Abstract
Background
Biochemical recurrence (BCR), or an elevation in prostate-specific antigen in men after treatment for localized prostate cancer, is an early indication of clinical progression, distant metastases, and mortality. Correlations have also recently been established between diabetes and the incidence and mortality of prostate cancer. However, it remains unknown whether diabetes may predict BCR.
Methods
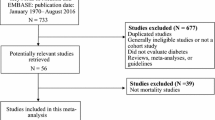
We performed a meta-analysis of published articles to investigate the prognostic value of diabetes for BCR in prostate cancer. Eight studies and 11,923 patients were included in our meta-analysis. The relative risk (RR) and its 95 % confidence interval (CI) were calculated.
Results
We found no apparent association between diabetes and BCR (adjusted RR 1.04; 95 % CI 0.87–1.22).
Conclusions
The evidence of this meta-analysis indicates that diabetes is not a predictor of risk of BCR in patients with prostate cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O et al (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J et al (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J et al (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300
Meyerhardt JA, Catalano PJ, Haller DG et al (2003) Impact of diabetes mellitus on outcomes in patients with colon cancer. J Clin Oncol 21(3):433–440
Liu H, Xia Y, Cui N (2006) Impact of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer. Med Oncol 23(3):341–346
Caudle AS, Kim HJ, Tepper JE et al (2008) Diabetes mellitus affects response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in the management of rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 15(7):1931–1936
Hwang EC, Kim YJ, Hwang IS et al (2011) Impact of diabetes mellitus on recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Urol 18(11):769–776
Jiralerspong S, Kim ES, Dong W et al (2013) Obesity, diabetes, and survival outcomes in a large cohort of early-stage breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol 24(10):2506–2514
Varlotto J, Medford-Davis LN, Recht A et al (2012) Confirmation of the role of diabetes in the local recurrence of surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 75(3):381–390
Zanders MM, Boll D, van Steenbergen LN et al (2013) Effect of diabetes on endometrial cancer recurrence and survival. Maturitas 74(1):37–43
Bansal D, Bhansali A, Kapil G et al (2013) Type 2 diabetes and risk of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Prostate Cancer Prostat Dis 16(2):151–158
Jian Gang P, Mo L, Lu Y et al (2015) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of prostate cancer: an update and cumulative meta-analysis. Endocr Res 40(1):54–61
Cai H, Xu Z, Xu T et al (2015) Diabetes mellitus is associated with elevated risk of mortality amongst patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of 11 cohort studies. Diabetes/Metab Res Rev 31(4):336–343
Chan JM, Latini DM, Cowan J et al (2005) History of diabetes, clinical features of prostate cancer, and prostate cancer recurrence-data from CaPSURE (United States). Cancer Causes Control 16(7):789–797
Jayachandran J, Aronson WJ, Terris MK et al (2010) Diabetes and outcomes after radical prostatectomy: are results affected by obesity and race? Results from the shared equal-access regional cancer hospital database. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 19(1):9–17
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D et al (2011) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality if nonrandomized studies in meta analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 2011 Mar 19
Patel T, Hruby G, Badani K et al (2010) Clinical outcomes after radical prostatectomy in diabetic patients treated with metformin. Urology 76(5):1240–1244
Spratt DE, Zhang C, Zumsteg ZS et al (2013) Metformin and prostate cancer: reduced development of castration-resistant disease and prostate cancer mortality. Eur Urol 63(4):709–716
Taira AV, Merrick GS, Galbreath RW et al (2014) Metformin is not associated with improved biochemical free survival or cause-specific survival in men with prostate cancer treated with permanent interstitial brachytherapy. J Contemp Brachyther 6(3):254–261
Rieken M, Kluth LA, Xylinas E et al (2014) Association of diabetes mellitus and metformin use with biochemical recurrence in patients treated with radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. World J Urol 32(4):999–1005
Lee H, Kuk H, Byun SS et al (2015) Preoperative glycemic control status as a significant predictor of biochemical recurrence in prostate cancer patients after radical prostatectomy. PLoS One 10(4):e0124761
Jiang Y, Ben Q, Shen H et al (2011) Diabetes mellitus and incidence and mortality of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Eur J Epidemiol 26(11):863–876
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C et al (2004) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 363(9418):1346–1353
Grossmann M, Thomas MC, Panagiotopoulos S et al (2008) Low testosterone levels are common and associated with insulin resistance in men with diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(5):1834–1840
Hwang IC, Park SM, Shin D et al (2015) Metformin association with lower prostate cancer recurrence in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 16(2):595–600
Garber K (2004) Energy boost: the Warburg effect returns in a new theory of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(24):1805–1806
Wu X, Fan Z, Masui H et al (1995) Apoptosis induced by an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody in a human colorectal carcinoma cell line and its delay by insulin. J Clin Investig 95(4):1897–1905
Polychronakos C, Janthly U, Lehoux JG et al (1991) Mitogenic effects of insulin and insulin-like growth factors on PA-III rat prostate adenocarcinoma cells: characterization of the receptors involved. Prostate 19(4):313–321
Lehrer S, Diamond EJ, Stagger S et al (2002) Increased serum insulin associated with increased risk of prostate cancer recurrence. Prostate 50(1):1–3
Saglam K, Aydur E, Yilmaz M et al (2003) Leptin influences cellular differentiation and progression in prostate cancer. J Urol 169(4):1308–1311
Pernot S, Terme M, Voron T et al (2014) Colorectal cancer and immunity: what we know and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 20(14):3738–3750
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Jiru Li for useful discussion and Medjaden Bioscience Limited Company for language services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, Q., Zhu, Y., Liu, H. et al. Diabetes and the risk of biochemical recurrence in patients with treated localized prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 1437–1443 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1316-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1316-x