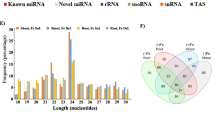
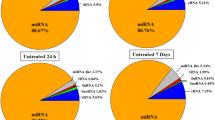
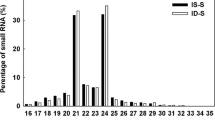
Abstract
Aims
To test if microRNAs are involved in iron (Fe) homeostasis in Oryza sativa.
Methods
Recombinant inbred lines (RILs) of rice with contrasting levels of iron in seeds (high iron line HL, low iron line LL) and parent Swarna were grown in Fe sufficient (+Fe) and deficient (−Fe) environment. miRNAs whose target genes underlie the QTLs mapped for iron concentration (mapped in our previous study) were identified using bioinformatics. The expression analysis of these miRNAs and their targets along with few other miRNAs involved in nutrient homeostasis was done in root and shoot tissue. Real time PCR was used to study the relative expression of miRNAs and their target genes.
Results
Out of nine miRNAs used in this study, 7 miRNAs-miR156, 168, 172, 162, 167, 171, and 398 showed down-regulation under Fe deficiency in root and shoot of high iron line when compared with Fe sufficient condition. Further, most of the miRNAs showed down-regulation while their target genes showed up-regulation under Fe deficiency in roots of all three genotypes (HL, LL and Swarna) suggesting roots are more responsive to Fe deficiency. Important role of miRNAs in iron homeostasis was analyzed by comparing the expression of these miRNAs in HL, LL and Swarna under + Fe and –Fe.
Conclusion
MicroRNAs showed differential expression in + Fe and –Fe environment. Further, their expression is more effectively regulated in root under Fe deficiency. This indicates that miRNAs might be playing regulatory roles in iron homeostasis in rice. This study suggests that Fe deficiency responsive miRNAs are involved in cross talk between other nutrients stress.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Tripura Venkata VGN, Kotla A, Mangrauthia SK, Neelamraju S (2014) Expression pattern of QTL based and other candidate genes in Madhukar x Swarna RILs with contrasting levels of iron and zinc in unpolished rice grains. Gene 546:430–436
Anuradha K, Agarwal S, Rao YV, Rao KV, Viraktamath BC, Sarla N (2012) Mapping QTLs and candidate genes for iron and zinc concentration in unpolished rice of Madhukar x Swarna RILs. Gene 508:233–240
Aukerman MA, Sakai H (2003) Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2-like target genes. Plant Cell 15:2730–2741
Bari R, Pant BD, Stitt M, Scheible WR (2006) Pho2, microRNA399, and phr1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant Physiol 141:988–999
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bashir K, Inoue H, Nagasaka S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Cloning and characterization of deoxymugineic acid synthase genes from graminaceous plants. J Biol Chem 281(43):32395–32402
Ben Amor B, Wirth S, Merchan F, Laporte P, Aubenton-Carafa Y, Hirsch J, Maizel A, Mallory A, Lucas A, Deragon JM, Vaucheret H, Thermes C, Crespi M (2009) Novel long non-protein coding RNAs involved in Arabidopsis differentiation and stress responses. Genome Res 19:57–69
Bernal M, Casero D, Singh V, Wilson GT, Grande A, Yang H, Dodani SC, Pellegrini M, Huijser P, Connolly EL, Merchant SS, Krämer U (2012) Transcriptome sequencing identifies SPL7-regulated copper acquisition genes FRO4/FRO5 and the copper dependence of iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24:738–761
Briat JF, Dubos C, Gaymard F (2015) Iron nutrition, biomass production, and plant product quality. Trends Plant Sci 20(1):33–40
Buckhout TJ, Yang TJW, Schmidt W (2009) Early iron-deficiency-induced transcriptional changes in Arabidopsis roots as revealed by microarray analyses. BMC Genomics 10:147
Chaignon V, Di Malta D, Hinsinger P (2002) Fe-deficiency increases Cu acquisition by wheat cropped in a Cu-contaminated vineyard soil. New Phytol 154:121–130
Chen BX (2004) A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303:2022–2025
Chiou TJ (2007) (2007) The role of microRNAs in sensing nutrient stress. Plant Cell Environ 30:323–332
Chiou TJ, Aung K, Lin SI, Wu CC, Chiang SF, Su C (2006) Regulation of phosphate homeostasis by microRNA in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:412–421
Ciaffi M, Paolacci AR, Celletti S, Catarcione G, Kopriva S, Astolfi S (2013) Transcriptional and physiological changes in the S assimilation pathway due to single or combined S and Fe deprivation in durum wheat (Triticum durum L.) seedlings. J Exp Bot 64:1663–1675
Ding Y, Chen Z, Zhu C (2011) Microarray-based analysis of cadmium-responsive microRNAs in rice (Oryza sativa). J Exp Bot 62:3563–73
Forieri I, Wirtz M, Hell R (2013) Toward new perspectives on the interaction of iron and sulphur metabolism in plants. Front Plant Sci 4:357
Hernandez G, Ramirez M, Valdes-Lopez O, Tesfaye M, Graham MA, Czechowski T, Schlereth A, Wandrey M, Erban A, Cheung F (2007) Phosphorus stress in common bean: root transcript and metabolic responses. Plant Physiol 144:752–767
Hernandez G, Valdes-Lopez O, Ramirez M, Goffard N, Weiller G, Aparicio-Fabre R, Fuentes SI, Erban A, Kopka J, Udvardi MK (2009) Global changes in the transcript and metabolic profiles during symbiotic nitrogen fixation in phosphorus-stressed common bean plants. Plant Physiol 151:1221–1238
Hindt MN, Guerinot ML (2012) Getting a sense for signals: regulation of the plant iron deficiency response. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:1521–1530
Hobert O (2008) Gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Science 319:1785–1786
Hsieh LC, Lin SI, Shih AC, Chen JW, Lin WY, Tseng CY, Li WH, Chiou TJ (2009) Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 151:2120–2132
Huang SQ, Peng J, Qiu CX, Yang ZM (2009) Heavy metal regulated new microRNAs from rice. J Inorg Biochem 103:282–287
Huang SQ, Xiang AL, Che LL, Chen S, Li H, Song JB, Yang ZM (2010) A set of miRNAs from Brassica napus in response to sulphate deficiency and cadmium stress. Plant Biotechnol J 8:887–899
Inoue H, Kobayashi T, Nozoye T, Takahashi M, Kakei Y, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2009) Rice OsYSL15 is an iron regulated iron(III)-deoxymugineic acid transporter expressed in the roots and is essential for iron uptake in early growth of the seedlings. J Biol Chem 284:3470–3479
Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, Wada Y, Watanabe S, Matsuhashi S, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2006) Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+- phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J 45:335–346
Ishimaru Y, Masuda H, Bashir K, Inoue H, Tsukamoto T, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Aoki N, Hirose T, Ohsugi R, Nishizawa NK (2010) Rice metal-nicotianamine transporter, OsYSL2, is required for the long-distance transport of iron and manganese. Plant J 62:379–390
Jones JD, Dangl JL (2006) The plant immune system. Nature 444:323–329
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799
Jung JH, Seo YH, Seo PJ, Reyes JL, Yun J, Chua NH, Park CM (2007) The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2736–2748
Khraiwesh B, Zhu JK, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:137–148
Kobayashi T, Nakayama Y, Itai RN, Nakanishi H, Yoshihara T, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2003) Identification of novel cis-acting elements, IDE1 and IDE2, of the barley IDS2 gene promoter conferring iron-deficiency-inducible, root-specific expression in heterogeneous tobacco plants. Plant J 36:780–793
Kobayashi T, Ogo Y, Itai RN, Nakanishi H, Takahashi M, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2007) The transcription factor IDEF1 regulates the response to and tolerance of iron deficiency in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:19150–19155
Kong WW, Yang ZM (2010) Identification of iron-deficiency responsive microRNA genes and cis-elements in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 48:153–159
Lauter ANM, Peiffer GA, Yin T, Whitham SA, Cook D, Shoemaker RC, Graham MA (2014) Identification of candidate genes involved in early iron deficiency chlorosis signaling in soybean (Glycine max) roots and leaves. BMC Genomics 15:702
Lee S, Persson DP, Hansen TH, Husted S, Schjoerring JK, Kim YS, Jeon US, Kim YK, Kakei Y, Masuda H, Nishizawa NK, An G (2011) Bioavailable zinc in rice seeds is increased by activation tagging of nicotianamine synthase. Plant Biotechnol J 9:865–873
Li WX, Oono Y, Zhu J, He XJ, WuJM IK, Lu XY, Cui X, Jin H, Zhu JK (2008) The Arabidopsis NFYA5 transcription factor is regulated transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally to promote drought resistance. Plant Cell 20:2238–2251
Liang G, Yang F, Yu D (2010) MicroRNA395 mediates regulation of sulfate accumulation and allocation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 62:1046–1057
Lim NC, Freake HC, Bruckner C (2005) Illuminating zinc in biological systems. Chem Eur J 11:38–49
Ling HQ, Bauer P, Bereczky Z, Keller B, Ganal M (2002) The tomato fer gene encoding a bHLH protein controls iron-uptake responses in roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13938–13943
Liu HH, Tian X, Li YJ, Wu CA, Zheng CC (2008) Microarray-based analysis of stress-regulated microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. RNA 14:836–843
Liu Q, Zhang YC, Wang CY, Luo YC, Huang QJ, Chen SY, Zhou H, Qu LH, Chen YQ (2009) Expression analysis of phytohormone-regulated microRNAs in rice, implying their regulation roles in plant hormone signalling. FEBS Lett 583:723–728
Mendoza-Soto AB, Sanchez F, Hernandez G (2012) MicroRNAs as regulators in plant metal toxicity response. Front Plant Sci 3:105
Ogo Y, Itai RN, Nakanishi H, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Mori S, Nishizawa NK (2007) The rice bHLH protein OsIRO2 is an essential regulator of the genes involved in Fe uptake under Fe-deficient conditions. Plant J 51:366–377
Qi YH, Wang SK, Shen CJ, Zhang SN, Chen Y, Xu YX, Liu Y, Wu YR, Jiang DA (2012) OsARF12, a transcription activator of auxin response gene, regulates root elongation and affects iron accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 193:109–120
Sailaja B, Anjum N, Vishnu Prasanth V, Sarla N, Subrahmanyam D, Voleti SR, Viraktamath BC, Mangrauthia SK (2014) Comparative study of susceptible and tolerant genotype reveals efficient recovery and root system contributes to heat stress tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:1228–1240. doi:10.1007/s11105-014-0728-y
Sunkar R, Zhu JK (2004) Novel and stress-regulated microRNAs and other small RNAs from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 16:2001–2019
Sunkar R, Girke T, Jain PK, Zhu JK (2005) Cloning and characterization of microRNAs from rice. Plant Cell 17:1397–1411
Sunkar R, Kapoor A, Zhu JK (2006) Posttranscriptional induction of two Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase genes in Arabidopsis is mediated by down-regulation of miR398 and important for oxidative stress tolerance. Plant Cell 18:2051–2065
Valdés-López O, Yang SS, Aparicio FR, Graham PH, Reyes JL, Vance CP, Hernández G (2010) MicroRNA expression profile in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under nutrient deficiency stresses and manganese toxicity. New Phytol 187:805–818
Vazquez F, Gasciolli V, Crete P, Vaucheret H (2004) The nuclear dsRNA binding protein HYL1 is required for microRNA accumulation and plant development, but not posttranscriptional transgene silencing. Curr Biol 14:346–351
Vigani G, Zocchi G, Bashir K, Philippar K, Briat JF (2013) Signals from chloroplasts and mitochondria for iron homeostasis regulation. Trends Plant Sci 18:305–311
Waters BM, Troupe GC (2012) Natural variation in iron use efficiency and mineral remobilization in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). Plant Soil 352:185–197
Waters BM, McInturf SA, Stein RJ (2012) Rosette iron deficiency transcript and microRNA profiling reveals links between copper and iron homeostasis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 63:5903–18
Welch RM, Norvell WA, Schaefer SC, Shaff JE, Kochian LV (1993) Induction of iron(III) and copper(II) reduction in pea (Pisum sativum L.) roots by Fe and Cu staus: does the root-cell plasmalemma Fe(III)-chelate reductase perform a general role in regulating cation uptake? Planta 190:555–561
Wu L, Zhanga Q, Zhoua H, Nia F, Wua X, Qia Y (2009) Rice MicroRNA effector complexes and targets. Plant Cell 21(11):3421–3435
Xie Z, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2003) Negative feedback regulation of dicer-Like1 in Arabidopsis by microRNA guided mRNA degradation. Curr Biol 13:784–789
Xie FL, Huang SQ, Guo K, Xiang AL, Zhu YY, Nie L, Yang ZM (2007) Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Brassica napus. FEBS Lett 581:1464–1474
Yamasaki H, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Kobayashi Y, Shikanai T, Pilon M (2007) Regulation of Copper Homeostasis by Micro-RNA in Arabidopsis. Biol Chem 282:16369–16378
Zhao B, Ge L, Liang R, Li W, Ruan K, Lin H, Jin Y (2009) Members of miR-169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription Factor. BMC Mol Biol 10:29
Zhao M, Ding H, Zhu JK, Zhang F, Li WX (2011) Involvement of miR169 in the nitrogen-starvation responses in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 190:906–15
Zhao L, Kim Y, Dinh TT, Chen X (2007) MiR172 regulates stem cell fate and defines the inner boundary of APETALA3 and PISTILLATA expression domain in Arabidopsis floral meristems. Plant J 51:840–849
Zhou X, Wang G, Zhang W (2007) UV-B responsive microRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Syst Biol 3:1–10
Zhou ZS, Huang SJ, Yang ZM (2008) Bioinformatic identification and expression analysis of new microRNAs from Medicago truncatula. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:538–542
Zhou X, Sunkar R, Jin H, Zhu JK, Zhang W (2009) Genome-wide identification and analysis of small RNAs originated from natural antisense transcripts in Oryza sativa. Genome Res 19:70–78
Zhou ZS, Zeng HQ, Liu ZP, Yang ZM (2012) Genome-wide identification of Medicago truncatula microRNAs and their targets reveals their different regulation by heavy metal. Plant Cell Environ 35:86–99
Zhu QH, Helliwell CA (2010) Regulation of flowering time and floral patterning by miR172. J Exp Bot 62(2):487–495
Zhu QH, Upadhyaya NM, Gubler F, Helliwell CA (2009) Over-expression of miR172 causes loss of spikelet determinacy and floral organ abnormalities in rice (Oryza sativa). BMC Plant Biol 9:149
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, Govt. of India, Network project on transgenics and functional genomics of crops—project 3019 on rice micronutrients (NPTC/FG/05/2672/33).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jian Feng Ma.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Real time expression of microRNAs in high iron line (HL) and low iron line (LL) rice seedlings under Fe sufficient and deficient condition compared to Swarna as control. Seven days old rice seedlings were transferred to plastic boxes containing nutrient solution for 10 days. For +Fe treatment, Fe-EDTA was present in the nutrient solution but for –Fe treatment, Fe-EDTA was not added. Seedlings were grown in hydroponics in a growth chamber at 30ºC/22ºC (day/night) temperatures with a 12-h-light/12-h-dark regime. Fold difference was calculated from 2−ΔΔCt method. Note: Y axis shows the fold expression and the scale is different in each graph. A- miR156; B- miR162; C- miR167; D- miR168; E- miR169; F- miR171; G- miR172; H- miR395; I- miR398. (JPEG 701 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Real time expression of microRNAs in low iron (LL) rice seedlings under Fe sufficient (A) and deficient (B) condition compared to high iron (HL) as control. Seven days old rice seedlings were transferred to plastic boxes containing nutrient solution for 10 days. For +Fe treatment, Fe-EDTA was present in the nutrient solution but for –Fe treatment, Fe-EDTA was not added. Seedlings were grown in hydroponics in a growth chamber at 30ºC/22ºC (day/night) temperatures with a 12-h-light/12-h-dark regime. Fold difference was calculated from 2−ΔΔCt method. Y axis shows the fold expression and the scale is different in each graph. (JPEG 339 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, S., Mangrauthia, S.K. & Sarla, N. Expression profiling of iron deficiency responsive microRNAs and gene targets in rice seedlings of Madhukar x Swarna recombinant inbred lines with contrasting levels of iron in seeds. Plant Soil 396, 137–150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2561-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2561-y