Abstract
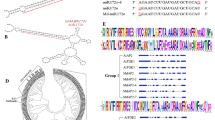
The microRNA miR156 is involved in the regulation of plant growth and development by specifically restricting the transcripts of target genes. In this study, the Md-miR156h gene and its target cDNA fragments, specifically, MdSPL2a-b, MdSPL4, MdSPL6a-g, MdSPL9a-b, MdSPL13a-e and MdSPL15, were isolated from the apple cultivar ‘Gala’. Phylogenetic analysis showed that 18 MdSPL genes were putative targets of miR156. Subsequently, the expression construct p35S:Md-miR156h was created and transformed into Arabidopsis plants. Expression analysis showed that Md-miR156h transcripts and mature miR156 accumulation increased, while its target transcripts AtSPL9 and AtSPL15 were downregulated in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. As a result, the transgenic plants exhibited an extended juvenile phase, increased numbers of leaves, short siliques and the partial abortion of seeds compared with the WT control plants. These results demonstrate that miR156 and its target SPL genes are involved in various developmental processes, especially flower development, and miR156 mediates a conserved post-transcriptional regulation pathway in the apple and Arabidopsis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ARF:
-
Auxin response factor
- SPL:
-
Squamosa promoter binding protein-like protein
- MRE:
-
MiRNA-responsive element
- LFY:
-
LEAFY
- FUL:
-
FRUITFULL
- AP1:
-
APETALA1
- RT:
-
Reverse transcriptase
- EST:
-
Expressed sequence tag
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower mosaic virus
- WT:
-
Wild type
- IPA1:
-
Ideal plant architecture 1
- WFP:
-
WEALTHY FARMER′S PANICLE
References
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Baurle I, Dean C (2006) The timing of developmental transitions in plants. Cell 125(4):655–664
Cardon GH, Hohmann S, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P (1997) Functional analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana SBP-box gene SPL3: a novel gene involved in the floral transition. Plant J 12:367–377
Cardon G, Hohmann S, Klein J, Nettesheim K, Saedler H, Huijser P (1999) Molecular characterisation of the Arabidopsis SBP-box genes. Gene 237:91–104
Chen CF, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou ZH, Lee DH, Nguyen JT et al (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33:179–187
Chen XB, Zhang ZL, Liu DM, Zhang K, Li AL, Mao L (2010) SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like transcription factors: star players for plant growth and development. J Integr Plant Biol 52:946–951
Chuck G, Cigan AM, Saeteurn K, Hake S (2007) The heterochronic maize mutant Corngrass1 results from overexpression of a tandem microRNA. Nat Genet 39:544–549
Fornara F, Coupland G (2009) Plant phase transitions make a SPLash. Cell 138:625–626
Gandikota M, Birkenbihl RP, Hohmann S, Cardon GH, Saedler H, Huijser P (2007) The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 3′ UTR of the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J 49:683–693
Gleave AP, Ampomah-Dwamena CA, Berthold S, Dejnoprat S, Karunairetnam S, Nain B et al (2008) Identification and characterization of primary microRNAs from apple (Malus domestica cv. Royal Gala). Tree Genet Genomes 4:343–358
Guo AY, Zhu QH, Gu X, Ge S, Yang J, Luo J (2008) Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of the plant specific SBP-box transcription factor family. Gene 418:1–8
Jiao YQ, Wang YH, Xue DW, Wang J, Yan MX, Liu GF et al (2010) Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat Genet 42:541–544
Kasschau KD, Xie Z, Allen E, Llave C, Chapman EJ, Krizan KA et al (2003) P1/HC-Pro, a viral suppressor of RNA silencing, interferes with Arabidopsis development and miRNA function. Dev Cell 4:205–217
Klein J, Saedler H, Huijser P (1996) A new family of DNA binding proteins includes putative transcriptional regulators of the Antirrhinum majus floral meristem identity gene SQUAMOSA. Mol Gen Genet 250:7–16
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Manning K, Tor M, Poole M, Hong Y, Thompson AJ, King GJ et al (2006) A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat Genet 38:948–952
Martin RC, Liu PP, Goloviznina NA, Nonogaki H (2010) microRNA, seeds, and Darwin?: diverse function of miRNA in seed biology and plant responses to stress. J Exp Bot 61:2229–2234
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song XJ, Ito M, Asano K et al (2010) OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet 42:545–549
Moreno MA, Harper LC, Krueger RW, Dellaporta SL, Freeling M (1997) Liguleless1 encodes a nuclear-localized protein required for induction of ligules and auricles during maize leaf organogenesis. Genes Dev 11:616–628
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Poethig RS (2010) The past, present, and future of vegetative phase change. Plant Physiol 154(2):541–544
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Riechmann JL, Heard J, Martin G, Reuber L, Jiang CZ, Keddie J et al (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110
Röbbelen G (1957) Über Heterophyllie bei Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Ber Dtsch Bot Ges 7:39–44
Ruth CM, Masashi A, Po-Pu L, Jessica RK, Jennifer LC, Wioletta EP et al (2010) The microRNA156 and microRNA172 gene regulation cascades at post-germinative stages in Arabidopsis. Seed Sci Res 20:79–87
Schwab R, Palatnik JF, Riester M, Schommer C, Schmid M, Weigel D (2005) Specific effects of microRNA on the plant transcriptome. Dev Cell 8:517–527
Schwarz S, Grande AV, Bujdoso N, Saedler H, Huijser P (2008) The microRNA regulated SBP-box genes SPL9 and SPL15 control shoot maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 67:183–195
Shikata M, Koyama T, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M (2009) Arabidopsis SBP-box genes SPL10, SPL11 and SPL2 control morphological change in association with shoot maturation in the reproductive phase. Plant Cell Physiol 50:2133–2145
Slack FJ, Basson M, Liu Z, Ambros V, Horvitz HR, Ruv-kun G (2000) The lin-41 RBCC gene acts in the C. elegans heterochronic pathway between the let-7 regulatory RNA and the LIN-29 transcription factor. Mol Cell 5:659–669
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Unte US, Sorensen AM, Pesaresi P, Gandikota M, Leister D, Saedler H, Huijser P (2003) SPL8, an SBP-box gene that affects pollen sac development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:1009–1019
Usami T, Horiguchi G, Yano S, Tsukaya H (2009) The more and smaller cells mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana identify novel roles for SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE genes in the control of heteroblasty. Development 136:955–964
Vazquez F, Gasciolli V, Crété P, Vaucheret H (2004) The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing. Curr Biol 14:346–351
Wang JW, Wang LJ, Mao YB, Cai WJ, Xue HW, Chen XY (2005) Control of root cap formation by microRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2204–2216
Wang JW, Schwab R, Czech B, Mica E, Weigel D (2008) Dual effects of miR156-targeted SPL genes and CYP78A5/KLUH on plastochron length and organ size in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 20:1231–1243
Wang JW, Czech B, Weigel D (2009) miR156-Regulated SPL transcription factors define an endogenous flowering pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 138:738–749
Wang JW, Park MY, Wang LJ, Koo Y, Chen XY et al (2011) MiRNA control of vegetative phase change in trees. PLoS Genet 7(2):e1002012
Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G (1993) Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75:855–862
Wu G, Poethig RS (2006) Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 133:3539–3547
Wu G, Park MY, Conway SR, Wang JW, Weigel D, Poethig RS (2009) The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 138:750–759
Xie KB, Wu CQ, Xiong LZ (2006) Genomic organization, differential expression and interaction of SQUAMOSA Promoter-Binding-Like transcription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol 142:280–293
Xing SP, Salinas M, Höhmann S, Berndtgen R, Huijsera P (2010) miR156-Targeted and Nontargeted SBP-Box Transcription Factors Act in Concert to Secure Male Fertility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:3935–3950
Yamaguchi A, Wu MF, Yang L, Wu G, Poethig RS, Wagner D (2009) The microRNA-regulated SBP-Box transcription factor SPL3 Is a direct upstream activator of LEAFY, FRUITFULL and APETALA1. Dev Cell 17:268–278
Yang Z, Wan X, Gu S, Hu Z, Xu H, Xu C (2008) Comparative study of SBP-box gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Gene 407:1–11
Yang L, Conway SR, Poethig RS (2011) Vegetative phase change is mediated by a leaf-derived signal that represses the transcription of miR156. Development 138:245–249
Yu HP, Song CG, Jia QD, Wang C, Li F, Nicholas KK et al (2010) Computational identification of microRNAs in apple expressed sequence tags and validation of their precise sequences by miR-RACE. Physiol Plant 141:56–70
Zhang Y, Schwarz S, Saedler H, Huijser P (2007) SPL8, a local regulator in a subset of gibberellin-mediated developmental processes in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 63:429–443
Zhang S, Zhou J, Han S, Yang W, Li W, Wei H et al (2010) Four abiotic stress-induced miRNA families differentially regulated in the embryogenic and non-embryogenic callus tissues of Larix leptolepis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 398:355–360
Zhang XH, Zou Z, Zhang JH, Zhang YY, Han QQ, Hu TX et al (2011) Over-expression of sly-miR156a in tomato results in multiple vegetative and reproductive trait alterations and partial phenocopy of the sft mutant. FEBS Lett 585:435–439
Zhu JK (2008) Reconstituting plant miRNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 29:9851–9852
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NSFC (31171946), PCSIRT (IRT1155) and 948 Project from Ministry of Agriculture of China (2011-G21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chao Sun and Qiang Zhao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Zhao, Q., Liu, D. et al. Ectopic expression of the apple Md-miRNA156h gene regulates flower and fruit development in Arabidopsis . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 112, 343–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0241-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0241-7