Abstract
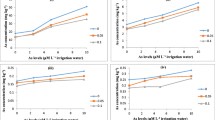
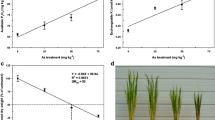
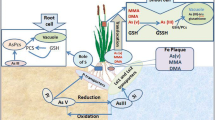
Experiments were conducted with rice (Oryza sativa L.) by adding 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 mg kg-1 of arsenic (As) to soil (with roxarsone and arsanilic acid, presented as As concentrations) at a field with an isolation chamber. The aims were to evaluate the effects of As- (roxarsone or arsanilic acid) contaminated soil on rice agronomic parameters and uptake of As in different plant parts of the rice plant. The results showed that As (roxarsone or arsanilic acid) could significantly reduce plant height, effective tiller number, straw weight and grain yield (P < 0.01). As concentrations in different parts of the plant varied with the growth stages, and behaved similarly. At the maturing stage, the level in different parts peaked in all treatments, with tissue As concentrations showing the pattern: root > leaf > stem > husk > grain. In addition, at the mature stage, the As concentrations in different parts of the rice plant increased with increasing concentrations of roxarsone and arsanilic acid. The highest concentration of As found in grain was 0.82 mg kg-1, which did not exceed the statutory permissible limit for rice grain (1.0 mg As kg-1), and in the leaf and stem it was approximately 6.0 mg kg-1, which was significantly higher than that in the controls. The results showed that rice could accumulate As from contaminated soil (roxarsone or arsanilic acid), which may be transferred to human beings via the food chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abedin MJ, Cresser M, Meharg AA, Feldmann J, Cotter-Howells J (2002a) Arsenic accumulation and metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 36:962–968
Abedin MJ, Feldmann J, Merharg AA (2002c) Uptake kinetics of arsenic species in rice plants. Plant Physiol 128:1120–1128
Abedin MJ, Howells CJ, Meharg AA (2002b) Arsenic uptake and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) irrigated with contaminated water. Plant Soil 240:311–319
Alam ZM, Rahman MM (2003) Accumilation of arsenic in rice plant from arsenic contaminated irrigation water and effect on nutrient content. In: Alam MZ, Rahman MM (eds) Fate of arsenic in the environment. ITN Centre, The Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology and the United Nations University, Bangladesh, pp 131–135
Aschbacher PW, Feil VJ (1991) Fate of [14C] Arsanilic acid in pigs and chickers. J Agric Food Chem 39:146–149
Bednar AJ, Garbarino JR, Ferrer I, Rutherford DW, Wershaw RL, Ranville JF, Wildeman TR (2003) Photodegradation of roxarsone in poultry litter leachates. Sci Total Environ 302:237–245
Bennett JP, Chiriboga E, Coleman J, Waller DM (2000) Heavy metals in wild rice form northern wisconsin. Sci Total Environ 246:261–269
Brown BL, Slaugher AD, Schreiber ME (2005) Controls on roxarsone transport in agricultural watersheds. Appl Geochem 20:123–133
Cullen WR, Reimer KJ (1989) Arsenic speciation in the environment. Chem Rev 89:713–764
Day PR (1965) Method of soil analysis, Part I, first edn. Agron. Monogr. ASA, Madison, WI, pp 552–562
Fran SR, Horton D, Burdette L (1988) Influence of MSMA on straighthead, arsenic uptake and growth response in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Arkansas AES Rep Ser 302:1–12
Liu WJ, Zhu YG, Smith FA, Smith SE (2004) Do phosphorus nutrition and iron plaque alter arsenate (As) uptake by rice seedings in hydroponic culture. New Phytol 162:481–488
Mandal BK, Suzuki KT (2002) Arsenic round the world: a review. Talanta 58:201–235
Marain AR, Masscheleyn PH, Patrick WHJ (1992) The influence of chemical form and concentrations of arsenic on rice growth and tissue arsenic concentrations. Plant Soil 139:175–183
Marin AR, Pezeshki SR, Masscheleyn PH, Choi HS (1993) Effect of dymethylarsenic acid (DMAA) on growth, tissue arsenic, and photosynthesis of rice plants. J Plant Nutr 16:865–880
Meharg AA (2004) Arsenic in rice-understanding a new disaster for South-East Asia. Trends Plant Sci 9:415–417
Meharg AA, Jardine L (2003) Arsenite transport into paddy rice (Oryza sativa) roots. New Phytol 157:39–44
Merharg AA, Rahman M (2003) Arsenic contamination of Bangladesh paddy field soils: implication for rice contribution to arsenic consumption. Sci Total Environ 37:229–234
Milam MR, Marin A, Sedberry JE, Bligh DP, Sheppard R (1988) Effect of water management, arsenic, and zinc on selected agronomic traits and rice grain yield. Northeast Research Station and Macon Ridge Research Station, Baton Rouge, USA. In Annual Progress Report, pp 105–108
Moore PA, Daniel TC, Gilmour JT (1998) Decreasing metal run off from poultry litter with aluminum sulfate. J Environ Qual 27:92–99
Morrison JL (1969) Distribution of arsenic from poultry litter in broiler chickens, soil, and crops. J Agr Food Chem 17:1288–1290
National Food Authority (1993) Australian Food Standard Code: March, 1993. Australian Govt. Pub. Service, Canberra
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1982) Methods of soil analysis, part 2: chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp 539–579
Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ, Williams JR, Unwin RJ (1999) Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales. Bioresour Technol 70:23–31
Onken BM, Hossner LR (1995) Plant uptake and determination of arsenic species in soil solution under flooded conditions. J Environ Qual 24:373–381
Overby LR, Lilian S (1965) Metabolism of arsanilic acid, I. Metabolism stability of doubly labeled arsanilic acid in chickens. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 7:850–854
Rossman TG. (2003) Mechanism of arsenic carcinogenesis an integrated approach. Mut Res 533:37–65
Rutherford DW, Bednar AJ, Garbarino JR, Needham R, Staver KW, Wershaw RL (2003) Environmental fate of roxarsone in poultry litter. Part II. Mobility of arsenic in soils amended with poultry litter. Environ Sci Technol 37:1515–1520
Tsutsumi M (1980) Intensification of arsenic toxicity to paddy rice by hydrogen sulphide and ferrous iron I. Induction of bronzing and iron accumulation in rice by arsenic. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 26:561–569
Woolson EA (1975) The persistence and chemical distribution of arsanilic acid in three soils. J Agric Food Chem 23:677–681
Xie ZM, Huang CY (1998) Control of arsenic toxicity in rice plants grown on an arsenic-polluted paddy soil. Soil Sci Plant Anal 29:2471–2477
Acknowledgements
Project support was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 30130140). The authors are very grateful to Prof. F.A. Liu, X.Q. Zhu and Z.Y. Su for improving the draft manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, FM., Chen, ZL., Zhang, L. et al. Arsenic Uptake and Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) at Different Growth Stages following Soil Incorporation of Roxarsone and Arsanilic Acid. Plant Soil 285, 359–367 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9021-7