Abstract
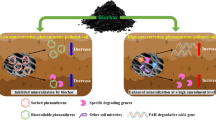
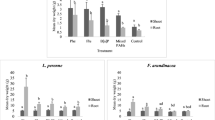
Apart from natural CO2 sequestration, biocalcification process can reduce bioavailability of certain pollutants. In the present study, experiments were conducted to evaluate the change in bioavailability for three polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) — anthracene (Ant), phenanthrene (Phe) and pyrene (Pyr) — either in normal soil extract that was spiked with PAHs (SESP) or spiked soil, after chemical calcification or biocalcification process. Results suggested that PAHs extractability in SESP (Ant: 2–4 mg/l, Phe: 3–6 mg/l and Pyr: 4.5–9 mg/l) after chemical precipitation of carbonate were not statistically different when compared to negative controls. However in biocalcification experiment the difference was statistically significant when conducted with SESP (P = 0.0425, α = 0.10) or soil (P = 0.035, α = 0.10). Supporting experiment revealed that the presence of microbial cells and sequence of Ca2+, CO3 −2 addition was important in determining the extent in PAHs bioavailability reduction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achal, V., Mukherjee, A., Basu, P. C., & Reddy, M. S. (2009). Lactose mother liquor as an alternative nutrient source for microbial concrete production by Sporosarcina pasteurii. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36, 433–438.
Achal, V., Pan, X., Fu, Q., & Zhang, D. (2012). Biomineralization based remediation of As (III) contaminated soil by Sporosarcina ginsengisoli. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 201–202, 178–184.
Aimrun, W., Amin, M. S. M., Ahmad, D., Hanafi, M. M., & Chan, C. S. (2007). Spatial variability of bulk soil electrical conductivity in a Malaysian paddy field: key to soil management. Paddy and Water Environment, 5, 113–121.
Alexander, M. (2000). Aging, bioavailability, and overestimation of risk from environmental pollutants. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 4259–4265.
Antemir, A., Hills, C. D., Carey, P. J., Gardner, K. H., Bates, E. R., & Crumbie, A. K. (2010). Long-term performance of aged waste forms treated by stabilization/solidification. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 65–73.
Banks, E. D., Taylor, N. M., Gulley, J., Lubbers, B. R., Giarrizzo, J. G., Bullen, H. A., et al. (2010). Bacterial calcium carbonate precipitation in cave environments: a function of calcium homeostasis. Geomicrobiology Journal, 27, 444–454.
Bäuerlein, E. (2003). Biomineralization of unicellular organisms: an unusual membrane biochemistry for the production of inorganic nano- and microstructures. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 42, 614–641.
Boopathy, R. (2000). Factors limiting bioremediation technologies. Bioresource Technology, 74, 63–67.
Chu, J., Stabnikov, V., & Ivanov, V. (2012). Microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation on surface or in the bulk of soil. Geomicrobiology Journal, 29, 544–549.
Chunxiang, Q., Jianyun, W., Ruixing, W., & Liang, C. (2009). Corrosion protection of cement-based building materials by surface deposition of CaCO3 by Bacillus pasteurii. Materials Science and Engineering, 29, 1273–1280.
Cicerone, D. S., Stewart, A. J., & Roh, Y. (1999). Diel cycles in calcite production and dissolution in a eutrophic basin. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 2169–2177.
Cornelissen, G., Breedveld, G. D., Kalaitzidis, S., Christanis, K., Kibsgaard, A., & Oen, A. M. P. (2006). Strong sorption of native PAHs to pyrogenic and unburned carbonaceous geosorbents in sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 1197–1203.
Dupraz, C., Reid, R. P., Braissant, O., Decho, A. W., Norman, R. S., & Visscher, P. T. (2009). Processes of carbonate precipitation in modern microbial mats. Earth-Science Reviews, 96, 141–162.
Fierer, N., & Schimel, J. P. (2002). Effects of drying–rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 34, 777–787.
Fortin, D., Ferris, F. G., & Beveridge, T. J. (1997). Surface-mediated mineral development by bacteria. Reviews in Mineralogy, 35, 161–180.
Fujita, Y., Redden, G. D., Ingram, J. C., Cortez, M. M., Ferris, F. G., & Smith, R. W. (2004). Strontium incorporation into calcite generated by bacterial ureolysis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68, 3261–3270.
Haluschak, P. (2006). Laboratory methods of soil analysis. Canada-Manitoba Soil Survey, 3–133.
Hundal, L. S., Thompson, M. L., Laird, D. A., & Carmo, A. M. (2001). Sorption of phenanthrene by reference smectites. Environmental Science & Technology, 35, 3456–3461.
Hunter, R. C., Phoenix, V. R., Saxena, A., & Beveridge, T. J. (2010). Impact of growth environment and physiological state on metal immobilization by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 56, 527–538.
Johnsen, A. R., Wick, L. Y., & Harms, H. (2005). Principles of microbial PAH-degradation in soil. Environmental Pollution, 133, 71–84.
Johnson, K. J., Ams, D. A., Wedel, A. N., Szymanowski, J. E. S., Weber, D. L., Schneegurt, M. A., et al. (2007). The impact of metabolic state on Cd adsorption onto bacterial cells. Geobiology, 5, 211–218.
Kettler, T. A., Doran, J. W., & Gilbert, T. L. (2001). Simplified method for particle size determination to accompany soil-quality assessment. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 65, 849–852.
Keykha, H. A., Huat, B. B. K., Asadi, A., & Kawasaki, S. (2012). Electro-biogrouting and its challenges. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 7, 1196–1204.
Kreitinger, J. P., Neuhauser, E. F., Doherty, F. G., & Hawthorne, S. B. (2007). Greatly reduced bioavailability and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to Hyalella azteca in sediments from manufactured-gas plant sites. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 26, 1146–1157.
Li, Y., Shi, Z., Wu, C., Li, H., & Li, F. (2008). Determination of potential management zones from soil electrical conductivity, yield and crop data. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B, 9, 68–76.
Mastral, A. M., & Callén, M. S. (2000). A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) emissions from energy generation. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 3051–3057.
Meylan, W. M., Howard, P. H., Boethling, R. S., Aronson, D., Printup, H., & Gouchie, S. (1999). Improved method for estimating bioconcentration/bioaccumulation factor from octanol/water partition coefficient. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 18, 664–672.
Mrozik, A., Piotrowska-Seget, Z., & Łabużek, S. (2003). Bacterial degradation and bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 12, 15–25.
Mustafa, T., Demirhan, C., & Mustafa, S. (2008). 5-Chloro-2-hydroxyanilinecopper (II) coprecipitation system for preconcentration and separation of lead and chromium at trace levels. Journal of Hazardous Material, 158, 137–141.
Ohki, S., & Arnold, K. (1990). Surface dielectric constant, surface hydrophobicity and membrane fusion. The Journal of Membrane Biology, 114, 195–203.
Ramirez, N., Cutright, T., & Ju, L. K. (2001). Pyrene biodegradation in aqueous solutions and soil slurries by Mycobacterium PYR-1 and enriched consortium. Chemosphere, 44, 1079–1086.
Reid, B. J., Northcott, G. L., Jones, K. C., & Semple, K. T. (1998). Evaluation of spiking procedures for the introduction of poorly water soluble contaminants into soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 32, 3224–3227.
Rivadeneyra, M. A., Delgado, G., Ramos-Cormenzana, A., & Delgado, R. (1998). Biomineralization of carbonates by Halomonas eurihalina in solid and liquid media with different salinities: crystal formation sequence. Research in Microbiology, 149, 277–287.
Rodrigues, A. C., Wuertz, S., Brito, A. G., & Melo, L. F. (2005). Fluorene and phenanthrene uptake by Pseudomonas putida ATCC 17514: kinetics and physiological aspects. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 90, 281–289.
Ross, S. M. (2009). Introduction to probability and statistics for engineers and scientists (4th ed.). New York: Academic Press.
Sathe, T. R., Agrawal, A., & Nie, S. M. (2006). Mesoporous silica beads included with semiconductor quantum dots and iron oxide nanocrystals: dual-function microcarriers for optical encoding and magnetic separation. Analytical Chemistry, 78, 5627–5632.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., Gschwend, P. M., & Imboden, D. M. (2003). Environmental organic chemistry (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Shu, Y. Y., Lai, T. L., Lin, H., Yang, T. C., & Chang, C. P. (2003). Study of factors affecting on the extraction efficiency of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soils using open-vessel focused microwave-assisted extraction. Chemosphere, 52, 1667–1676.
Skrbic, B., & Durisic-Mladenovic, N. (2007). Principal component analysis for soil contamination with organochlorine compounds. Chemosphere, 68, 2144–2152.
Song, Y. F., Jing, X., Fleischmann, S., & Wilke, B. M. (2002). Comparative study of extraction methods for the determination of PAHs from contaminated soils and sediments. Chemosphere, 48, 993–1001.
Stringfellow, W. T., & Alvarez-Cohen, L. (1999). Evaluating the relationship between the sorption of PAHs to bacterial biomass and biodegradation. Water Research, 33, 2535–2544.
Sverdrup, L. E., Nielsen, T., & Krogh, P. H. (2002). Soil ecotoxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in relation to soil sorption, lipophilicity, and water solubility. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 2429–2435.
Tang, J., Petersen, E. J., Huang, Q., & Weber, W. J. (2007). Development of engineered natural organic sorbents for environmental applications: 3. Reducing PAH mobility and bioavailability in contaminated soil and sediment systems. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 2901–2907.
van Noort, P. C. M. (2009). Estimation of amorphous organic carbon/water partition coefficients, subcooled aqueous solubilities, and n-octanol/water distribution coefficients of alkylbenzenes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere, 74, 1018–1023.
Warren, L. A., Maurice, P. A., Parmar, N., & Ferris, F. G. (2001). Microbially mediated calcium carbonate precipitation: Implications for interpreting calcite precipitation and for solid phase capture of inorganic contaminants. Geomicrobiology Journal, 18, 93–115.
Weber, W. J., Tang, J., & Huang, Q. (2006). Development of engineered natural organic sorbents for environmental applications: 1. Materials, approaches, and characterizations. Environmental Science & Technology, 40, 1650–1656.
Wicke, D., Böckelmann, U., & Reemtsma, T. (2007). Experimental and modeling approach to study sorption of dissolved hydrophobic organic contaminants to microbial biofilms. Water Research, 41, 2202–2210.
Wright, D. T., & Oren, A. (2005). Nonphotosynthetic bacteria and the formation of carbonates and evaporites through time. Geomicrobiology Journal, 22, 27–53.
Xiao, L., Qu, X., & Zhu, D. (2007). Biosorption of nonpolar hydrophobic organic compounds to Escherichia coli facilitated by metal and proton surface binding. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 2750–2755.
Zhao, D. H., & Gao, H. W. (2010). Turning calcium carbonate into a cost-effective wastewater-sorbing material by occluding waste dye. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 17, 97–105.
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (CGK) acknowledges the financial support from NRF under the project of enhancement of CO2 biomineralization employing alkaline metals releaser.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahanty, B., Kim, S. & Kim, C.G. Biocalcification Mediated Reduction of PAHs Bioavailability in Artificially Contaminated Soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1479 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1479-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1479-3