Abstract
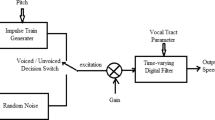
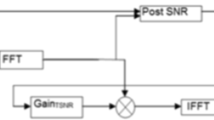
This paper presents a speech enhancement approach based on analysis–synthesis framework. An improved multi-band summary correlogram (MBSC) algorithm is proposed for pitch estimation and voiced/unvoiced (V/UV) detection. The proposed pitch detection algorithm achieves a lower pitch detection error compared with the reference algorithm. The denoising autoencoder (DAE) is applied to enhance the line spectrum frequencies (LSFs). The reconstruction loss could be decreased compare with the swallow model. The proposed approach is evaluated using the perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ) and the experimental results show that the proposed approach improves the performance of speech enhancement compared with the conventional speech enhancement approach. In addition, it could be applied to parametric speech coding even at low bit rate and low signal-noise ratio (SNR) environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boll, S. (1979). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 27(2), 113–120.
Ephraim, Y., & Malah, D. (1984). Speech enhancement using a minimum-mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 32(6), 1109–1121.
Paliwal, K., Schwerin, B., & Wójcicki, K. (2012). Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error short-time spectral modulation magnitude estimator. Speech Communication, 54(2), 282–305.
Martin, R. (2005). Speech enhancement based on minimum mean-square error estimation and super gaussian priors. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(5), 845–856.
Cohen, I. (2002). Optimal speech enhancement under signal presence uncertainty using log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 9(4), 113–116.
Sreenivas, T. V., & Kirnapure, P. (1996). Codebook constrained Wiener filtering for speech enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 4(5), 383–389.
Mohammadiha, N., Martin, R., & Leijon, A. (2013). Spectral domain speech enhancement using HMM state-dependent super-Gaussian priors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 20(3), 253–256.
Xie, F., & Compernolle, D. V. (1994). A family of MLP based nonlinear spectral estimators for noise reduction. In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 53–56). Australia.
Dahl, G. E., Sainath, T. N., Hinton, G. E. (2013). Improving deep neural networks for LVCSR using rectified linear units and dropout. In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 8609–8613). Canada.
Chen, R. F., Chan, C. F., So H. C. (2010). Noise suppression based on an analysis–synthesis approach. In Proc. Eur. Signal Process. Conf. (EUSIPCO) (pp. 1539–1543).
Cheveigne, A., & Kawahara, H. (2002). YIN, a fundamental frequency estimator for speech and music. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 111, 1917–1930.
Camacho, A., & Harris, J. (2008). A sawtooth waveform inspired pitch estimator for speech and music. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 124, 1638–1652.
Rouat, J., Liu, Y., & Morissette, D. (1997). A pitch determination and voiced/unvoiced decision algorithm for noisy speech. Speech Communication, 21, 191–207.
Tan, L. N., Alwan, A. (2011). Noise-robust F0 estimation using SNRweighted summary correlograms from multi-band comb filters. In Proc. IEEE ICASSP (pp. 4464–4467).
Chen, R. F., Chan, C. F., & So, H. C. (2012). Model-based speech enhancement with improved spectral envelope estimation via dynamics tracking. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 20(4), 1324–1336.
Toda T., Saruwatari, H., Shikano, K. (2001). Voice conversion algorithm based on gaussian mixture model with dynamic frequency warping of straight spectrum. In Proc of ICASSP (pp. 941–944).
Park, K. Y., & Kim, H. S. (2000). Narrowband to wideband conversion of speech using GMM based transformation. Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, 4, 1843–1846.
Hinton, G. E., Osindero, S., & Teh, Y. W. (2006). A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 18(7), 1527–1554.
Bengio, Y., Yao, L., Alain, G., et al. (2013). Generalized denoising autoencoders as generative models. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp: 899–907). USA.
Tan, L. N., Alwan, A. (2013). Multi-band summary correlogram-based pitch detection for noisy speech. In Speech communication (pp. 841–856).
Ephraim, Y., & Malah, D. (1985). Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 33(2), 443–445.
Supplee, L. M., Cohn, R. P., Collura, J. S., McCree, A. V. (1997). MELP: the new federal standard at 2400bps. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (1591–1594). Germany.
Garofolo, J. S. (1993). TIMIT: Acoustic-phonetic Continuous Speech Corpus, Linguistic Data Consortium.
Rice University, NOISEX-92 Database, [Online] Available: http://spib.rice.edu/spib/select noise.html.
Chu, W., Alwan, A. (2009). reducing F0 frame error of F0 tracking algorithm under noisy condition with an unvoiced/voiced classification frontend. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (3969-3972). Germany
Jabloun, F., & Champagne, B. (2003). Incorporating the human hearing properties in the signal subspace approach for speech enhancement. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 11(6), 700–708.
Rix, A. W., Beerends, J. G., Hollier, M. P., et al. (2001). Perceptual evaluation of speech quality (PESQ)-a new method for speech quality assessment of telephone networks and codecs. In Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 749–752). USA.
Talkin, D. (1995). Speech Coding and Synthesis. Elsevier (pp. 497–518).
Kotnik, B., Hoge, H., Kacic, Z. (2006). Evaluation of Pitch Detection Algorithms in Adverse Conditions. Proc. 3rd International Conference on Speech Prosody (pp. 149–152). Dresden, Germany.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National High-Tech Research and Development Program of China(863 Program) (No.2015AA016305), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No.61425017, No.61403386, No.61305003, No.61332017, No.61375027, No.61273288, No.61233009, No.61203258), the Major Program for the National Social Science Fund of China (13&ZD189) and the Integration and application of basic science data in Chinese information processing field (XXH12504-1-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Tao, J., Wen, Z. et al. Speech Enhancement Based on Analysis–Synthesis Framework with Improved Parameter Domain Enhancement. J Sign Process Syst 82, 141–150 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1025-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1025-1