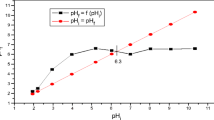
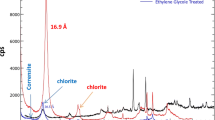
Abstract
Acid mine drainage (AMD) has long been a significant environmental problem that impairs water resources in historic or current mining industries throughout the world. One of the methods using passive treatment system at low cost to remove metals from solution involves the use of clays. The ability of three different adsorbents (montmorillonite K-10, bentonite (NT-25), and hydrotalcite (HT)) to remove Fe and Mn from aqueous solutions and acid mine drainage samples has been studied at different optimized conditions such as pH, amount of adsorbent and contact time. Flame atomic absorption spectrometer (FAAS) was used for measuring Fe and Mn concentrations. Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms were applied and isotherm coefficients were computed. A kinectic study was also developed for HT using the first order, second order and intraparticle diffusion models. A great amount of clay (more than 100 mg) and also contact times higher than 60 min had also no influence in the adsorption capacity for all adsorbents. HT was found to be the best among the studied clays removing more than 90 % of Fe and Mn for all AMD samples investigated. Moreover, the maximum adsorption capacity was 63.7 mg Mn g−1 HT and 666.7 mg Fe g−1 HT.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akcil, A., & Koldas, S. (2006). Acid mine drainage (AMD): causes, treatment and case studies. Journal of Cleaner Production, 14(12–13), 1139–1145.
Bhattacharyya, K. G., & Gupta, S. S. (2006). Adsorption of Fe (III) from water by natural and acid activated clays: studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Adsorption, 12, 185–204.
CONAMA (2005). Resolução nº 357/2005, de 17 de março de 2005. Dispõe sobre a classificação dos corpos de água e diretrizes ambientais para o seu enquadramento, bem como estabelece as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes, e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União, 18 de março de 2005, p. 7–8.
Crossgrove, J., & Zheng, W. (2004). Manganese toxicity upon overexposure. NMR in Biomedicine, 17(8), 544–553.
Dal Bosco, S. M., Jimenez, R. S., Vignado, C., Fontana, J., Geraldo, B., Figueiredo, F. C. A., Mandelli, D., & Carvalho, W. A. (2006). Removal of Mn(II) and Cd(II) from wastewaters by natural and modified clays. Adsorption, 12, 133–146.
Doye, I., & Duchesne, J. (2003). Neutralisation of acid mine drainage with alkaline industrial residues: laboratory investigation using batch-leaching tests. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 1197–1213.
Edwards, J. D., Barton, C. D., & Karathanasis, A. D. (2009). A small-scale sulfate-reducing bioreactor for manganese removal from a synthetic mine drainage. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 203, 267–275.
Ferreira, O. P., Alves, O. L., Macedo, J. S., Gimenez, I. F., & Ferreira, L. B. (2007). Ecomateriais: desenvolvimento e aplicação de materiais porosos funcionais para proteção ambiental. Química Nova, 30, 464–467.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57 A, 385–470.
Gaikwad, R. W., & Gupta, D. V. (2008). Review on removal of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 6(3), 81–98.
Gazea, B., Adam, K., & Kontopoulos, A. (1996). A review of passive systems for the treatment of acid mine drainage. Minerals Engineering, 9, 23–42.
Gupta, S. S., & Bhattacharyya, K. G. (2005). Interaction of metal ions with clays: i. A case study with Pb(II). Applied Clay Science, 30, 199–208.
Hallberg, K. B., & Johnson, D. B. (2005). Biological manganese removal from acid mine drainage in constructed wetlands and prototype bioreactors. Science of Total Environmental, 338, 115–124.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1998). Kinetic models for the sorption of dye from aqueous solution by wood. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 76(2), 183–191.
Johnson, D. B., & Hallberg, K. B. (2005). Acid mine drainage remediation options: a review. The Science of the Total Environment, 338, 3–14.
Kalin, M., Fyson, A., & Wheeler, W. N. (2006). The chemistry of conventional and alternative treatment systems for the neutralization of acid mine drainage. Science of the Total Environonment, 366, 395–408.
Kim, Y., Kim, J. H., Lee, K. G., & Kang, S. G. (2005). Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions in the solutions of clay minerals under various conditions. Journal of Ceramic Processing Research, 6(1), 25–30.
Lagergren, S. (1898). Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Kungliga Svenska vetenskapsakademiens Handlingar, 24(4), 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1916). The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 38, 2221–2295.
Lesley, B., Daniel, H., & Paul, Y. (2008). Iron and manganese removal in wetland treatment systems: rates, processes and implications for management. The Science of the Total Environment, 394, 1–8.
Letovsky, E., Heal, K. V., Carvalho, L., & Spears, B. M. (2012). Intracellular versus extracellular iron accumulation in freshwater periphytic mats across a mine water treatment lagoon. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 223, 1519–1530.
Matlock, M. M., Howerton, B. S., & Atwood, D. A. (2002). Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Research, 36, 4757–4764.
Mohan, D., & Chander, S. (2006). Removal and recovery of metal ions from acid mine drainage using lignite—a low cost sorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 137, 1545–1553.
Naseem, R., & Tahir, S. S. (2001). Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent. Water Research, 35(16), 3982–3986.
Paulino, A. T., Minasse, F. A. S., Guilherme, M. R., Reis, A. V., Muniz, E. C., & Nozaki, J. (2006). Novel adsorbent based on silkworm chrysalides for removal of heavy metals from wastewaters. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 301, 479–487.
Prasad, B., & Mortimer, R. G. (2011). Treatment of acid mine drainage using Fly Ash zeolite. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 218, 667–679.
Rodrigues, J. C., Costa, T. M. H., Gallas, M. R., & Moro, C. C. (2009). Influence of high-pressure processing on the structure and memory effect of synthetic layered double hydroxides. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 36, 439–446.
Rodríguez-Sarmiento, D. C., & Pinzón-Bello, J. A. (2001). Adsorption of sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate on organophilic bentonites. Applied Clay Science, 18, 173–181.
Sheoran, A. S., & Sheoran, V. (2006). Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: a critical review. Minerals Engineering, 19, 105–116.
Suárez, D. R., Zeifert, B. H., Garduño, M. H., Blásquez, J. S., & Serrano, A. R. (2007). Cu hydrotalcite-like compounds: morphological, structural and microstructural properties. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 434–435, 783–787.
Subramanian, B., & Gupta, G. (2006). Adsorption of trace elements from poultry litter by montmorillonite clay. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 128, 80–83.
Vaccari, A. (1998). Preparation and catalytic properties of cationic and anionic clays. Catalysis Today, 41, 53–71.
Vuori, K. M. (1995). Direct and indirect effects of iron in rivers ecosystems. Annales Zoologici Fennici, 32, 317–329.
Weber, W. J., Jr., & Morris, J. C. (1963). Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. Journal of the Sanitary Engineering Division, 89, 31–60.
Webster, J. G., Swedlund, P. J., & Webster, K. S. (1998). Trace metal adsorption onto an acid mine drainage. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 1361–1368.
Xu, C. Y., Schwartz, F. W., & Samuel, J. T. (1997). Treatment of acid mine water with calcite and quartz sand. Environmental Engineering Science, 141, 141–152.
Yapar, S., & Yilmaz, M. (2004). Removal of phenol by using montmorillonite, clinoptilolite and hydrotalcite. Adsorption, 10, 287–298.
Yoo, K., Hiroyoshi, N., & Tsunekawa, M. (2010). Removal of Mn ions by biological co-precipitation of Fe ions. Geosystem Engineering, 13(3), 91–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldani, E., Moro, C.C. & Maia, S.M. A Study Employing Differents Clays for Fe and Mn Removal in the Treatment of Acid Mine Drainage. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1401-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1401-4