Abstract
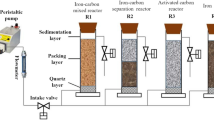
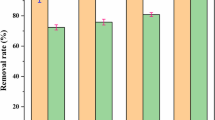
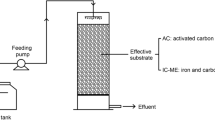
The aim of this study was to investigate the synergistic effects of the process of iron-carbon microelectrolysis (ICME) followed by struvite (MAP) crystallization on treating antibiotic wastewater. Characteristics of ICME effluent depended mainly on the iron to carbon mass ratio (Fe/C). The optimum reaction conditions of Fe/C ratio of 2:1 and reaction time of 90 min were observed. The ICME effluent was further treated by MAP crystallization using Na2HPO4·12H2O and MgCl2·6H2O as precipitation agents. The results showed that, the Mg2+/NH4 +-N/PO4 3−-P molar ratio of 1:1:1 and pH 8.5, were suitable for the crystallization process, which could obtain high-quality MAP containing 5.18 % N,10.23 % Mg, and 13.83 % P. Optimal total removal rate of COD and NH4 +-N removal rate achieved 84.6 and 89.9 %, respectively. The economic evaluation of NH4 +-N recovery by the synergistic process was also conducted, indicating that the synergistic process had the potential to benefit COD emission reduction and nitrogen recovery.

The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of treating antibiotic wastewater using iron and carbon combined process of microelectrolysis and struvite (MAP) crystallization. The MAP was of high purity and good crystal morphology, which could be used as a slow-release fertilizer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA. (1999). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. Washington, DC: American public health association (APHA).
Bi, W., Li, Y., & Hu, Y. (2014). Recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from alkaline hydrolysis supernatant of excess sludge by magnesium ammonium phosphate. Bioresource Technology, 166, 1–8.
Celen, I., & Turker, M. (2001). Recovery of ammonia as struvite from anaerobic digester effluents. Environmental Technology, 22(11), 1263–1272.
Cheng, H., Xu, W., Liu, J., Wang, H., He, Y., & Chen, G. (2007). Pretreatment of wastewater from triazine manufacturing by coagulation electrolysis, and internal microelectrolysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 146(1–2), 385–392.
Diwani, G. E., Rafie, S. E., El Ibiari, N. N., & El-Aila, H. I. (2007). Recovery of ammonia nitrogen from industrial wastewater treatment as struvite slow releasing fertilizer. Desalination, 214(1–3), 200–214.
Elmolla, E. S., & Chaudhuri, M. (2012). The feasibility of using combined Fenton-SBR for antibiotic wastewater treatment. Desalination, 285, 14–21.
Hao, X. D., Wang, C. C., Lan, L., & Von Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2008). Struvite formation, analytical methods and effects of pH and Ca2+. Water Science and Technology, 58(8), 1687–1692.
Huang, A. H., & Liu, J. C. (2014). Removal of ammonium as struvite from wet scrubber wastewater. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 225, 2062–2068.
Huang, L., Sun, G., Yang, T., Zhang, B., He, Y., & Wang, X. (2013). A preliminary study of anaerobic treatment coupled with micro-electrolysis for anthraquinone dye wastewater. Desalination, 309, 91–96.
Jain, S., Kumar, P., Vyas, R. K., Pandit, P., & Dalai, A. K. (2013). Occurrence and removal of antiviral drugs in environment: a review. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 224, 1410–1416.
Johnston, R. B., & Singer, P. C. (2007). Redox reactions in the Fe-As-O2 system. Chemosphere, 69(4), 517–525.
Lai, B., Zhoua, Y., Qin, H., Wu, C., Pang, C., Lian, Y., & Xu, J. (2012). Pretreatment of wastewater from acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) resin manufacturing by microelectrolysis. Chemical Engineering Journal, 179, 1–7.
Lai, B., Zhou, Y., Yang, P., Yang, J., & Wang, J. (2013). Degradation of 3,30-iminobis- propanenitrile in aqueous solution by Fe0/GAC micro-electrolysis system. Chemosphere, 90, 1470–1477.
Li, X. Z., & Zhao, Q. L. (2003). Recovery of ammonium-nitrogen from landfill leachate as a multi-nutrient fertilizer. Ecological Engineering, 20(2), 171–181.
Li, X. Z., Zhao, Q. L., & Hao, X. D. (1999). Ammonium removal from landfill leachate by chemical precipitation. Waste Management, 19(6), 409–415.
Liu, H. N., Li, G. T., Qu, J. H., & Liu, H. J. (2007). Degradation of azo dye Acid Orange 7 in water by Fe0/granular activated carbon system in the presence of ultrasound. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 144(1–2), 180–186.
Liu, P., Zhang, H., Feng, Y., Shen, C., & Yang, F. (2015). Integrating electrochemical oxidation into forward osmosis process for removal of trace antibiotics in wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 296, 248–255.
Lopata, K. R., Auerswald, L. P., & Cook, P. (2006). Ammonia toxicity and its effect on the growth of the South Africa abalone Haliotis midae Linnaeus. Aquaculture, 261(2), 678–687.
Mehta, C. M., & Batstone, D. J. (2013). Nucleation and growth kinetics of struvite crystallization. Water Research, 47(8), 2890–2900.
Miyittah, M. K., Gadekar, S., Pullammanappallil, P., Stanley, C. D., Bonzongo, J. C., & Rechcigl, J. E. (2012). Application of polymath chemical equilibrium simulation model for struvite precipitation in soils. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 223, 995–2001.
Münch, E. V., & Barr, K. (2001). Controlled struvite crystallization for removing phosphorus from anaerobic digester sidestreams. Water Research, 35(1), 151–159.
Nelson, N. O., Mikkelsen, R. L., & Hesterberg, D. L. (2003). Struvite precipitation in anaerobic swine lagoon liquid: effect of pH and Mg:P ratio and determination of rate constant. Bioresource Technology, 89(3), 229–236.
Oller, I., Malato, S., & Sánchez-Pérez, J. A. (2011). Combination of advanced oxidation processes and biological treatments for wastewater decontamination-a review. Science of the Total Environment, 409(20), 4141–4166.
Ozturk, I., Altinbas, M., Koyuncu, I., Arikan, O., & Gomec-Yangin, C. (2003). Advanced physico-chemical treatment experiences on young municipal landfill leachates. Waste Management, 23(5), 441–446.
Rahman, M. M., Liu, Y. H., Kwag, J. H., & Ra, C. S. (2011). Recovery of struvite from animal wastewater and its nutrient leaching loss in soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 186(2–3), 2026–2030.
Rahman, M. M., Salleh, M. A. M., Rashid, U., Ahsan, A., Hossain, M. M., & Ra, C. S. (2014). Production of slow release crystal fertilizer from wastewaters through struvite crystallization - A review. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7(1), 139–155.
Ruan, X. C., Liu, M. Y., Zeng, Q. F., & Ding, Y. H. (2010). Degradation and decolorization of reactive red X-3B aqueous solution by ozone integrated with internal micro-electrolysis. Separation and Purification Technology, 74(2), 195–201.
Ryu, H. D., Kim, D., & Lee, S. I. (2008). Application of struvite precipitation in treating ammonium nitrogen from semiconductor wastewater. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 156(1–3), 163–169.
Stefov, V., Šoptrajanov, B., Kuzmanovski, I., Lutz, H. D., & Engelen, B. (2005). Infrared and Raman spectra of magnesium ammonium phosphate hexahydrate (struvite) and its isomorphous analogues. III. Spectra of protiated and partially deuterated magnesium ammonium phosphate hexahydrate. Journal of Molecular Structure, 752(1–3), 60–67.
Stratful, I., Scrimshaw, M. D., & Lester, J. N. (2001). Conditions influencing the precipitation of magnesium ammonium phosphate. Water Research, 35(17), 4191–4199.
Su, C. C., Abarca, R. R. M., de Luna, M. D. G., & Lu, M. C. (2014). Phosphate recovery from fluidized-bed wastewater by struvite crystallization technology. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 45(5), 2395–2402.
Türker, M., & Çelen, I. (2007). Removal of ammonia as struvite from anaerobic digester effluents and recycling of magnesium and phosphate. Bioresource Technology, 98(8), 1529–1534.
Uludag-Demirer, S., & Othman, M. (2009). Removal of ammonium and phosphate from the supernatant of anaerobically digested waste activated sludge by chemical precipitation. Bioresource Technology, 100(13), 3236–3244.
Walter, M. V., & Vennes, J. W. (1985). Occurrence of multiple-antibiotic resistant enteric bacteria in domestic sewage and oxidative lagoons. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 50(4), 930–933.
Wang, C. C., Hao, X. D., Guo, G. S., & van Loosdrecht, M. C. M. (2010). Formation of pure struvite at neutral pH by electrochemical deposition. Chemical Engineering Journal, 159, 280–283.
Wu, S., Qi, Y., Gao, Y., Xu, Y., Gao, F., Yu, H., Lu, Y., Yue, Q., & Li, J. (2011). Preparation of ceramic-corrosion-cell fillers and application for cyclohexanone industry wastewater treatment in electrobath reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 196, 139–144.
Yang, X. (2009). Interior microelectrolysis oxidation of polyester wastewater and its treatment technology. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169, 480–485.
Yetilmezsoy, K., & Sapci-Zengin, Z. (2009). Recovery of ammonium nitrogen from the effluent of UASB treating poultry manure wastewater by MAP precipitation as a slow release fertilizer. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166, 260–269.
Yin, H., & Kong, M. (2014). Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from eutrophic waters using natural calcium-rich attapulgite-based versatile adsorbent. Desalination, 351, 128–137.
Ying, D., Peng, J., Li, K., Wang, Y., Pan, S., & Jia, J. (2013). Dual-cell reduction and group effect in an internal microelectrolysis reactor. Electrochimica Acta, 89, 861–867.
Yu, X., Zuo, J., Li, R., Gan, L., Li, Z., & Zhang, F. (2014). A combined evaluation of the characteristics and acute toxicity of antibiotic wastewater. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 106, 40–45.
Zhang, C., Zhou, M., Yu, X., Ma, L., & Yu, F. (2015). Modified iron-carbon as heterogeneous electro-Fenton catalyst for organic pollutant degradation in near neutral pH condition: Characterization, degradation activity and stability. Electrochimica Acta, 160, 254–262.
Zheng, H., Wang, Z., Deng, X., Herbert, S., & Xing, B. (2013). Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma, 206, 32–39.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments on the manuscript. Besides, this research was supported by the Shandong Province Science and Technology Development Program, China (grant no. 2013GSF11718), and Jinan Science and Technology Development Program, China (grant no. 201201136).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• Effects of Fe/C mass ratio on treatment efficiencies of antibiotic wastewater.
• 7-ADCD or 7-ACA was partly transformed into NH4 +-N by microelectrolysis.
• NH4 +-N concentrated was further recovered by struvite crystallization.
• MAP properties depended on Mg2+/NH4 +-N/PO4 3−-P molar ratio and pH.
• N- and P-rich MAP could be used as a slow-release fertilizer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Chen, S. & Wang, X. Sustainable Treatment of Antibiotic Wastewater Using Combined Process of Microelectrolysis and Struvite Crystallization. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 315 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2581-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2581-5