Abstract
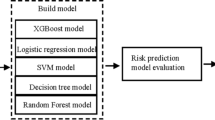
Disingenuously manipulating impact factor is the significant way to harm the fairness of impact factor. That behavior should be banned with effective means. In this paper, data mining techniques are used to solve this problem. Firstly, ten features are collected into feature set for nine normal journals and nine abnormal journals from 2005 to 2014. Then, three types of strong classification methods, k-nearest neighbor, decision tree and support vector machine are adopted to learn the well classification models. Moreover, eight algorithms are run on the data set to find out suitable methods for detecting impact factor manipulation in our experiment. Finally, two excellent algorithms in performance with precisions higher than 85 % are picked out and used to predict new journal samples. According to the results, random forest and one type of support vector machine are relatively more suitable than k-nearest neighbor in this case of detecting abnormal journals. When using those two methods to recognize other 90 journals in the field of nine disciplines from 2007 to 2014, they are verified to be broadly applicable. Unfortunately, four journals are recognized to be manipulated in some years. Therefore, in this paper, two data mining methods are discovered to be intelligent and automatic ways to detect and ban impact factor manipulation for journal managers.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billington, J., & Smith, A. T. (2015). Neural mechanisms for discounting head-roll-induced retinal motion. Journal of Neuroscience, 35(12), 4851–4856.
Breiman, L. (2001). Random forests. Machine Learning, 45(1), 5–32.
Campanario, J. M. (2014). The effect of citations on the significance of decimal places in the computation of journal impact factors. Scientometrics, 99(2), 289–298.
Campanario, J. M. (2015). Providing impact: The distribution of JCR journals according to references they contribute to the 2-year and 5-year journal impact factors. Journal of Informetrics, 9(2), 398–407.
Carrizosa, E., & Morales, D. R. (2013). Supervised classification and mathematical optimization. Computers and Operations Research, 40(1), 150–165.
Chang, C. C., & Lin, C. J. (2011). LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2(3), 27.
Cortes, C., & Vapnik, V. (1995). Suppot-vector networks. Machine Learning, 20(3), 273–297.
Cutler, D. R., Edwards, T. C., Beard, K. H., Cutler, A., & Hess, K. T. (2007). Random forests for classification in ecology. Ecology, 88(11), 2783–2792.
Davis, P. (2012). The emergence of a citation cartel. The Scholarly Kitchen, 10, 15–17.
Diaz-Uriarte, R., & de Andres, S. A. (2006). Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinformatics, 7, 1.
Ding, H., Takigawa, I., Mamitsuka, H., & Zhu, S. F. (2014). Similarity-based machine learning methods for predicting drug-target interactions: A brief review. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 15(5), 734–747.
Falagas, M. E., & Alexiou, V. G. (2008). The top-ten in journal impact factor manipulation. Archivum Immunologiae Et Therapiae Experimentalis, 56(4), 223–226.
Fowler, J. H., & Aksnes, D. W. (2007). Does self-citation pay? Scientometrics, 72(3), 427–437.
Garfield, E. (1955). Citation indexse for science-new dimension in documentation through association of ideas. Science, 122(3159), 108–111.
Garfield, E. (2006). The history and meaning of the journal impact factor. JAMA-Journal of the American Medical Association, 295(1), 90–93.
Gislason, P. O., Benediktsson, J. A., & Sveinsson, J. R. (2006). Random forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognition Letters, 27(4), 294–300.
Haghdoost, A., Zare, M., & Bazrafshan, A. (2014). How variable are the journal impact measures? Online Information Review, 38(6), 723–737.
Han, J., Kamber, M., & Pei, J. (2011). Data mining: Concepts and techniques. New York: Elsevier.
Hemmingsson, A., Mygind, T., Skjennald, A., & Edgren, J. (2002). Manipulation of impact factors by editors of scientific journals. American Journal of Roentgenology, 178(3), 767.
Heneberg, P. (2014). Parallel worlds of citable documents and others: Inflated commissioned opinion articles enhance scientometric indicators. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 65(3), 635–643.
Heneberg, P. (2016). From excessive journal self-cites to citation stacking: Analysis of journal self-citation kinetics in search for journals, which boost their scientometric indicators. PLoS One, 11(4), e0153730.
Henriksson, J., Piasecki, B. P., Lend, K., Burglin, T. R., & Swoboda, P. (2013). Finding ciliary genes: A computational approach. Method in Enzymology, 525, 327–350.
Hsu, C. W., & Lin, C. J. (2002). A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 13(2), 415–425.
Jacso, P. (2009). Five-year impact factor data in the Journal Citation Reports. Online Information Review, 33(3), 603–614.
Jain, A. K., Duin, R. P. W., & Mao, J. C. (2000). Statistical pattern recognition: A review. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 22(1), 4–37.
Khabsa, M., Elmagarmid, A., Ilyas, I., Hammady, H., & Ouzzani, M. (2016). Learning to identify relevant studies for systematic reviews using random forest and external information. Machine Learning, 102(3), 465–482.
Krauss, J. (2007). Journal self-citation rates in ecological sciences. Scientometrics, 73(1), 79–89.
Kuo, W., & Rupe, J. (2007). R-impact: Reliability-based citation impact factor. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 56(3), 366–367.
Lynch, J. G. (2012). Business journals combat coercive citation. Science, 335(6073), 1169.
Martin, B. R. (2016). Editors’ JIF-boosting stratagems-which are appropriate and which not? Research Policy, 45(1), 1–7.
Miller, J. B. (2002). Impact factors and publishing research. Scientist, 16(18), 11.
Mongeon, P., Waltman, L., & Rijcke, S. (2016). https://www.cwts.nl/blog?article=n-q2w2b4.
Seok, J. H., & Kim, J. H. (2015). Scene text recognition using a Hough forest implicit shape model and semi-Markov conditional random fields. Pattern Recognition, 48(11), 3584–3599.
Smith, R. (1997). Journal accused of manipulating impact factor. British Medical Journal, 314(7079), 463.
Strobl, C., Malley, J., & Tutz, G. (2009). An introduction to recursive partitioning: Rationale, application, and characteristics of classification and regression trees, bagging, and random forests. Psychological Methods, 14(4), 323–348.
Svetnik, V., Liaw, A., Tong, C., Culberson, J. C., Sheridan, R. P., & Feuston, B. P. (2003). Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences, 43(6), 1947–1958.
Thombs, B. D., Levis, A. W., Razykov, I., Syamchandra, A., Leentjens, A. F., Levenson, J. L., et al. (2015). Potentially coercive self-citation by peer reviewers: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 78(1), 1–6.
Tort, A. B. L., Targino, Z. H., & Amaral, O. B. (2012). Rising publication delays inflate journal impact factors. PLoS One, 7(12), e53374.
van Nierop, E. (2010). The introduction of the 5-year impact factor: does it benefit statistics journals? Statistica Neerlandica, 64(1), 71–76.
Van Noorden, R., & Tollefson, J. (2013). Brazilian citation scheme outed. Nature, 500(7464), 510–511.
Vens, C., Struyf, J., Schietgat, L., Dzeroski, S., & Blockeel, H. (2008). Decision trees for hierarchical multi-label classification. Machine Learning, 73(2), 185–214.
Wallner, C. (2009). Ban impact factor manipulation. Science, 323(5913), 461.
Wan, X. J., & Liu, F. (2014). Are all literature citations equally important? Automatic citation strength estimation and its applications. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 65(9), 1929–1938.
Wilhite, A. W., & Fong, E. A. (2012). Coercive citation in academic publishing. Science, 335(6068), 542–543.
Wu, X. D., Kumar, V., Quinlan, J. R., Ghosh, J., Yang, Q., Motoda, H., et al. (2008). Top 10 algorithms in data mining. Knowledge and Information Systems, 14(1), 1–37.
Yu, G., & Wang, L. (2007). The self-cited rate of scientific journals and the manipulation of their impact factors. Scientometrics, 73(3), 321–330.
Yu, G., Yang, D. H., & He, H. X. (2011). An automatic recognition method of journal impact factor manipulation. Journal of Information Science, 37(3), 235–245.
Yu, T., Yu, G., & Wang, M.-Y. (2014). Classification method for detecting coercive self-citation in journals. Journal of Informetrics, 8(1), 123–135.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editor and anonymous referees for their constructive comments that substantially helped improve the quality and presentation of this paper. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 71501040, 71473034), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2242014K10020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, DH., Li, X., Sun, X. et al. Detecting impact factor manipulation with data mining techniques. Scientometrics 109, 1989–2005 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2144-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-016-2144-6