Abstract
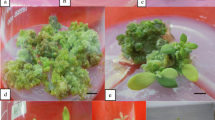
An efficient and reliable micropropagation system for Persian clover (Trifolium resupinatum L.) was developed using different explants and media. Node, hypocotyl and cotyledonary node explants were cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium supplemented with combinations of either 6-benzyladenine (BA) and indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) or BA, Kinetin (KIN) and IBA. Direct multiple shoots developed within 6 weeks in all explants in most media tested. The best shoot multiplication capacity was obtained from cotyledonary node explants on MS medium containing 7.1 μM BA and 1 μM IBA or 14.1 μM BA and 1 μM IBA. Elongated shoots were rooted on either MS medium alone or combination with different concentrations of indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA). High rooting was achieved in half strength MS medium containing 8 μM IBA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
6-benzyladenine
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
- IBA:
-
indole-3-butyric acid
- KIN:
-
Kinetin
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog (1962) medium
- NAA:
-
α-naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Brown DCW, Finstad KI & Watson EM (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in Herbaceus Dicots. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in Plants Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture. (pp. 345–416) Kluwer Academic Publisher
N Komalavalli MV Rao (1997) ArticleTitleIn vitro micropropagation of Gymnema elegans W&A, a rare medicinal plant Indian J. Exp. Biol. 35 1088–1092
N Komalavalli V Rao (2000) ArticleTitleIn vitro micropropagation of Gymnema sylvestre–A multipurpose medicinal plant Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 61 97–105
T Murashige F Skoog (1962) ArticleTitleA revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures Physiol. Plant. 15 473–497
S Özcan (1995) ArticleTitleIn vitro micropropagation of pea (Pisum sativum L.) from immature embryos Tr. J. Bot. 19 427–429
M Özgen S Özcan CS Sevimay C Sancak M Yı ıldı ız (1998) ArticleTitleHigh frequency adventitious shoot regeneration in sainfoin Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 52 205–208
F Pupilli F Damiani M Pezzotti S Arcioni (1989) ArticleTitlePlant regeneration from callus protoplast of Onobrycis viciifolia scop Plant Sci. 63 87–94
GW Snedecor WG Cochran (1967) Statistical Methods. The Iowa State University Press Iowa, USA
H Wang FB Holl (1988) ArticleTitleIn vitro culture and incidence of somaclonal variation in regenerated plants of Trifolium pratense L. Plant Sci. 55 159–167
T Yamada S Higuhi (1990) ArticleTitleIn vitro culture of genus Trifolium germplasm and plant regeneration J. Jap. Soc. Grassland Sci. 36 47–54
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uranbey, S., Sevimay, C.S. & Özcan, S. Development of high frequency multiple shoot formation in Persian clover (Trifolium resupinatum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 80, 229–232 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-0568-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-0568-9