Abstract
Purpose
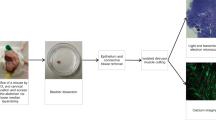
This study examined whether the laser-capture microdissection (LCM) method can achieve separation of urothelial cells from detrusor cells or superficial urothelial cells from intermediate/basal urothelial cells, using α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) and cytokeratin 20 (CK20). In addition, we investigated the changes in expression of muscarinic receptors in laser-captured urothelial and detrusor cells in rats with chronic cystitis.
Methods
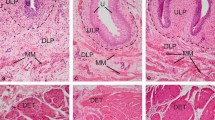
Female SD rats were injected with cyclophosphamide (75 mg/kg) intraperitoneally at day 1, 4, 7 and 10 to induce chronic cystitis. Saline was injected in the same protocol for controls. Bladder specimens were cut at 8 μm thickness, fixed in 70 % ethanol and lightly stained by hematoxylin and eosin, and then superficial urothelium, intermediate/basal urothelium and detrusor muscles were laser-captured separately. Real-time PCR was performed to examine expressions of α-SMA, CK20, muscarinic 2 receptors (M2R) and muscarinic 3 receptors (M3R).
Results
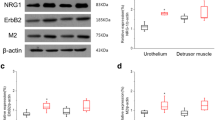
The expression of α-SMA mRNA in detrusor muscle cells was 200 times higher than that in urothelial cells in controls. CK20 mRNA expression in apical urothelial cells was 55 times more than that in detrusor muscle and four times more than that in intermediate/basal urothelial cells. Expressions of M2R and M3R mRNA were increased in urothelial cells and decreased in detrusor muscles following chronic cystitis.
Conclusions
The LCM could be useful for tissue collection of detrusor muscle and different layers of urothelial cells with minimal contamination of other cell types, and cell type-specific changes in molecular expression could accurately be analyzed. Increased expression of urothelial MR might enhance urothelial–afferent interactions to induce bladder overactivity/pain conditions associated with bladder inflammation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Birder LA (2010) Urothelial signaling. Auton Neurosci 153(1–2):33–40
Kim JC, Yoo JS, Park EY, Hong SH, Seo SI, Hwang TK (2008) Muscarinic and purinergic receptor expression in the urothelium of rats with detrusor overactivity induced by bladder outlet obstruction. BJU Int 101(3):371–375
Pradidarcheep W, Labruyere WT, Dabhoiwala NF, Lamers WH (2008) Lack of specificity of commercially available antisera: better specifications needed. J Histochem Cytochem 56(12):1099–1111
Jositsch G, Papadakis T, Haberberger RV, Wolff M, Wess J, Kummer W (2009) Suitability of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies for immunohistochemistry evaluated on tissue sections of receptor gene-deficient mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 379(4):389–395
Bonner RF, Emmert-Buck M, Cole K, Pohida T, Chuaqui R, Goldstein S et al (1997) Laser capture microdissection: molecular analysis of tissue. Science 278(5342):1481–1483
Liu HT, Kuo HC (2007) Increased expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily 1 in the bladder predicts the response to intravesical instillations of resiniferatoxin in patients with refractory idiopathic detrusor overactivity. BJU Int 100(5):1086–1090
Zheng XY, Hou CL, Chen AM, Li JF, Xu Z, Wang JH (2008) Optimal timing of operation for repairing atonic bladder after medullary cone injury: an experimental study in rats. Spinal Cord 46(8):574–581
Romih R, Veranic P, Jezernik K (2002) Appraisal of differentiation markers in urothelial cells. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 10(4):339–343
Kullmann FA, Artim DE, Birder LA, de Groat WC (2008) Activation of muscarinic receptors in rat bladder sensory pathways alters reflex bladder activity. J Neurosci 28(8):1977–1987
Matsumoto Y, Miyazato M, Furuta A, Torimoto K, Hirao Y, Chancellor MB et al (2010) Differential roles of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptor subtypes in modulation of bladder afferent activity in rats. Urology 75(4):862–867
Tong YC, Cheng JT, Hsu CT (2006) Alterations of M(2)-muscarinic receptor protein and mRNA expression in the urothelium and muscle layer of the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat urinary bladder. Neurosci Lett 406(3):216–221
Cheng JT, Yu BC, Tong YC (2007) Changes of M3-muscarinic receptor protein and mRNA expressions in the bladder urothelium and muscle layer of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 423(1):1–5
Dugan C, Malley S, Arms L, May V, Vizzard MA (2014) Role of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Activation in Micturition Reflexes in Cyclophosphamide (CYP)-Induced Cystitis in Female Rats. J Mol Neurosci 54(3):360–369
Yoshimura N, de Groat WC (1999) Increased excitability of afferent neurons innervating rat urinary bladder after chronic bladder inflammation. J Neurosci 19(11):4644–4653
Vizzard MA, Erdman SL, de Groat WC (1996) Increased expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in bladder afferent pathways following chronic bladder irritation. J Comp Neurol 370(2):191–202
O’Malley KJ, Dhir R, Nelson JB, Bost J, Lin Y, Wang Z (2009) The expression of androgen-responsive genes is up-regulated in the epithelia of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 69(16):1716–1723
Kvamme BO, Skern R, Frost P, Nilsen F (2004) Molecular characterisation of five trypsin-like peptidase transcripts from the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) intestine. Int J Parasitol 34(7):823–832
Espina V, Wulfkuhle JD, Coukos G, Geho DH, Petricoin EF 3rd, Liotta LA et al (2006) Laser-capture microdissection. Nat Protoc 1(2):586–603
Bschleipfer T, Schukowski K, Weidner W, Grando SA, Schwantes U, Kummer W et al (2007) Expression and distribution of cholinergic receptors in the human urothelium. Life Sci 80(24–25):2303–2307
Zarghooni S, Wunsch J, Bodenbenner M, Bruggmann D, Grando SA, Schwantes U et al (2007) Expression of muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the mouse urothelium. Life Sci 80(24–25):2308–2313
Mansfield KJ, Liu L, Moore KH, Vaux KJ, Millard RJ, Burcher E (2007) Molecular characterization of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptor expression in bladder from women with refractory idiopathic detrusor overactivity. BJU Int 99(6):1433–1438
Neuhaus J, Schulte-Baukloh H, Stolzenburg JU, di Fenizio PS, Horn LC, Ruffert H et al (2012) Individual receptor profiling as a novel tool to support diagnosis of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC). World J Urol 30(5):693–700
Matsumoto Y, Miyazato M, Yokoyama H, Kita M, Hirao Y, Chancellor MB et al (2012) Role of M2 and M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in activation of bladder afferent pathways in spinal cord injured rats. Urology 79(5):e1184–e1520
Giglio D, Ryberg AT, To K, Delbro DS, Tobin G (2005) Altered muscarinic receptor subtype expression and functional responses in cyclophosphamide induced cystitis in rats. Auton Neurosci 122(1–2):9–20
Grol S, Essers PB, van Koeveringe GA, Martinez-Martinez P, de Vente J, Gillespie JI (2009) M(3) muscarinic receptor expression on suburothelial interstitial cells. BJU Int 104(3):398–405
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (Grant No. DK088836, P01DK093424 and P20DK090919) and the Department of Defense (Grant No. W81XWH-12-1-0565).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest and no commercial affiliation in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugino, Y., O’Malley, K.J., Wang, Z. et al. Laser-capture microdissection for analysis of cell type-specific gene expression of muscarinic receptor subtypes in the rat bladder with cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis. Int Urol Nephrol 47, 637–642 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-0926-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-015-0926-z