Abstract
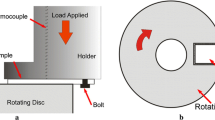
The purpose of this study was to determinate the influence of the molecular crosslinking in the wear resistance of a linear polyethylene (PE) sliding against a rough steel surface. A set of PEs with different degrees of crosslinks were obtained by chemical modification of a PE with varying concentrations of organic peroxide. The amount of gel, molecular weight between crosslinks (M c), crystallinity and Vickers microhardness were determined in the crosslinked PE’s. The tribological performance of the materials was evaluated under dry sliding conditions using a block-on-ring tester. The coefficient of friction and the wear rate were determined in experiments in which a sample of polymer was contacted with the peripheral surface of a steel ring rotating at constant velocity. The wear resistance of the crosslinked materials increases with the amount of gel and when M c decreases. The crosslinked PE showed a wear rate lower than the original PE when the amount of gel was larger than 80 % of the total mass. The coefficient of friction of the PE and crosslinked material was about 0.2 regardless of the normal load applied. The analysis of the worn surfaces by optical and SEM microscopy reveals that the primary mechanism involved in wear is abrasive wear.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chodak, I.: Properties of crosslinked polyolefin-based materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. (1995). doi:10.1016/0079-6700(95)98859-N
Peacock, A.J.: The chemistry of polyethylene. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. (2001). doi:10.1081/MC-100107860
Lazar, M., Rado, R., Rychly, J.: Crosslinking of polyolefins. Adv. Polym. Sci. (1990). doi:10.1007/3-540-52159-3_8
Shen, C., Dumbleton, J.H.: The friction and wear behavior of irradiated very high molecular weight polyethylene. Wear (1974). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(74)90149-5
Stachowiak, G.W., Batchelor, A.W.: Engineering Tribology, 2nd edn. Butterworth Heinemann, Boston (2001)
De Boer, J., Pennings, A.J.: Crosslinking of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene in the melt by means of 2,5-dimethyl-2,5-bis(tert-butyldioxy)-3-hexyne: 2. Crystallization behaviour and mechanical properties. Polymer (1982). doi:10.1016/0032-3861(82)90222-1
Narkis, M., Raiter, I., Shkolnik, S., Eyerer, P., Siegmannz, A.: Structure and tensile behavior of irradiation and peroxide-crosslinked polyethylenes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. (1987). doi:10.1080/00222348708248057
Khonakdar, H.A., Morshedian, J., Wagenknecht, U., Jafari, S.H.: An investigation of chemical crosslinking effect on properties of high-density polyethylene. Polymer (2003). doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(03)00363-X
Pérez, C.J., Cassano, G.A., Vallés, E.M., Failla, M.D., Quinzani, L.M.: Rheological study of linear high density polyethylenes modified with organic peroxide. Polymer (2002). doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(02)00076-9
Pérez, C.J., Cassano, G.A., Vallés, E.M., Quinzani, L.M., Failla, M.D.: Tensile mechanical behavior modified with organic peroxide. Polym. Eng. Sci. (2003). doi:10.1002/pen.10136
McKellop, H., Shen, F.W., Lu, B., Campbell, P., Salovey, R.: Development of an extremely wear-resistant ultra high molecular weight polyethylene for total hip replacements. J. Orthop. Res. (1999). doi:10.1002/jor.1100170203
Kurtz, S.M., Pruitt, L.A., Jewett, C.W., Foulds, J.R., Edidin, A.A.: Radiation and chemical crosslinking promote strain hardening behavior and molecular alignment in ultra high molecular weight polyethylene during multi-axial loading conditions. Biomaterials (1999). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(99)00038-1
Lewis, G.: Properties of crosslinked ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Biomaterials (2001). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(00)00195-2
Gul, R.M.: The effects of peroxide content on the wear behavior, microstructure and mechanical properties of peroxide crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene used in total hip replacement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. (2008). doi:10.1007/s10856-008-3368-7
Yim, C.I., Lee, K.J., Jho, J.Y., Choi, K.: Wear resistance of some modified ultra-high molecular weight polyethylenes and its correlation with tensile properties. Polym. Bull. (1999). doi:10.1007/s002890050486
Muratoglu, O.K., Bragdon, C.R., O’Connor, D.O., Jasty, M., Harris, W.H., Gul, R., et al.: Unified wear model for highly crosslinked ultra-high molecular weight polyethylenes (UHMWPE). Biomaterials (1999). doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(99)00039-3
Rose, R.M., Cimino, W.R., Ellis, E., Crugnola, A.N.: Exploratory investigations on the structure dependence of the wear resistance of polyethylene. Wear (1982). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(82)90048-5
Kampouris, E.M., Andreopoulos, A.G.: The effect of the gel content of crosslinked polyethylene on its physical properties. Eur. Polym. J. (1989). doi:10.1016/0014-3057(89)90240-1
Hendra, P.J., Peacock, A.J., Willis, H.A.: The morphology of linear polyethylenes crosslinked in their melts. The structure of melt crystallized polymers in general. Polymer (1987). doi:10.1016/0032-3861(87)90215-1
Quinn, F.A., Mandelkern, L.: Thermodynamics of crystallization in high polymers: poly-(ethylene). J. Am. Chem. Soc. (1958). doi:10.1021/ja01546a003
Henderson, P.J., Wallace, A.J.: Hardness and creep of cross-linked polyethylene. Polymer (1989). doi:10.1016/0032-3861(89)90251-6
Böhm, H., Betz, S., Ball, A.: The wear resistance of polymers. Tribol. Int. (1990). doi:10.1016/0301-679X(90)90055-T
Peacock, A.J.: Computer aided calculation of crosslinking efficiency. Polym. Commun. 25, 169–171 (1984)
Smedberg, A., Hjertberg, T., Gustafsson, B.: The role of entanglements in network formation in unsaturated low density polyethylene. Polymer (2004). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2004.05.005
Wood-Adams, P.M., Dealy, J.M., DeGroot, A.W., Redwine, O.D.: Effect of molecular structure on the linear viscoelastic behavior of polyethylene. Macromolecules (2000). doi:10.1021/ma991533z
Mandelkern, L.: Crystallization of Polymer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2002)
Kunert, K.A., Soszyfiska, H., Pislewski, N.: Structural investigation of chemically crosslinked low density polyethylene. Polymer (1981). doi:10.1016/0032-3861(81)90237-8
BaltáCalleja, F.J., Fakirov, S.: Microhardness of Polymers. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Simis, K.S., Bistolfi, A., Bellare, A., Pruitt, L.A.: The combined effects of crosslinking and high crystallinity on the microstructural and mechanical properties of ultra high molecular weight polyethylene. Biomaterials (2006). doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.09.033
Flores, A., Ania, F., Baltá-Calleja, F.J.: From the glassy state to ordered polymer structures: a microhardness study. Polymer (2009). doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2008.11.037
Tervoort, T.A., Visjager, J., Smith, P.: On abrasive wear of polyethylene. Macromolecules (2002). doi:10.1021/ma020579g
Anderson, J.C.: High density and ultra-high molecular weight polyethenes: their wear properties and bearing applications. Tribol. Int. (1982). doi:10.1016/0301-679X(82)90111-6
Bahadur, S., Stiglich, A.J.: The wear of high density polyethylene sliding against steel surfaces. Wear (1981). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(81)90021-1
Briscoe, B.J., Sinha, S.K.: Wear of polymers. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. (2002). doi:10.1243/135065002762355325
Unal, H., Sen, U., Mimaroglu, A.: Dry sliding wear characteristics of some industrial polymers against steel counterface. Tribol. Int. (2004). doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2004.03.002
Yim, C.I., Lee, K.J., Jho, J.Y., Choi, K.: Wear resistance of some modified ultra-high molecular weight polyethylenes and its correlation with tensile properties. Polym. Bull. (1999). doi:10.1007/s002890050486
Friedrich, K., Schlarb, A.K.: Tribology of Polymeric Nanocomposites. Academic Press, Elsevier (2008)
Matsubara, M., Watanabe, K.: The wear properties of high density polyethylene irradiated by gamma rays. Wear (1967). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(67)90005-1
Briscoe, B.J., Pogosian, A.K., Tabor, D.: The friction and wear of high density polythene: the action of lead oxide and copper oxide fillers. Wear (1974). doi:10.1016/0043-1648(74)90081-7
Tuckart, W., Molinari, E., Rossit, D., Failla, M.: Friction and wear behavior of irradiated polyethylene sliding against a rough steel surface. Tribol. Lett. (2014). doi:10.1007/s11249-014-0344-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molinari, E.C., Failla, M.D. & Tuckart, W.R. The Effect of Crosslinks on the Sliding Wear of High-Density Polyethylene. Tribol Lett 64, 27 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0763-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0763-y