Abstract
Purpose
Interferon beta is commonly used as therapeutic in the first line of therapy for multiple sclerosis. However, depending on the product, it induces an antibody response in up to 60% of patients. This study evaluated the impact of therapy related factors like dose, route of administration and administration frequency on the immunogenicity of one of the originator interferon beta drugs (Betaferon®) in an immune tolerant transgenic mouse model.
Methods
Immune tolerant transgenic mice received injections with Betaferon® via different routes, doses and injection frequencies. Anti-drug antibody (ADA) production was measured by ELISA to assess immunogenicity.
Results
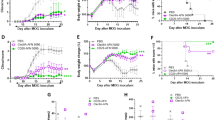
A single injection of Betaferon® was found to be sufficient for the induction of ADAs. The antibody titer was enhanced with increasing dose and treatment frequency. Among the tested administration routes, the intravenous route was the most immunogenic one, which is in contradiction with one of the dogma in immunogenicity research according to which subcutaneous administration is the most immunogenic route. Intramuscular, intraperitoneal and subcutaneous injections resulted in comparable immunogenicity.
Conclusion
This study shows that treatment related factors affect significantly immunogenicity of Betaseron® and therefore substantiate the need for further studies on these factors in patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADAs:
-
anti-drug antibodies
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- IM:
-
intramuscular
- IP:
-
intraperitoneal
- IV:
-
intravenous
- MS:
-
multiple sclerosis
- non-Tg:
-
non-transgenic
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PEG:
-
poly(ethylene glycol)
- rhIFNβ:
-
recombinant human interferon beta
- SC:
-
subcutaneous
- Tg:
-
transgenic
- TNFα:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
References
Paty D, Li DK. Interferon beta-1b is effective in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. II. MRI analysis results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. UBC MS/MRI Study Group and the IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology. 1993;43(4):662–7.
Deisenhammer F, Reindl M, Harvey J, Gasse T, Dilitz E, Berger T. Bioavailability of interferon beta 1b in MS patients with and without neutralizing antibodies. Neurology. 1999;52(6):1239–43.
Bertolotto A, Gilli F, Sala A, Malucchi S, Milano E, Melis F, et al. Persistent neutralizing antibodies abolish the interferon beta bioavailability in MS patients. Neurology. 2003;60(4):634–9.
Ross C, Clemmesen KM, Svenson M, Sørensen PS, Koch-Henriksen N, Skovgaard GL, et al. Immunogenicity of interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis patients: influence of preparation, dosage, dose frequency, and route of administration. Danish Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Ann Neurol. 2000;48(5):706–12.
Bertolotto A, Deisenhammer F, Gallo P, Sölberg Sørensen P. Immunogenicity of interferon beta: differences among products. J Neurol. 2004;251(Supl 2):II15–24.
Hermeling S, Jiskoot W, Crommelin D, Bornaes C, Schellekens H. Development of a transgenic mouse model immune tolerant for human interferon Beta. Pharm Res. 2005;22(6):847–51.
Van Beers M, Jiskoot W, Schellekens H. On the role of aggregates in the immunogenicity of recombinant human interferon beta in patients with multiple sclerosis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010;30(10):767–75.
Hartung H, Polman C, Bertolotto A, Deisenhammer F, Giovannoni G, Havrdova E, et al. Neutralising antibodies to interferon beta in multiple sclerosis: expert panel report. J Neurol. 2007;254(7):827–37.
Runkel L, Meier W, Pepinsky RB, Karpusas M, Whitty A, Kimball K, et al. Structural and functional differences between glycosylated and non-glycosylated forms of human interferon-β (IFN-β). Pharm Res. 1998;15(4):641–9.
Sorensen P. Neutralizing antibodies against interferon-beta. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2008;1(2):62–8.
Bendtzen K. Critical Review: assessment of interferon-β immunogenicity in multiple sclerosis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010;30(10):759–66.
Evidence of interferon beta-1a dose response in relapsing-remitting MS: the OWIMS Study. The Once Weekly Interferon for MS Study Group. Neurology. 1999;53(4):679–686.
Clanet M, Radue EW, Kappos L, Hartung HP, Hohlfeld R, Sandberg-Wollheim M, et al. European IFNbeta-1a (Avonex) dose-comparison study investigators. A randomized, double-blind, dose-comparison study of weekly interferon beta-1a in relapsing MS. Neurology. 2002;59(10):1507–17.
Freedman M, Francis GS, Sanders EA, Rice GP, O’Connor P, Comi G, et al. Once Weekly Interferon beta-1alpha for Multiple Sclerosis Study Group; University of British Columbia MS/MRI Research Group. Randomized study of once-weekly interferon beta-1la therapy in relapsing multiple sclerosis: three-year data from the OWIMS study. Mult Scler. 2005;11(1):41–5.
Cohen B, Rivera VM. PRISMS: the story of a pivotal clinical trial series in multiple sclerosis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(8):827–38.
van Beers M, Sauerborn M, Gilli F, Hermeling S, Brinks V, Schellekens H, et al. Hybrid transgenic immune tolerant mouse model for assessing the breaking of B cell tolerance by human interferon beta. J Immunol Methods. 2010;352(1–2):32–7.
Schellekens H. Factors influencing the immunogenicity of therapeutic proteins. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20 Suppl 6:vi3–9.
Singh S. Impact of product-related factors on immunogenicity of biotherapeutics. J Pharm Sci. 2011;100(2):357–87.
Barbosa M, Celis E. Immunogenicity of protein therapeutics and the interplay between tolerance and antibody responses. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12(15–16):674–81.
Perini P, Facchinetti A, Bulian P, Massaro AR, Pascalis DD, Bertolotto A, et al. Interferon-beta (INF-beta) antibodies in interferon-beta1a- and interferon-beta1b-treated multiple sclerosis patients. Prevalence, kinetics, cross-reactivity, and factors enhancing interferon-beta immunogenicity in vivo. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001;12(1):56–61.
Braun A, Kwee L, Labow MA, Alsenz J. Protein aggregates seem to play a key role among the parameters influencing the antigenicity of interferon alpha (IFN-α) in normal and transgenic mice. Pharm Res. 1997;14(10):1472–8.
Schellekens H, Jiskoot W. Erythropoietin-Associated PRCA: still an unsolved mystery. J Immunotoxicol. 2006;3(3):123–30.
Administration. FaD. Adalimumab. 2002. Pharmacology Reviews: Adalimumab product approval information—licensing action.; 2002 December 31. Available from: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2008/125057s110TOC.cfm
Peng A, Kosloski M, Nakamura G, Ding H, Balu-Iyer SV. PEGylation of a factor VIII-phosphatidylinositol complex: pharmacokinetic and immunogenicity in hemophilia A mice. AAPS J. 2011;14(1):35–42.
Van Regenmortel M, Boven K, Bader F. Immunogenicity of biopharmaceuticals: an example from erythropoietin. BioPharm Int. 2005;18(8):36–52.
Acknowledgments and Disclosures
We acknowledge Darren P. Baker, Ph.D. from BiogenIdec for kindly providing the IFNβ-1a (Avonex® drug substance) which we used in the ELISA to detect ADAs. We thank Abdul Basmeleh for performing the ELISAs described in this article.
GK, WJ and VB declare no financial and commercial conflict of interest. HS has participated in meeting and publications sponsored by Amgen, Johnson & Johnson, Roche, Sandoz and Hospira. Part of his research is directly or indirectly sponsored by Roche and Amgen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kijanka, G., Jiskoot, W., Schellekens, H. et al. Effect of Treatment Regimen on the Immunogenicity of Human Interferon Beta in Immune Tolerant Mice. Pharm Res 30, 1553–1560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-0992-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-0992-9