Abstract
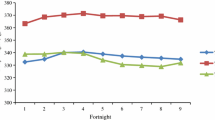
A study was carried out to evaluate the influence of vitamin and trace mineral supplementation on milk production and composition in grazing dairy ewes during the dry season. Ewes (n = 50) were assigned at weaning to blocks and treatments. Ewes were daily conducted (8 h/day) on a pasture based on Italian ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum). At fold, ewes received a basal diet composed by ad libitum oat hay and a definite amount of a pelleted concentrate. Dietary treatments included: (1) the control concentrate containing background of vitamin and trace mineral only, and (2) the experimental concentrate containing the premix supplement (10 g/kg of dry matter). Vitamin and trace mineral supplementation did not affect ewes’ body weight. Milk, fat- and protein-corrected milk, fat percentage, and clotting properties were improved in ewes fed supplemented concentrate. There was a week × treatment interaction (P < 0.05) for yield of milk and corrected milk that was greatest at peak production in ewes fed the premix. Our findings indicate that in grazing dairy ewe, the dietary vitamin and trace mineral supplementation during dry season led to an increase of milk production and quality, with positive improvement in milk clotting aptitude.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC. 2000. Official Methods of Analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 17th ed. Arlington, VA, USA.
Ballet, N., Robert, J.C. and Williams, P.E.V., 2000. Vitamins in forages. In: Givens D.J., Owen E, Axford R.F.E. and Omed H.M. eds. Forage Evaluation in Ruminant Nutrition. CAB International, Wallingford, UK.
Goetsch, A.L., Detweiler, G., Sahlu, T., Hayes, J. and Puchala, R., 2003. Effects of separate offering of forage and concentrate on feed intake and growth of Alpine doelings, Small Ruminant Research, 48, 209–216.
Hemingway, R.G., 2003. The influences of dietary intakes and supplementation with selenium and vitamin E on reproduction disease and reproductive efficiency in cattle and sheep, Veterinary Research Communications, 27, 159-174.
INRA. 1989. Ruminant Nutrition. Recommended Allowances and Feed Tables. INRA, Paris.
Jumba, I.O., Suttle, N.F., Hunter, E.A. and Wandiga, S.O., 1995. Effects of soil origin and mineral composition and herbage species on the mineral composition of forages in the Mount Elgon Region of Kenya. 2. Trace Elements, Tropical Grasslands, 29, 47-52.
Kincaid, R.L., Lefebvre, L.E., Cronrath, J.D., Socha, M.T. and Johnson A.B., 2003. Effect of dietary cobalt supplementation on cobalt metabolism and performance of dairy cattle, Journal of Dairy Science, 86, 1405-1414.
Larsen, H.G., Moksnes, K. and Overnes, G., 1988. Influence of selenium on antibody production in sheep, Research in Veterinary Science, 45, 4-10.
Liu, Z.L., Yang, D.P., Chen, P., Dong, W.X. and Wang, D.M., 2008. Supplementation with selenium and vitamin E improves milk fat depression and fatty acid composition in dairy cows fed fat diet, Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences, 21, 838-844.
Mcdowell, L.R., 1997. Minerals for grazing ruminants in tropical regions. 3 rd Edition. Bulletin. University of Florida, USA.
Morgante, M., Beghelli, D., Pauselli, M., Dall’Ara, P., Capuccella, M. and Ranucci S., 1999. Effect of administration of vitamin E and selenium during the dry period on mammary health an milk cell counts in dairy ewes, Journal of Dairy Science, 82, 623-631.
NRC. 1985. Nutrient Requirements of Sheep, Sixth Revised edition. National Academy of Science, Washington, DC.
Pallauf, J. and Muller, A.S., 2006. Inorganic feed additives, Biology of Growing Animals, 4, 179-249.
Park, Y.W., Juarez, M., Ramos, M. and Haenlein, G.F.W., 2007. Physicochemical characteristics of goat and sheep milk. Small Ruminant Research, 68, 88–113.
Pechova, A., Janstova, B., Misurova, L., Drackova, M., Vorlova, L. and Pavlata, L., 2008. Impact of supplementation of various selenium forms in goats on quality and composition of milk, cheese and yoghurt, Acta Veterinaria Brno, 77, 407-414.
Petrera, F., Calamari, L. and Bertin, G., 2009. Effect of either sodium selenite or Se–yeast supplementation on selenium status and milk characteristics in dairy goats, Small Ruminant Research, 82, 130–138
Pulina, G., Macciotta, N. and Nudda, A., 2005. Milk composition and feeding in the Italian dairy sheep, Italian Journal of Animal Science, 4, 5-14.
Ramirez, R.G., Haenlein, G.F.W. and Nunez-Gonzales, M.A., 2000. Seasonal variation of macro and trace mineral contents in 14 Browse species that grow in northeastern Mexico, Small Ruminant Research, 39, 153-159.
SAS. 2001. SAS/STAT User’s Guide. Statistical Analysis System Inst, Cary, NC.
Tufarelli, V., Dario, M. and Laudadio, V., 2009. Milk yield and composition of lactating Comisana ewes fed total mixed rations containing nitrogen sources with different ruminal degradability, Livestock Science, 122, 349–353.
Tufarelli, V., Lacalandra, G.M., Aiudi, G., Binetti, F. and Laudadio, V., 2011. Influence of feeding level on live body weight and semen characteristics of Sardinian rams reared under intensive conditions, Tropical Animal Health and Production, 43, 339-345.
Tufarelli, V. and Laudadio, V., 2011. Effect of wheat middlings-based total mixed ration on milk production and composition responses of lactating dairy ewes. Journal of Dairy Science, 94, 376-381.
Van Metre, D.C. and Callan, R.J., 2001. Selenium and vitamin E, Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice, 17, 373-402.
Van Soest, P.J., Robertson, J.B. and Lewis, B.A., 1991. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and non-starch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition, Journal of Dairy Science, 74, 3583–3592.
Tufarelli, V., Dario, M. and Laudadio, V., 2009. Milk yield and composition of lactating Comisana ewes fed total mixed rations containing nitrogen sources with different ruminal degradability, Livestock Science, 122, 349–353.
Woodfield, D.R. and Easton, H.S., 2004. Advances in pasture plant breeding for animal productivity and health, New Zealand Veterinary Journal, 52, 300-10.
Zannoni, M. and Annibaldi, S., 1981. Standardization of the renneting ability of milk by Formagraph, Scienza e Tecnologia Lattiero-Casearia, 32,79–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11250-014-0601-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tufarelli, V., Khan, R.U. & Laudadio, V. Vitamin and trace element supplementation in grazing dairy ewe during the dry season: effect on milk yield, composition, and clotting aptitude. Trop Anim Health Prod 43, 955–960 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-011-9789-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-011-9789-1