Abstract
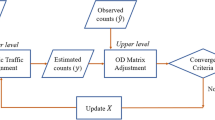
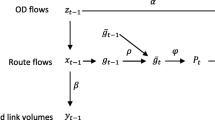
In this paper a special conjugate Bayesian method, for reconstructing and estimating traffic flows, based on α-shifted-Gamma \( \Upgamma (\theta ,\,\lambda ) \) models \( H(\alpha ,\,\theta ,\,\lambda ) \) is given. If the numbers of users traveling through different routes are assumed to be independent \( H(\alpha ,\,\theta ,\,\lambda) \) variables with common \( \lambda,\) the link, origin–destination (OD) and node flows are also \( H(\alpha ,\,\theta ,\,\lambda ) \) random variables. We assume that the main source of information is plate scanning, which permits us to identify, totally or partially, the vehicle route, OD and link flows by scanning their corresponding plate numbers at an adequately selected subset of links. The reconstruction of the sample flows can be done exactly or approximately, depending on the intensity of the plate scanning sampling procedure. To this end a generalized least squares technique is used together with the conservation laws. A Bayesian approach using special conjugate families is proposed that allows us to estimate different traffic flows, such as route, OD-pair, scanned link or counted link flows. A detailed description of how the prior assessment, the sampling, the posterior updating and the obtention of the Bayesian distribution is given. Finally, one example of application is used to illustrate the methods and procedures.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, B.C., Castillo, E., Sarabia, J.M.: Conjugate exponential family priors for exponential family likelihoods. Statistics 25, 71–77 (1993)
Asakura, Y., Hato, E., Kashiwadani, M.: Origin–destination matrices estimation model using automatic vehicle identification data and its application to the Han-Shin expressway network. Transportation 27, 419–438 (2000)
Ashok, K., Ben Akiva, M.: Alternative approaches for real-time estimation and prediction of time-dependent origin–destination flows. Transp. Sci. 34(1), 21–36 (2000)
Bell, M.G.H.: The estimation of an origin–destination matrix from traffic counts. Transp. Sci. 10, 198–217 (1983)
Ben-Akiva, M., Lerman, S.R.: Discrete Choice Analysis: Theory and Application to Travel Demand. MIT Press, Cambridge (1985)
Bianco, L., Confessore, G., Gentili, M.: Combinatorial aspects of the sensor location problem. Ann. Oper. Res. 144, 201–234 (2006)
Cascetta, E.: Estimation of trip matrices from traffic counts and survey data: a generalized least squares estimatorm. Transp. Res. 18B, 289–299 (1984)
Cascetta, E., Nguyen, S.: A unified framework for estimating or updating origin/destination matrices from traffic counts. Transp. Res. 22B, 437–455 (1988)
Castillo, E., Conejo, A., Castillo, C., Mínguez, R., Ortigosa, D.: A perturbation approach to sensitivity analysis in mathematical programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 128(1), 49–74 (2006a)
Castillo, E., Conejo, A., Mínguez, R., Castillo, C.: A closed formula for local sensitivity analysis in mathematical programming. Eng. Optim. 38(1), 93–112 (2006b)
Castillo, E., Conejo, A., Menéndez, J.M., Jiménez, P.: The observability problem in traffic network models. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 23, 208–222 (2008a)
Castillo, E., Jiménez, P., Menéndez, J.M., Conejo, A.: The observability problem in traffic models: algebraic and topological methods. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 9(2), 275–287 (2008b)
Castillo, E., Menéndez, J.M., Jiménez, P.: Trip matrix and path flow reconstruction and estimation based on plate scanning and link observations. Transp. Res. B 42(5), 455–481 (2008c)
Castillo, E., Menéndez, J.M., Sánchez-Cambronero, S.: Predicting traffic flow using Bayesian networks. Transp. Res. B 42(5), 482–509 (2008d)
Castillo, E., Menéndez, J.M., Sánchez-Cambronero, S.: Traffic estimation and optimal counting location without path enumeration using Bayesian Networks. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 23(3), 189–207 (2008e)
Castillo, E., Rivas, A., Jiménez, P., Menéndez, J.M.: Observability in traffic networks. Plate scanning added by counting information. Transportation 39(6), 1301–1333 (2012)
Doblas, J., Benítez, F.G.: An approach to estimating and updating origin–destination matrices based upon traffic counts preserving the prior structure of a survey matrix. Transp. Res. 39B, 565–591 (2005)
Gentili, M., Mirchandani, P.B.: Locating active sensors on traffic networks. Ann. Oper. Res. 136, 229–257 (2005)
Hazelton, M.L.: Inference for origin–destination matrices: estimation, reconstruction and prediction. Transp. Res. B 35(7), 667–676 (2001)
Hazelton, M.L.: Some comments on origin–destination matrix estimation. Transp. Res. 37A, 811–822 (2003)
Hellinga, B., Van Aerde, M.: A statistical analysis of the reliability of using RGS vehicle probes as estimators of dynamic O–D departure rates. IVHS J. 2(1), 21–44 (1994)
Klieter, G.: Bayesian diagnosis in expert systems. Proceedings of the AIJ92, 1992
Lo, H.P., Chan, C.P.: Simultaneous estimation of an origin–destination matrix and link choice proportions using traffic counts. Transp. Res. A 37, 771–788 (2003)
Lo, H.P., Zhang, N., Lam, W.H.K.: Estimation of an origin–destination matrix with random link choice proportions: a statistical approach. Transp. Res. B 30(4), 309–324 (1996)
Maher, M.J.: Inferences on trip matrices from observations on link volumes: a Bayesian statistical approach. Transp. Res. 17B(6), 435–447 (1983)
Maher, M.J., Zhang, X.: Algorithms for the solution of the congested trip matrix estimation problem. In: Transportation and Traffic Theory, Proceedings of the 14th International Symposium on Transportation and Traffic Theory, pp. 445–469. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1999
Maher, M., Zang, X., Van Vliet, D.: A bi-level programming approach for trip matrix estimation and traffic control problems with stochastic user equilibrium link flows. Transp. Res. B 35(1), 23–40 (2001)
Mahmassani, H.S., Sinha, K.: A Bayesian updating of trip generation parameters. J. Transp. Eng. (ASCE). 107 (1981)
Mínguez, R., Sánchez-Cambronero, S., Castillo, E., Jiménez, P.: Optimal traffic plate scanning location in road networks. Transp. Res. B 44, 282–298 (2010)
Praskher, J.N., Bekhor, S.: Route choice models used in the stochastic user equilibrium problem: a review. Transp. Rev. 24, 437–463 (2004)
Spiess, H.: A maximum likelihood model for estimating origin–destinations matrices. Transp. Res. B 21(5), 395–412 (1987)
Sun, S.L., Zhang, C.S., Yu, G.Q.: A Bayesian network approach to traffic flow forecasting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 7(1), 124–132 (2006)
Vardi, Y.: Network tomography: estimating source–destination traffic intensities from link data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 91, 365–377 (1996)
Watling, D.P.: Maximum likelihood estimation of an origin–destination matrix from a partial registration plate survey. Transp. Res. B 28(4), 289–314 (1994)
Yang, H.: Heuristic algorithm for the bi-level origin–destination matrix estimation problem. Transp. Res. 29B, 1–12 (1995)
Yang, H., Sasaki, T., Iida, Y., Asakura, Y.: Estimation of origin–destination matrices from link traffic counts on congested networks. Transp. Res. 26B, 417–434 (1992)
Zhou, X., Mahmassani, H.S.: Dynamic origin–destination demand estimation using automatic vehicle identification data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 7(1), 105–114 (2006)
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the Spanish Ministry of Science and Technology (Projects BIA2005-07802-C02-01 and TRA2010-17818), to the Council of Education and Science of Castilla-La Mancha (A06-016) for partial support of this work, to Prof. Antonio Conejo for providing computer facilities and to prof. M. Maher for his very stimulating discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo, E., Jiménez, P., Menéndez, J.M. et al. A Bayesian method for estimating traffic flows based on plate scanning. Transportation 40, 173–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-012-9443-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-012-9443-4