Abstract
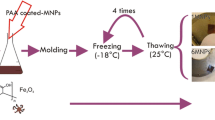
Hydrogels based on p(4-VP) of different dimensions were prepared and, after chemical modification, were used in the removal of one of the most potent toxic materials, cyanide. Macro and micron p(4-VP) hydrogel swelling behavior was evaluated in various aquatic environments. HCl, bromoethane, 1-bromobutane, 1-bromohexane, and 2-bromoethylamine were used as quaternizing agents to generate positive charges on both p(4-VP) macrogels and microgels. The modified p(4-VP) macrogels and microgels were used in cyanide ion removal for the first time from aqueous environments. The p(4-VP)-HCl at macro and micro sizes removed almost 49 and 61 mg cyanide ions per gram hydrogel in deionized water after modification, respectively. Moreover, the absorption capacity of the modified p(4-VP) hydrogel did not change significantly in tap, drinking, and creek waters. Parameters that affect the absorption process, such as cyanide concentration, contact time, hydrogel amount, and contaminated water source, were investigated. Additionally, magnetic field responsive macro and micro p(4-VP) hydrogel composites provided many advantages, such as easy handling after cyanide absorption, e.g., ready removal of cyanide-loaded p(4-VP) composites with an externally applied magnetic field. Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms were applied to the data obtained for cyanide uptake from aqueous environments.

Magnetic field responsive (nanoparticle composite in the removal cyanide from aqueous solutions





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Aal, S. E. (2006). Synthesis of copolymeric hydrogels using gamma radiation and their utilization in the removal of some dyes in wastewater. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 102(4), 3720–3731.
Acheampong, M. A., Meulepas, R. J. W., & Lens, P. N. L. (2010). Removal of heavy metals and cyanide from gold mine wastewater. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 85(5), 590–613.
Barakat, M. A., & Sahiner, N. (2008). Cationic hydrogels for toxic arsenate removal from aqueous environment. Journal of Environmental Management, 88(4), 955–961.
Behnamfard, A., & Salarirad, M. M. (2009). Equilibrium and kinetic studies on free cyanide adsorption from aqueous solution by activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(1), 127–133.
Dash, R. R., Gaur, A., & Balomajumder, C. (2009a). Cyanide in industrial wastewaters and its removal: A review on biotreatment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 163(1), 1–11.
Dash, R. R., Balomajumder, C., & Kumar, C. (2009b). Removal of cyanide from water and wastewater using granular activated carbon. Chemical Engineering Journal, 146(3), 408–413.
Freundlich, H. M. F. (1906). Over the adsorption in solution. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57, 385–471.
Fujii, S., Dupin, D., Araki, T., Armes, S. P., & Ade, H. (2009). First direct imaging of electrolyte-induced deswelling behavior of pH-responsive microgels in aqueous media using scanning transmission X-ray microscopy. Langmuir, 25(5), 2588–2592.
Huertas, M. J., Saez, L. P., Roldan, M. D., Luque-Almagro, V. M., Martinez-Luque, M., Blasco, R., Castillo, F., Moreno-Vivian, C., & Garcia-Garcia, I. (2010). Alkaline cyanide degradation by Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes CECT5344 in a batch reactor. Influence of pH. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 179(1–3), 72–78.
Hurriyet Daily News (2011). Retrieved from http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/n.php?n=8216constructing-a-new-dam-is-not-a-permanent-precaution8217-2011-05-09.
Kaewkannetra, P., Imai, T., Garcia-Garcia, F. J., & Chiu, T. Y. (2009). Cyanide removal from cassava mill wastewater using Azotobactor vinelandii TISTR 1094 with mixed microorganisms in activated sludge treatment system. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 172(1), 224–228.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40, 1361–1403.
Liu, X., Ma, Z., Xing, J., & Liu, H. (2004). Preparation and characterization of amino-silane modified superparamagnetic silica nanospheres. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 270(1–2), 1–6.
Moussavi, G., & Khosravi, R. (2010). Removal of cyanide from wastewater by adsorption onto pistachio hull wastes: Parametric experiments, kinetics and equilibrium analysis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183(1–3), 724–730.
Noroozifar, M., Khorasani-Motlagh, M., & Fard, P. A. (2009). Cyanide uptake from wastewater by modified natrolite zeolite–iron oxyhydroxide system: Application of isotherm and kinetic models. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 166(2–3), 1060–1066.
Osathaphan, K., Boonpitak, T., Laopirojana, T., & Sharma, V. K. (2008). Removal of cyanide and zinc–cyanide complex by an ion-exchange process. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 194(1–4), 179–183.
Ozay, O., Ekici, S., Baran, Y., Kubilay, S., Aktas, N., & Sahiner, N. (2010a). Utilization of magnetic hydrogels in the separation of toxic metal ions from aqueous environments. Desalination, 260(1–3), 57–64.
Ozay, O., Akcali, A., Otkun, M. T., Silan, C., Aktas, N., & Sahiner, N. (2010b). P(4-VP) based nanoparticles and composites with dual action as antimicrobial materials. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 79(2), 460–466.
Ozay, O., Aktas, N., & Sahiner, N. (2011). Hydrogels as a potential chromatographic system: Absorption, speciation, and separation of chromium species from aqueous media. Separation Science and Technology, 46(9), 1450–1461.
Rao, P., Lo, I. M. C., Yin, K., & Tang, S. C. N. (2011). Removal of natural organic matter by cationic hydrogel with magnetic properties. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(7), 1690–1695.
Sahiner, N. (2009). A facile method for the preparation of poly(4-vinylpyridine) nanoparticles and their characterization. Turkish Journal of Chemistry, 33(1), 23–31.
Sahiner, N., & Ozay, O. (2011a). Highly charged p(4-vinylpyridine-co-vinylimidazole) particles for versatile applications: Biomedical, catalysis and environmental. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 71(6), 607–615.
Sahiner, N., & Ozay, O. (2011b). Responsive tunable colloidal soft materials based on p(4-VP) for potential biomedical and environmental applications. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 378(1–3), 50–59.
Sahiner, N., Ozay, O., & Aktas, N. (2011a). 4-Vinylpyridine-based smart nanoparticles with N-isopropylacrylamide, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate, acrylic acid, and methacrylic acid for potential biomedical applications. Current Nanoscience, 7(3), 453–462.
Sahiner, N., Ozay, O., & Aktas, N. (2011b). Arsenic (V) removal with modifiable bulk and nano p(4-vinylpyridine)-based hydrogels: The effect of hydrogel sizes and quarternization agents. Desalination, 279(1–3), 344–352.
Shen, Z., Han, B., & Wickramasinghe, S. R. (2006). Cyanide removal from industrial praziquantel wastewater using integrated coagulation–gas-filled membrane absorption. Desalination, 195(1–3), 40–50.
Tang, Q., Sun, X., Li, Q., Lin, J., & Wu, J. (2009). Synthesis of polyacrylate/polyethylene glycol interpenetrating network hydrogel and its sorption for Fe3+ ion. Journal of Materials Science, 44(3), 726–733.
Üzüm, Ö. B., & Karadağ, E. (2007). Swelling characterization of poly (acrylamide-co-N-vinylimidazole) hydrogels crosslinked by TMPTA and semi-IPN’s with PEG. Journal of Polymer Research, 14(6), 483–488.
Yeddou, A. R., Nadjemi, B., Halet, F., Ould-Dris, A., & Capart, R. (2010). Removal of cyanide in aqueous solution by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in presence of activated carbon prepared from olive stones. Minerals Engineering, 23(1), 32–39.
Zheng, Y., Hua, S., & Wang, A. (2010). Adsorption behavior of Cu2+ from aqueous solutions onto starch-g-poly(acrylic acid)/sodium humate hydrogels. Desalination, 263(1–3), 170–175.
Zhu, M., Xiong, L., Wang, T., Liu, X., Wang, C., & Tong, Z. (2010). High tensibility and pH-responsive swelling of nanocomposite hydrogels containing the positively chargeable 2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate monomer. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 70(5), 267–271.
Acknowledgments
N. Sahiner is grateful to the Turkish Academy of Science for the financial support under the 2008 TUBA-GEBIP program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahiner, N., Ozay, O. & Aktas, N. The Removal of Cyanide Ions from Aquatic Environments by Quaternizable p(4-VP) Hydrogels of Different Dimensions. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1393 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1393-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1393-0