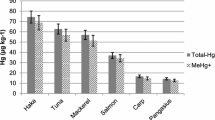
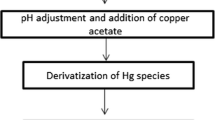
Abstract
A simple, rapid procedure for the determination of organic mercury in sediments, plants and fish tissues has been developed and validated. Extraction and separation of organic mercury compounds from the sample matrix was achieved by an established procedure based on an acid leaching of the sample (H2SO4/KBr/CuSO4), followed by extraction of the organic mercury halide with toluene and back-extraction with an aqueous solution of thiosulphate. Detection and quantification of mercury, in the liquid extracts, was made by atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS), following thermal decomposition of the sample. The method was evaluated using Certified Reference Material (CRM) BCR 463 (tuna fish), BCR 580 (estuarine sediment), IAEA-140TM (sea plant homogenate) and NRCC TORT-2 (lobster hepathopancreas). The recovery factors for organic mercury in all tested CRM were between 81–107%. The precision of the method has relative standard deviations of less than 10% for sediments and fish tissues and of less than 16% for plant material. The method was successfully applied to natural samples of sediments, plants, macroalgae and fish tissues collected from an estuarine ecosystem and could, therefore, be used for routine analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway, B. J.: 1995, ‘Trace metals in soils’, Blackie Academic & Professional, London.
Abreu, S., Pereira, E., Vale, C. and Duarte, C.: 2000, ‘Accumulation of mercury in sea bass from a contaminated lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal)’, Mar Pollut Bull. 40(4), 293–297.
Bryce, D. W., Stockwell, P. B. and Corns, W. T.: 2004, ‘Mercury speciation: A fully automatic gas chromatographic/atomic fluorescence instrument’, RMZ- Materials and Geoenvironment: Mercury as a Global Pollutant 51(3), 1876–1879.
Canário, J., Antunes, P., Lavrado, J. and Vale, C.: 2004, ‘Simple method for monomethylmercury determination in estuarine sediments’, Trend.Anal.Chem. 23(10–11), 799–806.
Coelho, J. P., Pereira, M. E., Duarte, A. and Pardal, M. A.: 2005, ‘Macroalgae response to a mercury contamination gradient in a temperate coastal lagoon (Ria de Aveiro, Portugal)’, Estuar Coast and Shelf S. 65(3), 492–500.
Colon, L. A. and Barry, E. F.: 1990, ‘Evaluation of an alternating current plasma emission detector for high-performance liquid chromatography’, J. Chromatogr. 513, 159–166.
Costley, C., Mossop, K., Dean, J., Garden, L., Marshall, J. and Carroll, J.: 2000, ‘Determination of mercury in environmental and biological samples using pyrolysis atomic absorption spectrometry with gold amalgamation’, Anal. Chim. Acta 405, 179–183.
Dong, L.-M., Yan, X.-P., Li, Y., Jiang, Y., Wang, S.-W. and Jiang, D.-Q.: 2004, ‘On-line coupling of flow injection displacement sorption preconcentration to high performance liquid chromatography for speciation analysis of mercury in seafood’, J. Chromatogr. 1036, 119–125.
Falter, R., and Schöler, H. F.: 1994, ‘Interfacing high-performance liquid chromatography and cold-vapour atomic absorption spectrometry with on-line UV irradiation for the determination of organic mercury compounds’, J. Chromatogr. 675(1–2), 253–256.
Falter, R., Hintelmann, H. and Quevauviller, Ph.: 1999, ‘Conclusion of the workshop on “sources of error in methylmercury determination during sample preparation, derivatisation and detection”, Chemosphere 39(I), 1039–1049.
Hall, G. and Pelchat, P.: 1997, ‘Evaluation of a direct solid sampling atomic absorption spectrometry for the trace determination of mercury in geological samples’, Analyst 122, 921–924.
Harrington, C. F., Romeril, J. and Catterick, T.: 1998, ‘The speciation of mercury and organomercury compounds by high performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry’, Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrosc. 12, 911–916.
Heller, A. and Weber, J.: 1998. ‘Seasonal variation of mercury (II) and monomethylmercury in Spartina Alterniflora from the Great Bay estuary, NH’, Sci. Total Environ. 221, 181–188.
Hintelmann, H.: 1999, ‘Comparison of different extraction techniques used for methylmercury analysis with respect to accidental formation of methylmercury during sample preparation’, Chemosphere 39(7), 1093–1105.
Horvat, M.: 1996, ‘Mercury analysis and speciation in environment samples’, in W. Baeyens (ed.), Global and Regional Mercury Cycles, Fluxes and Mass Balances, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, pp. 1–31.
Landaluze, J., Diego, A., Raposo, J. and Madariaga, J.: 2004, ‘Methylmercury determination in sediments and fish tissues from the Nerbioi-Ibaizabal estuary (Basque Country, Spain)’, Anal. Chim. Acta 508, 107–117.
Mendelssohn, I., Kleiss, B. and Wakeley, J.: 1995, ‘Factors controlling the formation of oxidized root channels in wetland plants: A review and annotated bibliography’, Wetlands 15, 37–47.
Miller, J. N. and Miller, J. C.: 2000, Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, Pearson Education Limited, Great Britain, 120 pp.
Pereira, M. E., Duarte, A. C., Millward, G. E., Vale, C. and Abreu, S. N.: 1998, ‘Tidal export of particulate mercury from the most contaminated area of Aveiro's Lagoon, Portugal’, Sci. Total Environ. 213, 157–163.
Pereiro, I. R., Wasik, A. and Lobinski, R.: 1998, ‘Characterization of multicapillary gas chromatography–microwave-induced plasma atomic emission spectrometry for the expeditious analysis for organometallic compounds’, J. Chromatogr. 795(2), 359–370.
Quevaullier, Ph.: 1999, ‘Certification of methylmercury in sediment: From controversial facts to scientific evidence’, Chemosphere 39(7), 1153–1165.
Ramalhosa, E., Río Segade, S., Pereira, E., Vale, C. and Duarte, A.: 2001, ‘Simple methodology for methylmercury and inorganic mercury determinations by high–performance liquid chromatography-cold vapour atomic fluorescence spectrometry’, Anal. Chim. Acta 448, 135–143.
Rebelo, J. E.: 1994, ‘Ichthyofauna of Ria de Aveiro and the lagunar life cycle of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, Linnaeus, 1758)’, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Aveiro, 180 pp.
Salih, B., Say, R., Denizli, A., Genc, Ö. and Piskin, E.: 1998, ‘Determination of inorganic and organic mercury compounds by capillary gas chromatography coupled with atomic absorption spectrometry after preconcentration on dithizone-anchored poly(ethylene glycol dimethacrylate-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) microbeads’, Anal. Chim. Acta 371(2–3), 177–185.
Ullrich, S. M., Tanton, T. W. and Abdrashitova, S. A.: 2001, ‘Mercury in the aquatic environment: A review of factors affecting methylation’, Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Tech. 31(4), 241–293.
Velado, N. G. O., Pereiro, R. and Medel, A. S.: 1998, ‘Glow discharge atomic emission spectrometry as a detector in gas chromatography for mercury speciation’, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 13(9), 905–909.
Wan, C. C., Chen, C. S. and Jiang, S. J.: 1997, ‘Determination of mercury compounds in water samples by liquid chromatography–inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry with an in situ nebulizer/vapor generator’, J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 7, 683–687.
Wasik, A., Pereiro, I. R., Dietz, C., Szpunar, J. and Lobinski, R.: 1998, ‘Speciation of mercury by ICP-MS after on line capillary cryofocussing and ambient temperature multicapillary gas chromatography’, Anal. Commun. 35, 331–335.
Wiener, J. G., Krabbenhoft, D. P., Heinza, G. H. and Scheuhammer, A. M.: 2002, ‘Ecotoxicology of Mercury’ in D. J. Hoffman et al. (ed.), Handbook of Ecotoxicology, CRC Press, Boca Raton-Florida, pp. 409–463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Válega, M., Abreu, S., Pato, P. et al. Determination of Organic Mercury in Biota, Plants and Contaminated Sediments Using a Thermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometry Technique. Water Air Soil Pollut 174, 223–234 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9100-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-9100-7