Abstract
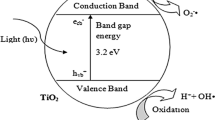
The results for the degradation efficiency of 4-chloronitrobenzene (4-CNB) by various advanced oxidation processes in a batch mode using nano-structured titanium dioxide demonstrated the order of O3/US/TiO2 > US/O3 > O3/TiO2 > O3 > US/TiO2 > US. The utilized TiO2 nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Moreover, all processes obeyed pseudo-first order kinetics. Then, the effect of the main operational conditions including pH, ozone, initial 4-CNB concentration, TiO2 dosage and ultrasonic power on 4-CNB degradation was studied in the coupled O3/US/TiO2 process as the most significant treatment method with a high synergistic effect. The optimal pH and TiO2 dosage were selected to be 9 and 50 mg/L owing to the efficient indirect attack of hydroxyl radicals and less screening effects of TiO2 particles on ultrasonic waves, respectively. By increasing the amount of O3 concentration and ultrasonic power, the degradation of 4-CNB was enhanced due to the more production of reactive oxygen species. However, the opposite trend was observed for 4-CNB concentration because the same amounts of generated oxidizing species under the identical experimental conditions had to degrade more organic pollutants and its degradation intermediates. Eventually, the total organic carbon (TOC) was utilized to monitor the mineralization of 4-CNB in the above-mentioned processes and the same results were obtained with lower rate constants compared to degradation rate constants.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ye, Z. Chen, X. Liu, Y. Ben, J. Shen, J. Hazard. Mater. 167, 1021–1027 (2009)
J.M. Shen, Z. Chen, Z. Xu, X. Li, B. Xu, F. Qi, J. Hazard. Mater. 152, 1325–1331 (2008)
Z. Guo, S. Zheng, Z. Zheng, F. Jiang, W. Hu, L. Ni, Water Res. 39, 1174–1182 (2005)
N. Getoff, Res. Chem. Intermed. 27, 343–358 (2001)
M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, M. Shokri, B. Vahid, Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 1009–1014 (2008)
Y.L. Pang, A.Z. Abdullah, S. Bhatia, Desalination 277, 1–14 (2011)
P. Pichat, L. Cermenati, A. Albini, D. Mas, H. Delprat, C. Guillard, Res. Chem. Intermed. 26, 161–170 (2000)
M.N. Chong, B. Jin, C.W. Chow, C. Saint, Water Res. 44, 2997–3027 (2010)
T.J. Mason, J.P. Lorimer, Applied Sonochemistry: The Uses of Power Ultrasound in Chemistry and Processing, 1st edn. (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002)
M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, M. Shokri, B. Vahid, Glob. Nest J. 10, 8–15 (2008)
M. Kubo, K. Matsuoka, A. Takahashi, N. Shibasaki-Kitakawa, T. Yonemoto, Ultrason. Sonochem. 12, 263–269 (2005)
A. Mahyar, M.A. Behnajady, N. Modirshahla, Photochem. Photobiol. 87, 795–801 (2011)
M. Anpo, Pure Appl. Chem. 72, 1265–1270 (2000)
E. Selli, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4, 6123–6128 (2002)
T. Mousanejad, M. Khosravi, S. Tabatabaii, A.R. Khataee, K. Zare, Res. Chem. Intermed. 40, 711–722 (2014)
Z. He, S. Song, M. Xia, J. Qiu, H. Ying, B. Lü, J. Chen, Chemosphere 69, 191–199 (2007)
Y. Yang, J. Ma, Q. Qin, X. Zhai, J. Molecul, Catal. A 267, 41–48 (2007)
C.D. Vecitis, T. Lesko, A.J. Colussi, M.R. Hoffmann, J. Phys. Chem. 114, 4968–4980 (2010)
X. Xu, H. Shi, D. Wang, J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 6, 553–558 (2005)
K. Thamaphat, P. Limsuwan, B. Ngotawornchai, J. Kasetsart, Nat. Sci. 42, 357–361 (2008)
B. Vahid, A.R. Khataee, Electrochim. Acta 88, 614–620 (2013)
N. Shimizu, C. Ogino, M.F. Dadjour, T. Murata, Ultrason. Sonochem. 14, 184–190 (2007)
J. Wang, Y. Jiang, Z. Zhang, X. Zhang, T. Ma, G. Zhang, Y. Li, Ultrason. Sonochem. 14, 545–551 (2007)
F.J. Beltrán, F.J. Rivas, O. Gimeno, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 80, 973–984 (2005)
M.H. Priya, G. Madras, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 45, 913–921 (2006)
M.H. Priya, G. Madras, J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 179, 256–262 (2006)
A.R. Khataee, A. Akbarpour, B. Vahid, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. E 45, 930–936 (2013)
K. Rajeshwar, M. Osugi, W. Chanmanee, C. Chenthamarakshan, M. Zanoni, P. Kajitvichyanukul, R. Krishnan-Ayer, J. Photochem. Photobiol., C 9, 171–192 (2008)
C.H. Chiou, C.Y. Wu, R.S. Juang, Sep. Purif. Technol. 62, 559–564 (2008)
A. Rodríguez, R. Rosal, J. Perdigón-Melón, M. Mezcua, A. Agüera, M. Hernando, E. García-Calvo, Hdb. Environ. Chem. 5, 127–175 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Tabriz Branch, Islamic Azad University for the financial support of this research, which is based on a research project contract.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vahid, B., Mousanejad, T. & Khataee, A. Sonocatalytic ozonation, with nano-TiO2 as catalyst, for degradation of 4-chloronitrobenzene in aqueous solution. Res Chem Intermed 41, 7029–7042 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1796-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-014-1796-1