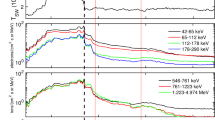
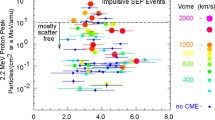
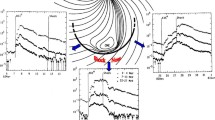
Abstract
Energetic particles constitute an important component of the heliospheric plasma environment. They range from solar energetic particles in the inner heliosphere to the anomalous cosmic rays accelerated at the interface of the heliosphere with the local interstellar medium. Although stochastic acceleration by fluctuating electric fields and processes associated with magnetic reconnection may account for some of the particle populations, the majority are accelerated by the variety of shock waves present in the solar wind. This review focuses on “gradual” solar energetic particle (SEP) events including their energetic storm particle (ESP) phase, which is observed if and when an associated shock wave passes Earth. Gradual SEP events are the intense long-duration events responsible for most space weather disturbances of Earth’s magnetosphere and upper atmosphere. The major characteristics of gradual SEP events are first described including their association with shocks and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), their ion composition, and their energy spectra. In the context of acceleration mechanisms in general, the acceleration mechanism responsible for SEP events, diffusive shock acceleration, is then described in some detail including its predictions for a planar stationary shock, shock modification by the energetic particles, and wave excitation by the accelerating ions. Finally, some complexities of shock acceleration are addressed, which affect the predictive ability of the theory. These include the role of temporal and spatial variations, the distinction between the plasma and wave compression ratios at the shock, the injection of thermal plasma at the shock into the process of shock acceleration, and the nonlinear evolution of ion-excited waves in the vicinity of the shock.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Adriani et al., Observations of the 2006 December 13 and 14 solar particle events in the 80 MeVn-1-3 GeVn-1 range from space with the PAMELA detector. Astrophys. J. 742, 102 (2011)
W.I. Axford, Acceleration of cosmic rays by shock waves, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 17th, vol. 12 (1981), p. 155
W.I. Axford, E. Leer, G. Skadron, The acceleration of cosmic rays by shock waves, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 15th, vol. 11, (1977), p. 132
D. Band et al., Batse observations of gamma ray burst spectra. 1—Spectral diversity. Astrophys. J. 413, 281 (1993)
A.R. Bell, The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 182, 147 (1978)
A.R. Bell, Turbulent amplification of magnetic field and diffusive shock acceleration of cosmic rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 353, 550 (2004)
A.R. Bell, S.G. Lucek, Cosmic ray acceleration to very high energy through the non-linear amplification by cosmic rays of the seed magnetic field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 321, 433 (2001)
R.D. Blandford, J.P. Ostriker, Particle acceleration by astrophysical shocks. Astrophys. J. 221, L29 (1978)
P. Bochsler, E. Möbius, Energetic neutral atoms: an additional source for heliospheric pickup ions. Astrophys. J. 721, L6 (2010)
T.J. Bogdan, M.A. Lee, P. Schneider, Coupled quasi-linear wave damping and stochastic acceleration of pickup ions in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 161 (1991)
C. Bonifazi, G. Moreno, Reflected and diffuse ions backstreaming from the Earth’s bow shock, 2. Origin. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4405 (1981)
H.H. Breneman, E.C. Stone, Solar coronal and photospheric abundances from solar energetic particle measurements. Astrophys. J. 299, L57 (1985)
D. Burgess, E. Möbius, M. Scholer, Ion acceleration at the Earth’s bow shock. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9901-5
M. Bzowski, M. Krolikowska, Are the sungrazing comets the inner source of pickup ions and energetic neutral atoms? Astron. Astrophys. 435, 723 (2005)
H.V. Cane, T.T. von Rosenvinge, C.M.S. Cohen, R.A. Mewaldt, Two components in major solar particle events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 30, 8017 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002GL016580
H.V. Cane, R.A. Mewaldt, C.M.S. Cohen, T.T. von Rosenvinge, Role of flares and shocks in determining solar energetic particle abundances. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A06S90 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011071
P.J. Cargill, L. Vlahos, G. Baumann, J.F. Drake, A. Nordlund, Current fragmentation and particle acceleration in solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9888-y
S.V. Chalov, H.J. Fahr, Energetic particles from the outer heliosphere appearing as a secondary pick-up ion component. Astron. Astrophys. 401, L1 (2003)
C.M.S. Cohen et al., New observations of heavy-ion-rich solar particle events from ACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2697 (1999a)
C.M.S. Cohen et al., Inferred charge states of high energy solar particles from the solar isotope spectrometer on ACE. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 149 (1999b)
C.M.S. Cohen et al., Heavy ion abundances and spectra from the large solar energetic particle events of October-November 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S16 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JA011004
R.B. Decker, The modulation of low-energy proton distributions by propagating interplanetary shock waves: a numerical simulation. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4537 (1981)
M.I. Desai et al., Spectral properties of heavy ions associated with the passage of interplanetary shocks at 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 611, 1156 (2004)
M.I. Desai et al., Heavy-ion elemental abundances in large solar energetic particle events and their implications for the seed population. Astrophys. J. 649, 470 (2006a)
M.I. Desai, G.M. Mason, J.E. Mazur, J.R. Dwyer, Solar cycle variations in the composition of the suprathermal heavy-ion population near 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 645, L81 (2006b)
L.O’C. Drury, An introduction to the theory of diffusive shock acceleration of energetic particles in tenuous plasmas. Rep. Prog. Phys. 46, 973 (1983)
L.O’C. Drury, W.I. Axford, D. Summers, Particle acceleration in modified shocks. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 198, 833 (1982)
J.A. Earl, The effect of adiabatic focusing upon charged particle propagation in random magnetic fields. Astrophys. J. 205, 900 (1976)
D. Eichler, A cosmic ray mediated shock in the solar system. Astrophys. J. 247, 1089 (1981)
D.C. Ellison, R. Ramaty, Shock acceleration of electrons and ions in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 298, 400 (1985)
A.G. Emslie et al., Energy partition in two solar flare/CME events. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A10104 (2004). doi:10.1029/2004JA010571
A.G. Emslie, B.R. Dennis, G.D. Holman, H.S. Hudson, Refinements to flare energy estimates: a followup to “Energy partition in two solar flare/CME events” by A.G. Emslie et al. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A11103 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JA011305
A. Falcone et al., Observation of GeV solar energetic particles from the 1997 November 6 event using Milagrito. Astrophys. J. 588, 557 (2003)
E. Fermi, On the origin of the cosmic radiation. Phys. Rev. 75, 1169 (1949)
E. Fermi, Galactic magnetic fields and the origin of cosmic radiation. Astrophys. J. 119, 1 (1954)
L.A. Fisk, G. Gloeckler, Acceleration of suprathermal tails in the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 686, 1466 (2008)
L.A. Fisk, G. Gloeckler, Particle acceleration in the heliosphere: implications for astrophysics. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9899-8
L.A. Fisk, M.A. Lee, Shock acceleration of energetic particles in corotating interaction regions in the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 237, 620 (1980)
V. Florinski, R.B. Decker, J.A. le Roux, G.P. Zank, An energetic-particle-mediated termination shock observed by Voyager 2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L12101 (2009). doi:10.1029/2009GL038423
S.E. Forbush, Three unusual cosmic-ray increases possibly due to charged particles from the Sun. Phys. Rev. 70, 771 (1946)
M.A. Forman, L.O’C. Drury, Time dependent shock acceleration: approximations and exact solutions, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 18th, vol. 2 (1983), p. 267
J. Geiss, G. Gloeckler, L.A. Fisk, R. von Steiger, C+ pickup ions in the heliosphere and their origin. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 23373 (1995)
J. Giacalone, The efficient acceleration of thermal protons by perpendicular shocks. Astrophys. J. 628, L37 (2005)
J. Giacalone, J.R. Jokipii, The transport of cosmic rays across a turbulent magnetic field. Astrophys. J. 520, 204 (1999)
J. Giacalone, J.R. Jokipii, Magnetic field amplification by shocks in turbulent fluids. Astrophys. J. 663, L41 (2007)
J. Giacalone, J.R. Jokipii, Suprathermal ions associated with strong interplanetary shocks, in Particle Acceleration and Transport. AIP Conf. Proc., vol. 1436 (AIP, New York, 2012), p. 130
J. Giacalone, M. Neugebauer, The energy spectrum of energetic particles downstream of turbulent collisionless shocks. Astrophys. J. 673, 629 (2008)
J. Giacalone, J.F. Drake, J.R. Jokipii, The acceleration mechanism of anomalous cosmic rays. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9915-z
G. Gloeckler et al., Acceleration of interstellar pickup ions in the disturbed solar wind observed on Ulysses. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 17637 (1994)
G. Gloeckler et al., Interception of comet Hyakutake’s ion tail at a distance of 500 million kilometres. Nature 404, 576 (2000a)
G. Gloeckler, L.A. Fisk, J. Geiss, N.A. Schwadron, T.H. Zurbuchen, Elemental composition of the inner source pickup ions. J. Geophys. Res. 105, 7459 (2000b)
G. Gloeckler et al., Sources, injection and acceleration of heliospheric ion populations, in Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles Observed the Heliosphere: ACE 2000 Symposium, ed. by R.A. Mewaldt et al., AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 528 (AIP, New York, 2000c), p. 221
N. Gopalswamy, Coronal mass ejections of Solar Cycle 23. J. Astrophys. Astron. 27, 243 (2006)
N. Gopalswamy et al., Interacting coronal mass ejections and solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 572, L103 (2002)
N. Gopalswamy, S. Yashiro, S. Krucker, G. Stenborg, R.A. Howard, Intensity variation of large solar energetic particle events associated with coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. 109, A12105 (2004). doi:10.1029/2004JA010602
N. Gopalswamy, H. Xie, S. Yashiro, S. Akiyama, P. Mäkelä, I.G. Usoskin, Properties of ground level enhancement events and the associated solar eruptions during Solar Cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9890-4
B.E. Gordon, M.A. Lee, E. Möbius, K.J. Trattner, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at interplanetary traveling shocks and Earth’s bow shock revisited. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 28263 (1999)
T. Hada, C.F. Kennel, T. Terasawa, Excitation of compressional waves and the formation of shocklets in the Earth’s foreshock. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 4423 (1987)
E.A. Helder, J. Vink, A.M. Bykov, Y. Ohira, J.C. Raymond, R. Terrier, Observational signatures of particle acceleration in supernova remnants. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9919-8
M.M. Hoppe, C.T. Russell, L.A. Frank, T.E. Eastman, E.W. Greenstadt, Upstream hydromagnetic waves and their association with backstreaming ion populations—ISEE 1 and 2 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4471 (1981)
P.D. Hudson, Reflection of charged particles by plasma shocks. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 131, 23 (1965)
P.A. Isenberg, A hemispherical model of anisotropic interstellar pickup ions. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 4719 (1997)
J.R. Jokipii, Propagation of cosmic rays in the solar wind. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 9, 27 (1971)
J.R. Jokipii, Rate of energy gain and maximum energy in diffusive shock acceleration. Astrophys. J. 313, 842 (1987)
J.R. Jokipii, M.A. Lee, Compression acceleration in astrophysical plasmas and the production of f(v)∝v −5 spectra in the heliosphere. Astrophys. J. 713, 475 (2010)
S.W. Kahler, The correlation between solar energetic particle peak intensities and speeds of coronal mass ejections: effects of ambient particle intensities and energy spectra. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 20947 (2001)
S.W. Kahler et al., Associations between coronal mass ejections and solar energetic proton events. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 9683 (1984)
C.F. Kennel, F.V. Coroniti, F.L. Scarf, W.A. Livesey, C.T. Russell, E.J. Smith, A test of Lee’s quasi-linear theory of ion acceleration by interplanetary traveling shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 91, 11917 (1986)
B. Klecker, E. Möbius, M.A. Popecki, Ionic charge states of solar energetic particles: a clue to the source. Space Sci. Rev. 130, 273 (2007)
J. Kota, Anomalous cosmic rays at a blunt termination shock, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 30th, vol. 1 (2008), p. 853
G.F. Krymsky, A regular mechanism for the acceleration of charged particles on the front of a shock wave. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 234, 1306 (1977)
H. Kucharek et al., On the source and acceleration of energetic He+: a long-term observation with ACE/SEPICA. J. Geophys. Res. 108(A10), 8040 (2003). doi:10.1029/2003JA009938
J. Kunches (2005). http://umbra.nascom.nasa.gov/SEP/
D. Lario, G.C. Ho, R.B. Decker, E.C. Roelof, M.I. Desai, C.W. Smith, ACE observations of energetic particles associated with transient interplanetary shocks, in Solar Wind Ten. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 679 (AIP, New York, 2003) 640
M.A. Lee, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration upstream of the Earth’s bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. 87, 5063 (1982)
M.A. Lee, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at interplanetary traveling shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 6109 (1983)
M.A. Lee, Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at an evolving coronal/interplanetary shock. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 158, 38 (2005)
M.A. Lee, H.J. Völk, Hydromagnetic waves and cosmic ray diffusion theory. Astrophys. J. 198, 485 (1975)
R.A. Leske et al., Solar isotopic composition as determined using solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 130, 195 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11214-007-9185-3
G. Li, G.P. Zank, Mixed particle acceleration at CME-driven shocks and flares. Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L02101 (2005a). doi:10.1029/2004GL021250
G. Li, G.P. Zank, Multiple CMEs and large gradual SEP events, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 29th, vol. 1 (2005b), p. 173
G. Li, G.P. Zank, W.K.M. Rice, Acceleration and transport of heavy ions at coronal mass ejection-driven shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A06104 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004JA010600
G. Li et al., Shock geometry and spectral breaks in large SEP events. Astrophys. J. 702, 998 (2009)
G. Li, R. Moore, R.A. Mewaldt, L. Zhao, A.W. Labrador, A twin-CME scenario for ground level enhancement events. Space Sci. Rev. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11214-011-9823-7
R.P. Lin, Energy release and particle acceleration in flares: summary and future prospects. Space Sci. Rev. 159, 421 (2011). doi:10.1007/s11214-011-9801-0
C. Lopate, Fifty years of ground level solar particle event observations, in Solar Eruptions and Energetic Particles, ed. by N. Gopalswamy, R.A. Mewaldt, J. Torsti, AGU Monograph Series (AGU, Washington, 2006), p. 283
E.A. Lucek, T.S. Horbury, I. Dandouras, H. Reme, Cluster observations of the Earth’s quasi-parallel bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A07S02 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JA012756
G. Mann, A. Klassen, H. Aurass, H.-T. Classen, Formation and development of shock waves in the solar corona and the near-Sun interplanetary space. Astron. Astrophys. 400, 329 (2003)
G.M. Mason et al., Particle acceleration and sources in the November 1997 solar energetic particle events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 141 (1999a)
G.M. Mason, J.E. Mazur, J.R. Dwyer, 3He enhancements in large solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 525, L133 (1999b)
G.M. Mason et al., Abundances of heavy and ultraheavy ions in 3He-rich solar flares. Astrophys. J. 606, 555 (2004)
S. Masson et al., Acceleration of relativistic protons during the 20 January 2005 flare and CME. Sol. Phys. 257, 305 (2009)
J.E. Mazur, G.M. Mason, M.D. Looper, R.A. Leske, R.A. Mewaldt, Charge states of solar energetic particles using the geomagnetic cutoff technique: SAMPEX measurements in the 6 November 1997 solar particle event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 173 (1999)
D.J. McComas, N.A. Schwadron, An explanation of the Voyager paradox: particle acceleration at a blunt termination shock. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L04102 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005GL025437
K.G. McCracken, H. Moraal, P.H. Stoker, Investigation of the multiple-component structure of the 20 January 2005 cosmic ray ground level enhancement. J. Geophys. Res. 113, A12101 (2008). doi:10.1029/2007JA012829
R.B. McKibben, Azimuthal propogation of low-energy solar-flare protons as observed from spacecraft very widely separated in solar azimuth. J. Geophys. Res. 77, 3957 (1972)
R.A. Mewaldt, Solar energetic particle composition, energy spectra, and space weather. Space Sci. Rev. 124, 303 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11214-006-9091-0
R.A. Mewaldt et al. (eds.), Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles Observed in the Heliosphere: ACE 2000 Symposium. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 528 (2000). Cover picture
R.A. Mewaldt et al., Proton, helium, and electron spectra during the large solar particle events of October-November 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09S18 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JA011038
R.A. Mewaldt, C.M.S. Cohen, G.M. Mason, The source material for large solar energetic particle events, in Solar Eruptions and Energetic Particles, ed. by N. Gopalswamy, R.A. Mewaldt, J. Torsti, AGU Monograph Series, vol. 165 (2006), p. 115
R.A. Mewaldt et al., On the differences in composition between solar energetic particles and solar wind. Space Sci. Rev. 130, 207 (2007)
R.A. Mewaldt et al., How efficient are coronal mass ejections at accelerating solar energetic particles? in Particle Acceleration and Transport in the Heliosphere and Beyond. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1039 (2008), p. 111
R.A. Mewaldt et al., STEREO observations of energetic neutral hydrogen atoms during the 2006 December 5 solar flare. Astrophys. J. 693, L11 (2009)
R.A. Mewaldt et al., Observations and interpretations of energetic neutral hydrogen atoms from the December 5, 2006 solar event, in Twelfth International Solar Wind Conference. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 1216 (AIP, New York, 2010), p. 592
R.A. Mewaldt et al., Energy spectra, composition, and other properties of ground-level events during Solar Cycle 23. Space Sci. Rev. (2012). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9884-2
P.M. Morse, H. Feshbach, Methods of Theoretical Physics (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1953), pp. 865–869
M. Neugebauer, J. Giacalone, Multispacecraft observations of interplanetary shocks: nonplanarity and energetic particles. J. Geophys. Res. 110, A12106 (2005). doi:10.1029/2005JA011380
M. Neugebauer et al., Encounter of the Ulysses spacecraft with the ion tail of Comet McNaught. Astrophys. J. 667, 1262 (2007)
C.K. Ng, D.V. Reames, Focused interplanetary transport of approximately 1 MeV solar energetic protons through self-generated Alfvén waves. Astrophys. J. 424, 1032 (1994)
C.K. Ng, D.V. Reames, A.J. Tylka, Effect of proton-amplified waves on the evolution of solar energetic particle composition in gradual events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2145 (1999)
V. Ontiveros, A. Vourlidas, Quantitative measurements of coronal mass ejection-driven shocks from LASCO observations. Astrophys. J. 693, 267 (2009)
E.N. Parker, The passage of energetic charged particles through interplanetary space. Planet. Space Sci. 13, 9 (1965)
G. Paschmann et al., Characteristics of reflected and diffuse ions upstream from the Earth’s bow shock. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4355 (1981)
V.S. Ptuskin, Cosmic-ray acceleration by long-wave turbulence. Pis’ma Astron. Zh. 14, 599 (1988)
V.S. Ptuskin, Propagation, confinement models, and large-scale dynamical effects of galactic cosmic rays. Space Sci. Rev. 99, 281 (2001)
K.R. Pyle, J.A. Simpson, A. Barnes, J.D. Mihalov, Shock acceleration of nuclei and electrons in the heliosphere beyond 24 AU. Astrophys. J. 282, 107 (1984)
J.C. Raymond, S. Krucker, R.P. Lin, V. Petrosian, Observational aspects of particle acceleration in large solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9897-x
D.V. Reames, Acceleration of energetic particles by shock waves from large solar flares. Astrophys. J. 358, L63 (1990)
D.V. Reames, Coronal abundances determined from energetic particles. Adv. Space Res. 15, 41 (1995)
D.V. Reames, Particle acceleration by CME-driven shock waves, in Proc. Int. Conf. Cosmic Rays 26th. AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 516 (AIP, New York, 2000), pp. 289–300
D.V. Reames, C.K. Ng, Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 504, 1002 (1998)
D.V. Reames, C.K. Ng, Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles on the intensity plateau. Astrophys. J. 723, 1286 (2010)
D.V. Reames et al., Energy spectra of ions accelerated in impulsive and gradual solar events. Astrophys. J. 483, 515 (1997a)
D.V. Reames, S.W. Kahler, C.K. Ng, Spatial and temporal invariance in the spectra of energetic particles in gradual solar events. Astrophys. J. 491, 414 (1997b)
D.V. Reames et al., Late-phase acceleration of energetic ions in corotating interaction regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 2917 (1997c)
E.C. Roelof, Propagation of solar cosmic rays in the interplanetary magnetic field, in Lectures in High-Energy Astrophysics, ed. by H. Ögelman, J.R. Wayland, NASA SP-199 (NASA, Washington, 1969), p. 111
E.T. Sarris, J.A. Van Allen, Effects of interplanetary shock waves on energetic charged particles. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 4157 (1974)
K.M. Schure, A.R. Bell, L. O’C. Drury, A.M. Bykov, Diffusive shock acceleration and magnetic field amplification. Space Sci. Rev. (2012, this issue). doi:10.1007/s11214-012-9871-7
N.A. Schwadron, D.J. McComas, Pickup ions from energetic neutral atoms. Astrophys. J. 712, L157 (2010)
N.A. Schwadron, M.A. Lee, D.J. McComas, Diffusive acceleration at the blunt termination shock. Astrophys. J. 675, 1584 (2008)
S.J. Schwartz, D. Burgess, Quasi-parallel shocks—a patchwork of three-dimensional structures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 373 (1991)
E.C. Stone et al., The advanced composition explorer. Space Sci. Rev. 86, 1 (1998)
B.T. Tsurutani, E.J. Smith, D.E. Jones, Waves observed upstream of interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 88, 5645 (1983)
A.J. Tylka, W.F. Dietrich, A new and comprehensive analysis of proton spectra in ground-level enhanced (GLE) solar particle events, in Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 31st (2009). http://icrc2009.uni.lodz.pl/proc/pdf/icrc0273.pdf
A.J. Tylka, M.A. Lee, A model for spectral and compositional variability at high energies in large, gradual solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 646, 1319 (2006)
A.J. Tylka, D.V. Reames, C.K. Ng, Observations of systematic temporal evolution in elemental composition during gradual solar energetic particle events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 26, 2141 (1999)
A.J. Tylka, P.R. Boberg, R.E. McGuire, C.K. Ng, D.V. Reames, Temporal evolution in the spectra of gradual solar energetic particle events, in Acceleration and Transport of Energetic Particles Observed in the Heliosphere: ACE 2000 Symposium, ed. by R.A. Mewaldt et al., AIP Conference Proceedings, vol. 528 (AIP, New York, 2000), pp. 147–152
A.J. Tylka et al., Evidence for remnant flare suprathermals in the source population of solar energetic particles in the 2000 Bastille Day event. Astrophys. J. 558, L59 (2001)
A.J. Tylka et al., Shock geometry, seed populations, and the origin of variable elemental composition at high energies in large gradual solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 625, 474 (2005)
R. Vainio, On the generation of Alfvén waves by solar energetic particles. Astron. Astrophys. 406, 735 (2003)
P. van Nes, R. Reinhard, T.R. Sanderson, K.-P. Wenzel, R.D. Zwickl, The energy spectrum of 35- to 1600-keV protons associated with interplanetary shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 89, 2122 (1984)
L. Wang, R.P. Lin, S. Krucker, G.M. Mason, A statistical study of solar electron events over one solar cycle. Astrophys. J. (2012, submitted)
M.E. Wiedenbeck et al., How common is energetic 3He in the inner heliosphere? in Solar Wind 10 Proceedings of the Tenth International Solar Wind Conference, ed. by M. Velli, R. Bruno, F. Malara, AIP Conf. Proc., vol. 679 (AIP, New York, 2003), pp. 652–655
G.P. Zank, G. Li, V. Florinski, Q. Hu, D. Lario, C.W. Smith, Particle acceleration at perpendicular shock waves: model and observations. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A06108 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005JA011524
M. Zhang, M.A. Lee, Stochastic acceleration of energetic particles in the heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. (2011). doi:10.1007/s11214-011-9754-3
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the hospitality of the International Space Science Institute, the stimulating program of the Workshop on Particle Acceleration in Cosmic Plasmas, and the patience of Dr. Andre Balogh while awaiting this typescript. The contribution of M.A.L. was supported, in part, by NASA grants NNX08AJ13G, NNX11AO97G and NNX12AB32G. The contribution of R.A.M. was sponsored by NASA under grants NNX8AI11G, NNX06AC21G, and under subcontract SA2715-26309 from UC Berkeley under NASA contract NAS5-03131. The contribution of J.G. was supported, in part, by NASA grants NNX11AO64G and NNX10AF24G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M.A., Mewaldt, R.A. & Giacalone, J. Shock Acceleration of Ions in the Heliosphere. Space Sci Rev 173, 247–281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-012-9932-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-012-9932-y