina) in an Oregon (USA) estuary. Aquat Bot 76(4):329–337
Cabaço S, Santos R (2012) Seagrass reproductive effort as an ecological indicator of disturbance. Ecol Indic 23:116–122. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.03.022
Coyer J, Diekmann O, Serrao E, Procaccini G, Milchakova N, Pearson G, Stam W, Olsen J (2004) Population genetics of dwarf eelgrass Zostera noltii throughout its biogeographic range. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 281:51–62
Craine JM (2009) Resource strategies of wild plants. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Duarte CM, Fourqurean JW, Krause-Jensen D, Olesen B (2006) Dynamics of seagrass stability and change. In: Larkum AW, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 271–294
Ellsworth L, Kauffman J (2010) Native bunchgrass response to prescribed fire in ungrazed mountain big sagebrush ecosystems. Fire Ecol 6(3):86–96
Fishman JR, Orth RJ (1996) Effects of predation on Zostera marina L. seed abundance. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 198(1):11–26
Fonseca MS, Bell SS (1998) Influence of physical setting on seagrass landscapes near Beaufort, North Carolina, USA. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 171:109–121
Greve TM, Krause-Jensen D, Rasmussen MB, Christensen PB (2005) Means of rapid eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) recolonisation in former dieback areas. Aquat Bot 82(2):143–156
Hammerstrom KK, Kenworthy WJ, Fonseca MS, Whitfield PE (2006) Seed bank, biomass, and productivity of Halophila decipiens, a deep water seagrass on the west Florida continental shelf. Aquat Bot 84(2):110–120
Harwell MC, Orth RJ (2002) Seed bank patterns in Chesapeake Bay eelgrass (Zostera marina L.): a bay-wide perspective. Estuaries 25(6):1196–1204
Harwell MC, Rhode JM (2007) Effects of edge/interior and patch structure on reproduction in Zostera marina L. in Chesapeake Bay, USA. Aquat Bot 87(2):147–154. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.04.007
Hemminga MA, Duarte CM (2000) Seagrass ecology. Cambridge University Press, London
Hughes AR, Stachowicz JJ (2009) Ecological impacts of genotypic diversity in the clonal seagrass Zostera marina. Ecology 90(5):1412–1419
Inglis GJ (2000a) Disturbance-related heterogeneity in the seed banks of a marine angiosperm. J Ecol 88(1):88–99
Inglis GJ (2000b) Variation in the recruitment behaviour of seagrass seeds: implications for population dynamics and resource management. Pac Conserv Biol 5(4):251–259
Källström B, Nyqvist A, Åberg P, Bodin M, André C (2008) Seed rafting as a dispersal strategy for eelgrass (Zostera marina). Aquat Bot 88(2):148–153. doi:10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.09.005
Karlsson PS, Mendez M (2005) The resource economy of plant reproduction. In: Reekie E, Bazzaz FA (eds) Reproductive allocation in plants. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1–49
Keddy CJ (1987) Reproduction of annual eelgrass: variation among habitats and comparison with perennial eelgrass (Zostera marina L.). Aquat Bot 27(3):243–256. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(87)90044-1
Lee K-S, Park J-I, Kim YK, Park SR, Kim J-H (2007) Recolonization of Zostera marina following destruction caused by a red tide algal bloom: the role of new shoot recruitment from seed banks. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 342:105–115
Meling-López AE, Ibarra-Obando SE (1999) Annual life cycles of two Zostera marina L. populations in the Gulf of California: contrasts in seasonality and reproductive effort. Aquat Bot 65(1):59–69
Moore KA, Short FT (2006) Zostera: biology, ecology, and management. In: Larkum AW, Orth RJ, Duarte CM (eds) Seagrasses: biology, ecology and conservation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 361–386
Morita T, Okumura H, Abe M, Kurashima A, Maegawa M (2007) Density and distribution of seeds in bottom sediments in Zostera marina beds in Ago Bay, central Japan. Aquat Bot 87(1):38–42
Olesen B (1999) Reproduction in Danish eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) stands: size-dependence and biomass partitioning. Aquat Bot 65(1):209–219
Olesen B, Sand-Jensen K (1994) Patch dynamics of eelgrass Zostera marina. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 106:147–156
Park SR, Kim YK, Kim J-H, Kang C-K, Lee K-S (2011) Rapid recovery of the intertidal seagrass Zostera japonica following intense Manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) harvesting activity in Korea. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 407(2):275–283
Plus M, Deslous-Paoli J-M, Dagault F (2003) Seagrass (Zostera marina L.) bed recolonisation after anoxia-induced full mortality. Aquat Bot 77(2):121–134
Santamaŕia-Gallegos NA, Sánchez-Lizaso JL, Félix-Pico EF (2000) Phenology and growth cycle of annual subtidal eelgrass in a subtropical locality. Aquat Bot 66(4):329–339
Schubert PR, Karez R, Reusch TBH, Dierking J (2013) Isotopic signatures of eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) as bioindicator of anthropogenic nutrient input in the western Baltic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 72(1):64–70. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.04.029
Short FT (1983) The seagrass, Zostera Marina L.: plant morphology and bed structure in relation to sediment ammonium in izembek lagoon, Alaska. Aquat Bot 16(2):149–161
Trémolières M (2004) Plant response strategies to stress and disturbance: the case of aquatic plants. J Biosci 29(4):461–470
van Katwijk MM, Bos AR, Kennis P, de Vries R (2010) Vulnerability to eutrophication of a semi-annual life history: a lesson learnt from an extinct eelgrass (Zostera marina) population. Biol Conserv 143(1):248–254. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2009.08.014
van Lent F, Verschuure JM (1994) Intraspecific variability of Zostera marina L. (eelgrass) in the estuaries and lagoons of the southwestern Netherlands. I. Population dynamics. Aquat Bot 48(1):31–58
Waycott M, Duarte CM, Carruthers TJ, Orth RJ, Dennison WC, Olyarnik S, Calladine A, Fourqurean JW, Heck KL, Hughes AR (2009) Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(30):12377–12381
Wisehart LM, Dumbauld BR, Ruesink JL, Hacker SD (2007) Importance of eelgrass early life history stages in response to oyster aquaculture disturbance. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 344:71–80
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all the lab mates for their countless hours of field and laboratory assistance. This work was supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest of China (201003068) and Public Interest Research Project (20130504).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, LZ., Li, WT., Zhang, XM. et al. Sexual reproduction and seed dispersal pattern of annual and perennial Zostera marina in a heterogeneous habitat. Wetlands Ecol Manage 22, 671–682 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-014-9363-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-014-9363-5