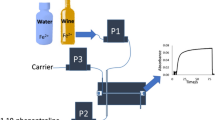
Abstract
Determination of hexavalent chromium (Cr (VI)) in tannery effluent is an important analytical objective for environmental monitoring and assessment. Here, a simple, accurate, and sensitive automated flow injection analysis (FIA) method is proposed in this paper. The procedure is based on a highly selective reaction between Ponceau S and Cr (VI) under acidic condition. The absorbance of the complex compounds was measured using an optical detector at 505 nm. The chemical factors and FIA variables that affect the system were fully discussed and optimized via univariate experimental design. Under the optimal conditions, a linear dynamic range of 0.1–3.0 mg/L with a satisfactory determination coefficient (R 2) of 0.9996 was obtained. The detection limit and relative standard deviation were 0.08 mg/L and 2.27%, respectively. Finally, the method was successfully applied to determine Cr (VI) in field samples of tannery effluent and the results have no significant difference comparing with one official method, indicating this FIA method could be practically promising for determination of Cr (VI) in tannery effluent.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcin, G. (2013). Removal and Recovery of Chromium from Solutions Simulating Tannery Wastewater by Strong Acid Cation Exchanger. Journal of Chemistry, 2013(2013), 1–7.
Anderson, R. A. (1997). Chromium as an essential nutrient for humans. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 26(1), S35–S41.
Armenta, S., Garrigues, S., & de la Guardia, M. (2008). Green Analytical Chemistry. Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 27(6), 497–511.
Bajza, Z., & Vrcek, I. V. (2001). Water quality analysis of mixtures obtained from tannery waste effluents. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 50(1), 15–18.
Bakircioglu, D., Topraksever, N., & Kurtulus, Y. B. (2015). Separation/Preconcentration System Based on Emulsion-Induced Breaking Procedure for Determination of Cadmium in Edible Oil Samples by Flow Injection-Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Food Analytical Methods, 8(9), 2178–2184.
Bannur, S. V., Kulgod, S. V., Metkar, S. S., Mahajan, S. K., & Sainis, J. K. (1999). Protein Determination by Ponceau S Using Digital Color Image Analysis of Protein Spots on Nitrocellulose Membranes. Analytical Biochemistry, 267(2), 382–389. doi:10.1006/abio.1998.3020.
Barnhart, J. (1997). Occurrences, uses, and properties of chromium. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 26(1), S3–S7.
Berry, W. J., Boothman, W. S., Serbst, J. R., & Edwards, P. A. (2004). Predicting the toxicity of chromium in sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23(12), 2981–2992.
Burbridge, D. J., Koch, I., Zhang, J., & Reimer, K. J. (2012). Chromium speciation in river sediment pore water contaminated by tannery effluent. Chemosphere, 89(7), 838–843.
Coedo, A., Dorado, T., Padilla, I., & Alguacil, F. J. (2000). Speciation of chromium in steelmaking solid wastes by selective retention on ion-exchange media and determination by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 15(12), 1564–1568.
Collins, C. H., Pezzin, S. H., Rivera, J. F. L., Bonato, P. S., Windmöller, C. C., Archundia, C., et al. (1997). Liquid chromatographic separation of aqueous species of Cr (VI) and Cr (III). Journal of Chromatography. A, 789(1), 469–478.
Dai, S., Zhang, X., Yu, L., & Yang, Y. (2010). The determination of trace lead in drinking water by flow injection spectrophotometry. Spectrochimica Acta, Part A, 75(1), 330–333.
Deep, A., Sharma, A. L., Tuteja, S. K., & Paul, A. K. (2014). Phosphinic acid functionalized carbon nanotubes for sensitive and selective sensing of chromium(VI). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 278, 559–565. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.06.043.
Derbyshire, M., Lamberty, A., & Gardiner, P. H. (1999). Optimization of the simultaneous determination of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) by ion chromatography with chemiluminescence detection. Analytical Chemistry, 71(19), 4203–4207.
El-Shahawi, M. S., Al-Saidi, H. M., Bashammakh, A. S., Al-Sibaai, A. A., & Abdelfadeel, M. A. (2011). Spectrofluorometric determination and chemical speciation of trace concentrations of chromium (III and; VI) species in water using the ion pairing reagent tetraphenyl-phosphonium bromide. Talanta, 84(1), 175–179. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2010.12.039.
Fabiani, C., Ruscio, F., Spadoni, M., & Pizzichini, M. (1997). Chromium (III) salts recovery process from tannery wastewaters. Desalination, 108(1), 183–191.
Gałuszka, A., Migaszewski, Z., & Namieśnik, J. (2013). The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the SIGNIFICANCE mnemonic of green analytical practices. TrAC, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 50, 78–84. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2013.04.010.
Gomez, V., & Callao, M. (2006). Chromium determination and speciation since 2000. TrAC, Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 25(10), 1006–1015.
Gürkan, R., Ulusoy, H. İ., & Akçay, M. (2012). Simultaneous determination of dissolved inorganic chromium species in wastewater/natural waters by surfactant sensitized catalytic kinetic spectrophotometry. Arabian Journal Chemistry.
Health Canada (2012). Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality—Summary Table. Water, Air and Climate Change Bureau, Healthy Environmentsand Consumer Safety Branch, Health. Canada, Ottawa, Ontario.
Hsu, L.-C., Liu, Y.-T., & Tzou, Y.-M. (2015). Comparison of the spectroscopic speciation and chemical fractionation of chromium in contaminated paddy soils. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 296, 230–238.
Huang, S., Qiu, H., Zhu, F., Lu, S., & Xiao, Q. (2015). Graphene quantum dots as on-off-on fluorescent probes for chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid. Microchimica Acta, 182(9), 1723–1731. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1508-6.
Jin, W., Wu, G., & Chen, A. (2014). Sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of chromium(vi) based on gold nanoparticle-decorated titania nanotube arrays. Analyst, 139(1), 235–241. doi:10.1039/C3AN01614E.
Ju-Nam, Y., Ojeda, J. J., & de Medina, H. L. (2015). Determination of Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates. Flow Injection Analysis of Food Additives, 1, 261.
Korshoj, L. E., Zaitouna, A. J., & Lai, R. Y. (2015). Methylene Blue-Mediated Electrocatalytic Detection of Hexavalent Chromium. Analytical Chemistry, 87(5), 2560–2564.
Ngah, W. W., & Hanafiah, M. (2008). Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: a review. Bioresource Technology, 99(10), 3935–3948.
Okutucu, B., Dınçer, A., Habib, O., & Zıhnıoglu, F. (2007). Comparison of five methods for determination of total plasma protein concentration. Journal of Biochemical and Biophysical Methods, 70(5), 709–711. doi:10.1016/j.jbbm.2007.05.009.
Ortega, L. M., Lebrun, R., Noël, I. M., & Hausler, R. (2005). Application of nanofiltration in the recovery of chromium (III) from tannery effluents. Separation and Purification Technology, 44(1), 45–52.
Pawlikowski, M., Szalinska, E., Wardas, M., & Dominik, J. (2006). Chromium originating from tanneries in river sediments: a preliminary investigation from the upper Dunajec River (Poland). Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 15(6), 885.
Phansi, P., Henríquez, C., Palacio, E., Nacapricha, D., & Cerdà, V. (2014). An automated in-chip-catalytic–spectrophotometric method for determination of copper (II) using a multisyringe flow injection analysis-multipumping flow system. Analytical Methods, 6(21), 8494–8504.
Planavsky, N. J., Reinhard, C. T., Wang, X., Thomson, D., McGoldrick, P., Rainbird, R. H., et al. (2014). Low Mid-Proterozoic atmospheric oxygen levels and the delayed rise of animals. Science, 346(6209), 635–638.
Pradela-Filho, L. A., Oliveira, B. C., Takeuchi, R. M., & Santos, A. L. (2015). A Prussian blue-carbon paste electrode for selective cathodic amperometric determination of nitrite using a flow-injection analysis system with carrier recycling. Electrochimica Acta, 180, 939–946. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.09.030.
Rinklebe, J., Shaheen, S. M., Schröter, F., & Rennert, T. (2016). Exploiting biogeochemical and spectroscopic techniques to assess the geochemical distribution and release dynamics of chromium and lead in a contaminated floodplain soil. Chemosphere, 150, 390–397.
Simoes, E. F., Leitão, J. M., Barbosa, R. M., & da Silva, J. C. E. (2012). Flow injection analysis for nitric oxide quantification based on reduced fluoresceinamine. Analytical Methods, 4(4), 1089–1097.
Soni, S. K., Ashutosh Awasthi, R. S., Singh, M., & Kalra, A. (2013). In vitro Cr(VI) reduction by cell-free extracts of chromate-reducing bacteria isolated from tannery effluent irrigated soil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(3), 1661–1674.
Sun, J., Zhang, J., & Jin, Y. (2013). 11-Mercaptoundecanoic acid directed one-pot synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent gold nanoclusters and their use as probes for sensitive and selective detection of Cr3+ and Cr6+. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 1(1), 138–143. doi:10.1039/C2TC00021K.
Timerbaev, A., Semenova, O., Buchberger, W., & Bonn, G. (1996). Speciation studies by capillary electrophoresis-Simultaneous determination of chromium (III) and chromium (VI). Fresenius’ Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 354(4), 414–419.
Ulusoy, H. İ., Gürkan, R., Yılmaz, Ö., & Akçay, M. (2012). Development of a cloud point extraction and preconcentration method for chromium (III) and total chromium prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 67(2), 131–139.
USEPA, UEPA (2012). Edition of the drinking water standards and health advisories. Washington, DC.
Wang, L., Xinshen, Z., Hui, L., DONGMEI, S., Jing, S., Yujie, Y., et al. (2010). Reverse reference flow injection spectrophotometry for the determination of chromium (vi) extracted from leather by artificial perspiration. Journal of the Society of Leather Technologists and Chemists, 94(6), 262–267.
Xavier, A. M., Logeswari, A., Mano, S., Thirumarimurugan, M., & Kannadasan, T. (2013). Removal of chromium from real tannery effluent by using bioadsorbents. International Journal of Engineering and Science, 2(7), 35–40.
Zhang, J. R., Zeng, A. L., Luo, H. Q., & Li, N. B. (2016). Fluorescent silver nanoclusters for ultrasensitive determination of chromium(VI) in aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 304, 66–72. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.10.036.
Zhengjun, G., Xinshen, Z., Guohe, C., & Xinfeng, X. (2005). Flow injection kinetic spectrophotometric determination of trace amounts of Se (IV) in seawater. Talanta, 66(4), 1012–1017.
Zhou, T., Huang, Y., Yuan, D., Feng, S., Zhu, Y., & Ma, J. (2016). A sensitive flow-injection analysis method with iminodiacetate chelation and spectrophotometric detection for on board determination of trace dissolved aluminum in seawater. Analytical Methods, 8(22), 4473–4481.
Zongo, I., Leclerc, J.-P., Maïga, H. A., Wéthé, J., & Lapicque, F. (2009). Removal of hexavalent chromium from industrial wastewater by electrocoagulation: a comprehensive comparison of aluminium and iron electrodes. Separation and Purification Technology, 66(1), 159–166. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2008.11.012.
Melchert, W. R., Reis, B. F., & Rocha, F. R. P. (2012). Green chemistry and the evolution of flow analysis. A review. Analytica Chimica Acta, 714, 8–19. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2011.11.044.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No.2015FY110900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, F., Liu, H., Wu, F. et al. Automated Determination of Chromium (VI) in Tannery Effluent Using Flow Injection Analysis with an Optical Flow Cell and Detector. Water Air Soil Pollut 228, 32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3162-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-3162-y