ABSTRACT
Purpose
Biolabile cationic lipids were developed for efficient intracellular delivery of DNA and siRNA.
Methods
The compounds have been designed starting from the membrane lipid DOPC in a way they may loose their cationic charge when exposed to an acidic and/or enzymatic stimulus, such as those met during the journey of a lipoplex in biological media.
Results
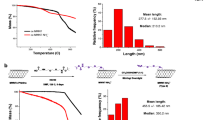
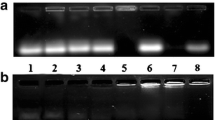
They demonstrated remarkable efficiency to deliver DNA in various cell lines (BHK-21, Calu-3, NCI-H292, and A549), with no significant cytotoxicity. Furthermore, two of the compounds (carbonate-based DOPC derivatives) revealed able to deliver small interfering RNA in U87Luc and A549Luc cancer cells and to mediate a selective 70–80% knockdown of the stably transfected luciferase gene.
Conclusions
The results show that the described bioresponsive cationic lipids have high DNA and siARN delivery activity which is encouraging in view of delivering a therapeutic nucleic acid to pulmonary tissues in vivo.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Behr JP. DNA strongly binds to micelles and vesicles containing lipopolyamines or lipointercalants. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:5861–4.
Felgner PL, Gadek TR, Holm M, Roman R, Chan HW, Wenz M, Noethrop JP, Ringold GM, Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:7413–7.
Felgner JH, Kumar R, Sridhar CN, Wheeler CJ, Tsai YJ, Border R, Ramsey P, Martin M, Felgner PL. Enhanced gene delivery and mechanism studies with a novel series of cationic lipid formulations. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:2550–61.
Godbey WT, Wu KK, Mikos A. Tracking the intracellular path of poly(ethylenimine)/DNA complexes for gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:5177–81.
Lu JJ, Langer R, Chen J. A novel mechanism is involved in cationic lipid-mediated functional siRNA delivery. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:763–71.
Ming X, Sato K, Juliano RL. Unconventional internalization mechanisms underlying functional delivery of antisense oligonucleotides via cationic lipoplexes and polyplexes. J Control Release. 2011;153:83–92.
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B, Behr JP. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:7297–301.
Koynova R, Wang L, MacDonald RC. An intracellular lamellar-nonlamellar phase transition rationalizes the superior performance of some cationic lipid transfection agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:14373–8.
Wagner E, Plank C, Zatloukal K, Cotten M, Birnstiel ML. Influenza virus hemagglutinin HA-2 N-terminal fusogenic peptides augment gene transfer by transferrin-polylysine-DNA complexes: toward a synthetic virus-like gene-transfer vehicle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:7934–8.
Capecchi MR. High efficiency transformation by direct microinjection of DNA into cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1980;22:479–88.
Pozharski E, MacDonald RC. Lipoplex thermodynamics: determination of DNA-cationic lipoid interaction energies. Biophys J. 2003;85:3969–78.
Xu XH, Szoka FC. Mechanism of DNA release from cationic liposome/DNA complexes used in cell transfection. Biochemistry. 1996;35:5616–23.
Prata CAH, Zhao YX, Barthelemy P, Li YG, Luo D, McIntosh TJ, Lee SJ, Grinstaff MW. Charge-reversal amphiphles for gene delivery. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:12196–7.
Zhang XX, Prata CAH, McIntosh TJ, Barthelemy P, Grinstaff MW. The effect of charge-reversal amphiphile spacer composition on DNA and siRNA delivery. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010;21:988–93.
Zhang XX, Allen PG, Grinstaff MW. Macropinocytosis is the major pathway responsible for DNA transfection in CHO cells by a charge-reversal amphiphile. Mol Pharm. 2011;8:758–66.
MacDonald RC, Ashley GW, Shida MM, Rakhmanova VA, Tarahovsky YS, Pantazatos DP, Kennedy MT, Pozharski EV, Baker KA, Jones RD, Rosenzweig HS, Choi KL, Qiu RZ, McIntosh TJ. Physical and biological properties of cationic triesters of phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1999;77:2612–29.
MacDonald RC, Rakhmanova VA, Choi KL, Rosenzweig HS, Lahiri MK. O-Ethylphosphatidylcholine: a metabolizable cationic phospholipid which is a serum-compatible DNA transfection agent. J Pharm Sci. 1999;88:896–904.
Pierrat P, Creusat G, Laverny G, Pons F, Zuber G, Lebeau L. A Cationic phospholipid–detergent conjugate as a new efficient carrier for siRNA delivery. Chem Eur J. 2012;18:3835–9.
Pierrat P, Laverny G, Creusat G, Wehrung P, Strub JM, Van Dorsselaer A, et al. Phospholipid-detergent conjugates as efficient lipidic carriers for siRNA delivery. Chem Eur J. in press, doi:10.1002/chem.201203071.
Lebeau L, Olland S, Oudet P, Mioskowski C. Rational design and synthesis of phospholipids for the two-dimensional crystallization of DNA gyrase, a key element in chromosome organization. Chem Phys Lipids. 1992;62:93–103.
Zanta MA, Boussif O, Adib A, Behr JP. In vitro gene delivery to hepatocytes with galactosylated polyethylenimine. Bioconjugate Chem. 1997;8:839–44.
Foillard S, Zuber G, Doris E. Polyethylenimine-carbon nanotube nanohybrids for siRNA-mediated gene silencing at cellular level. Nanoscale. 2011;3:1461–4.
Dikmen ZG, Gellert GC, Jackson S, Gryaznov S, Tressler R, Dogan P, Wright WE, Shay JW. In vivo inhibition of lung cancer by GRN163L: a novel human telomerase inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7866–73.
Gentine P, Bubel A, Crucifix C, Bourel-Bonnet L, Frisch B. Manufacture of liposomes by isopropanol injection: characterization of the method. J Liposome Res. 2011;22:18–30.
Gorman CM, Aikawa M, Fox B, Fox E, Lapuz C, Michaud B, Nguyen H, Roche E, Sawa T, WienerKronish JP. Efficient in vivo delivery of DNA to pulmonary cells using the novel lipid EDMPC. Gene Ther. 1997;4:983–92.
Shpirt AM, Kononov LO, Maltsev SD, Shibaev VN. Chemical synthesis of polyprenyl sialyl phosphate, a probable biosynthetic intermediate of bacterial polysialic acid. Carbohydr Res. 2011;346:2849–54.
Farquhar D, Khan S, Wilkerson MC, Andersson BS. Biologically-cleavable phosphate protective groups: 4-acyloxy-1,3,2-dioxaphosphorinanes as neutral latent precursors of dianionic phosphates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:655–8.
Crich D, Picard S. Highly stereoselective synthesis of α-D-mannopyranosyl phosphosugars. J Org Chem. 2009;74:9576–9.
Yang Y, Babiak P, Reymond JL. New monofunctionalized fluorescein derivatives for the efficient high-throughput screening of lipases and esterases in aqueous media. Helv Chim Acta. 2006;89:404–15.
Thomas JD, Sloan KB. Overcoming steric effects in the coupling reaction of alkyloxycarbonyloxymethyl (AOCOM) halides with phenols: an efficient synthesis of AOCOM phenolic prodrugs. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:109–12.
Ostergaard J, Larsen C. Bioreversible derivatives of phenol. 2. Reactivity of carbonate esters with fatty acid-like structures towards hydrolysis in aqueous solutions. Molecules. 2007;12:2396–412.
Ross PC, Hui SW. Lipoplex size is a major determinant of in vitro lipofection efficiency. Gene Ther. 1999;6:651–9.
Hübner W, Blume A. Interactions at the lipid–water interface. Chem Phys Lipids. 1998;96:99–123.
Geall AJ, Blagbrough IS. Rapid and sensitive ethidium bromide fluorescence quenching assay of polyamine conjugate—DNA interactions for the analysis of lipoplex formation in gene therapy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000;22:849–59.
Rosenzweig HS, Rakhmanova VA, McIntosh TJ, MacDonald RC. O-Alkyl dioleoylphosphatidylcholinium compounds: the effect of varying alkyl chain length on their physical properties and in vitro DNA transfection activity. Bioconjugate Chem. 2000;11:306–13.
Wang L, Koynova R, Parikh H, MacDonald RC. Transfection activity of binary mixtures of cationic O-substituted phosphatidylcholine derivatives: the hydrophobic core strongly modulates physical properties and DNA delivery efficacy. Biophys J. 2006;91:3692–706.
Munnecke DM. Enzymatic-hydrolysis of organophosphate insecticides, a possible pesticide disposal method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976;32:7–13.
Heeg K, Reimann J, Kabelitz D, Hardt C, Wagner H. A rapid colorimetric assay for the determination of IL-2-producing Helper T-cell frequencies. J Immunol Methods. 1985;77:237–46.
Hui SW, Langner M, Zhao YL, Ross P, Hurley E, Chan K. The role of helper lipids in cationic liposome-mediated gene transfer. Biophys J. 1996;71:590–9.
Koltover I, Salditt T, Radler JO, Safinya CR. An inverted hexagonal phase of cationic liposome-DNA complexes related to DNA release and delivery. Science. 1998;281:78–81.
Sanders N, Rudolph C, Braeckmans K, De Smedt SC, Demeester J. Extracellular barriers in respiratory gene therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61:115–27.
Rosenecker J, Naundorf S, Gersting SW, Hauck RW, Gessner A, Nicklaus P, Müller RH, Rudolph C. Interaction of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid with polyplexes and lipoplexes: analysing the role of proteins and glycoproteins. J Gene Med. 2003;5:49–60.
Merkel OM, Beyerle A, Librizzi D, Pfestroff A, Behr TM, Sproat B, Barth PJ, Kissel T. Nonviral siRNA delivery to the lung: Investigation of PEG-PEI polyplexes and their in vivo performance. Mol Pharm. 2009;6:1246–60.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS AND DISCLOSURES
This work was supported by the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (ANR, France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 26 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierrat, P., Kereselidze, D., Wehrung, P. et al. Bioresponsive Deciduous-Charge Amphiphiles for Liposomal Delivery of DNA and siRNA. Pharm Res 30, 1362–1379 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-0976-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-013-0976-9