Abstract
Purpose
The percentage of patients receiving haemodialysis (HD) treatment and of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) within the elderly population is increasing day by day. Functional dependence, malnutrition, cognitive impairment or depression impairs the quality of life and increases mortality in both diseases. This study aims to assess HD and AD patients through comprehensive geriatric assessment (CGA) and compare their results.
Method
A total of 579 patients (121 HD, 188 AD patients and 270 control subjects) over the age of 65, who were followed at geriatric and nephrology departments between January 2011 and July 2012, were included in this prospective cross-sectional study. Mini-Mental State Examination, Mini-Nutritional Assessment, Geriatric Depression Scale and basic and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living indexes were applied to all patients. The results obtained were compared among the patient groups.
Results
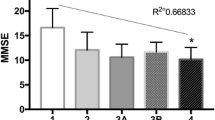
The mean age of the participants was 72.6 ± 8.2. Based on the CGA findings, the results for both groups were considerably different from control group. While depression scores were observed higher in HD patients than in AD patients, cognition, nutrition and functional capacity were mostly affected in AD patients.
Conclusion
The management of geriatric HD patients is substantially complex. Depression, cognitive impairment and decrease in functional capacity can often be overlooked, so findings may be ascribed to underlying kidney impairment. Therefore, comprehensive geriatric assessment should be regularly performed in HD patients in order to detect problems at an early stage, to take necessary preventative measures, to initiate treatment as soon as possible and to enhance quality of life.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowling CB, Muntner P (2012) Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease among older adults: a focus on the oldest old. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 67(12):1379–1386
Canaud B, Tong L, Tentori F, Akiba T, Karaboyas A, Gillespie B, Akizawa T, Pisoni RL, Bommer J, Port FK (2011) Clinical practices and outcomes in elderly hemodialysis patients: results from the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study (DOPPS). Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(7):1651–1662
Süleymanlar G, Utaş C, Arinsoy T, Ateş K, Altun B, Altiparmak MR, Ecder T, Yilmaz ME, Çamsari T, Başçi A, Odabas AR, Serdengeçti K (2011) A population-based survey of chronic REnal disease in Turkey—the CREDIT study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:1862–1871
Parker TF (2012) The economic burden of geriatric ESRD. Semin Dial 25(6):664–667
Elias MF, Dore GA, Davey A (2013) Kidney disease and cognitive function. Contrib Nephrol 179:42–57
Feng L, Yap KB, Yeoh LY, Ng TP (2012) Kidney function and cognitive and functional decline in elderly adults: findings from the Singapore longitudinal aging study. J Am Geriatr Soc 60(7):1208–1214
De Giorgi A, Fabbian F, Pala M, Mallozzi Menegatti A, Misurati E, Manfredini R (2012) Falls and renal function: a dangerous association. G Ital Nefrol 29(3):293–300
Edalat-Nejad M, Qlich-Khani M (2013) Quality of life and sleep in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 24(3):514–518
Wilhelm-Leen ER, Hall YN K, Tamura M, Chertow GM (2009) Frailty and chronic kidney disease: the third national health and nutrition evaluation survey. Am J Med 122(7):664–671
Saeed Z, Ahmad AM, Shakoor A, Ghafoor F, Kanwal S (2012) Depression in patients on hemodialysis and their caregivers. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 23(5):946–952
Aucella F, Stoico L, Cicchella A, Gesuete A, Greco A, Grandaliano G, Pilotto A (2012) Comprehensive geriatric assessment in the hemodialysis elderly population. J Nephrol 25(Suppl 19):S85–S89
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34(7):939–944
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. Text Revision, Washington DC
Isik AT, Bozoglu E, Eker D (2012) AChE and BuChE inhibition by rivastigmin have no effect on peripheral insulin resistance in elderly patients with alzheimer disease. J Nutr Health Aging 16(2):139–141
Gillette-Guyonnet S, Lauque S, Ousset PJ (2005) Nutrition and Alzheimer’s disease. Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil 3(Suppl 1):S35–S41
Guerin O, Soto ME, Brocker P, Robert PH, Benoit MB, Vellas B, REAL.FR Group (2005) Nutritional status assessment during alzheimer’s disease: results after one year (the REAL French Study Group). J Nutr Health Aging. 9(2):81–84
Kovacs J, Pakaski M, Juhasz A, Feher A, Drotos G, Fazekas CO, Horvath TL, Janka Z, Kalman J (2012) Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition and serum lymphokines in Alzheimer’s disease: friend or foe? Neuropsychopharmacol Hung 14(1):19–27
Dukkipati R, Kopple JD (2009) Causes and prevention of protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney failure. Semin Nephrol 29:39–49
Post JB, Morin KG, Sano BM, Jegede AB, Langhoff E, Spungen AM (2012) Increased presence of cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients in the absence of neurological events. Am J Nephrol 35:120–126
Maurizio B, Manuela A, Di Enrico St, Claudia C, Giovanna L, Luigi T, Fausto R, Graziano O (2011) Mini mental state examination over time in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Psychosom Res 71:50–54
Fazekas G, Fazekas F, Schmidt R, Kapeller P, Offenbacher H, Krejs GJ (1995) Brain MRI findings and cognitive impairment in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis treatment. J Neurol Sci 134(1–2):83–88
Agganis BT, Weiner DE, Giang LM, Scott T, Tighiouart H, Griffith JL, Sarnak MJ (2010) Depression and cognitive function in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 56(4):704–712
Mok WY, Chu LW, Chung CP, Chan NY, Hui SL (2004) The relationship between non-cognitive symptoms and functional impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 19(11):1040–1046
Opara JA (2012) Activities of daily living and quality of life in alzheimer disease. J Med Life 12 5(2):162–167
Choi J, Myung W, Chung JW, Kang HS, Na DL, Kim SY, Lee JH, Han SH, Choi SH, Kim S, Kim S, Carroll BJ, Kim DK (2013) Association between functional impairment, depression, and extrapyramidal signs in neuroleptic-free patients with Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 26(3):144–150
Sood MM, Rigatto C, Bueti J, Jassal V, Miller L, Verrelli M, Bohm C, Mojica J, Roberts D, Komenda P (2011) The role of functional status in discharge to assisted care facilities and in-hospital death among dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis 58(5):804–812
Farrokhi F, Jassal SV (2013) Routine use of an abbreviated 4-item scale to assess dependence in essential activities of daily living amongst elderly hemodialysis patients: a validation study. Int Urol Nephrol 45(1):259–264
Steffens DC, Skoog I, Norton MC, Hart AD, Tschanz JT, Plassman BL, Wyse BW, Welsh-Bohmer KA, Breitner JC (2000) Prevalence of depression and its treatment in an elderly population: the cache county study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57(6):601–607
Gracia-García P, De-la-Cámara C, Santabárbara J, Lopez-Anton R, Quintanilla MA, Ventura T, Marcos G, Campayo A, Saz P, Lyketsos C,Lobo A (2013) Depression and incident alzheimer disease: the impact of disease severity. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 20: S1064-7481(13)00158-9
Nebes RD, Reynolds CF, Boada F, Meltzer CC, Fukui MB, Saxton J, Halligan EM, DeKosky ST (2002) Longitudinal increase in the volume of white matter hyperintensities in late-onset depression. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 17(6):526–530
Boulware LE, Liu Y, Fink NE, Coresh J, Ford DE, Klag MJ, Powe NR (2006) Temporal relation among depression symptoms, cardiovascular disease events, and mortality inend-stage renal disease: contribution of reverse causality. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1(3):496–504
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Turkish Kidney Foundation and Bilal Görçin, MD who followed the HD patients. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Hulya Ellidokuz for her help in statistical evaluation of the study. We would also like to thank Dr. Doğan Kaplan and Rana Tekcan for their help in the English translation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicting interests. This study did not have a sponsor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soysal, P., Isik, A.T., Buyukaydin, B. et al. A comparison of end-stage renal disease and Alzheimer’s disease in the elderly through a comprehensive geriatric assessment. Int Urol Nephrol 46, 1627–1632 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0739-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-014-0739-5