Abstract
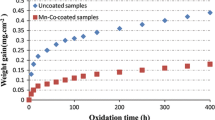
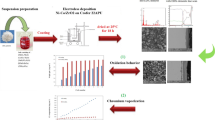
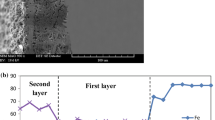
An issue associated with chromia-scale formation on ferritic stainless steels is an associated increase in electrical resistance over time, due to the oxide growth. Further, the migration of chromium via chromia-scale evaporation into solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) cathodes can result in degradation in cell electrochemical performance. In this research, manganese and cobalt were deposited by the pack cementation method onto Crofer 22 APU ferritic stainless steel. Isothermal and cyclic oxidation was carried out to evaluate the role of coating materials during oxidation. Area-specific resistance (ASR) of the Mn–Co-coated substrates was also tested at 800 °C. The results demonstrate that the coating layer transforms to MnCo2O4, CoFe2O4, CoCr2O4, and Co3O4 spinels during oxidation. This scale is protective, and acts as an effective barrier against chromium migration into the outer oxide. Mn–Co oxide and cobalt oxides also cause a reduction in ASR, in comparison to that of bare steel.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Horita, Y. Xiong, K. Yamaji, N. Sakai and H. Yokokawa, Stability of Fe–Cr alloy interconnects under CH4–H2O atmosphere for SOFCs. Journal of Power Sources 118, 35–43 (2003).
J. W. Fergus, Metallic interconnects for solid oxide fuel cells. Materials Science and Engineering A 397, 271–283 (2005).
C. Lee and J. Bae, Oxidation-resistant thin film coating on ferritic stainless steel by sputtering for solid oxide fuel cells. Thin Solid Films. 516, 6432–6437 (2008).
X. Chen, P. Y. Hou, C. P. Jacobson, S. J. Visco and L. C. De Jonghe, Protective coating on stainless steel interconnect for SOFCs: oxidation kinetics and electrical properties. Solid State Ionics 176, 425–433 (2005).
Z. Yang, G. G. Xia, S. P. Simner and J. W. Stevenson, Thermal growth and performance of manganese cobaltite spinel protection layers on ferritic stainless steel SOFC interconnects. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 152, 1896–1901 (2005).
N. Laosiripojana and S. Assabumrungrat, Catalytic steam reforming of methane, methanol, and ethanol over Ni/YSZ: the possible use of these fuels in internal reforming SOFC. Journal of Power Sources 163, 943–951 (2007).
W. J. Quadakkers, J. Piron-Abellan, V. Shemet and L. Singheiser, Metallic interconnectors for solid oxide fuel cells- A review. Materials at High Temperatures. 20, 115–127 (2003).
W. Z. Zhu and S. C. Deevi, Development of interconnect materials for solid oxide fuel cells. Materials Science and Engineering A. 384, 227–243 (2003).
Z. Yang, G. Xia, G. Maupin and J. Stevenson, Conductive protection layers on oxidation resistant alloys for SOFC interconnect applications. Surface & Coatings Technology 201, 4476–4483 (2006).
P. Huczkowski, N. Christiansen, V. Shemet, J. P. Abellan, L. Singheiser and W. J. Quadakkers, Oxidation induced lifetime limits of chromia forming ferritic interconnector steels. Journal of Fuel Cell Science and Technology. 1, 30–34 (2004).
H. Kurokawa, C. P. Jacobson, L. C. DeJonghe and S. J. Visco, Chromium vaporization of bare and of coated iron-chromium alloys at 1073 K. Solid State Ionics. 178, 287–296 (2007).
S. Lee, J. Hong, H. Kim, J. W. Son, J. H. Lee, B. K. Kim, H. W. Lee and K. J. Yoonz, Highly Dense Mn–Co Spinel Coating for Protection of Metallic Interconnect of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 161, F1389–F1394 (2014).
Z. Yang, G. Xia, X. Li and J. W. Stevenson, (Mn, Co)3O4 spinel coatings on ferritic stainless steels for SOFC interconnect applications. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 32, 3648–3654 (2007).
Z. G. Yang, G. G. Xia, S. P. Simner and J. W. Stevenson, Mn1.5Co1.5O4 Spinel Protection Layers on Ferritic Stainless Steels for SOFC Interconnect Applications, Electrochemical Solid-State. Letters 8, A168–A170 (2005).
W. Wei, W. Chen and D. G. Ivey, Anodic electrodeposition of nanocrystalline coatings in the Mn–Co–O system. Chemistry of Materials. 19, 2816–2822 (2007).
M. R. Bateni, P. Wei, X. Deng and A. Petric, Spinel coatings for UNS 430 stainless steel interconnects. Surface & Coatings Technology 201, 4677–4684 (2007).
P. Wei, X. Deng, M. R. Bateni and A. Petric, Oxidation and electrical conductivity behavior of spinel coatings for metallic interconnects of solid oxide fuel cells. Corrosion. 63, 529–536 (2007).
W. Wei, W. Chen and D. G. Ivey, Oxidation resistance and electrical properties of anodically electrodeposited Mn–Co oxide coatings for solid oxide fuel cell interconnect applications. Journal of Power Sources 186, 428 (2009).
X. Deng, P. Wei, M. R. Bateni and A. Petric, Cobalt plating of high temperature stainless steel interconnects. Journal of Power Sources 160, 1225–1229 (2006).
H. Ebrahimifar and M. Zandrahimi, Mn coating on AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel by pack cementation method for SOFC interconnect applications. Solid State Ionics 183, 71–79 (2011).
H. Ebrahimifar and M. Zandrahimi, Oxidation and electrical behavior of AISI 430 coated with cobalt spinels for SOFC interconnect applications. Surface & Coatings Technology 206, 75–81 (2011).
D. Schmidt and M. Galetz, M. Schu¨ tze, Deposition of Manganese and Cobalt on Ferritic–Martensitic Steels via Pack Cementation Process. Oxidation of Metals 79, 589–599 (2013).
W. J. Quadakkers, J. Piron-Abellan, V. Shemet and L. Singheiser, Metallic interconnectors for solid oxide fuel cells—a review. Materials at High Temperatures 20, 115–127 (2003).
C. Wagner, Types of Reaction in the Oxidation of Alloys. Z. Elektrochem. 63, 772–782 (1959).
G. C. Wood and D. P. Whittle, Chromium Oxide Scale Growth on Iron-Chromium Alloys: i. The Influence of Variables on the Oxidation of Fe-28% Cr. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 115, 126–133 (1968).
L. Chen, E. Y. Sun, J. Yamanis and N. Magdefrau, Oxidation Kineticsof Mn1.5Co1.5O4-Coated Haynes 230 and Crofer 22 APU for Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Interconnects. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 157, B931–B942 (2010).
B. Hua, J. Pu, W. Gong, J. F. Zhang, F. S. Lu and L. Jian, Cyclic Oxidation of Mn–Co Spinel Coated SUS 430 Alloy in the Cathodic Atmosphere of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Journal of Power Sources 185, (1), 419–422 (2008).
N. Shaigan, D. G. Ivey and W. Chen, Oxidation and electrical behavior of nickel/lanthanum chromite-coated stainless steel interconnects. Journal of Power Sources 183, 651–659 (2008).
T. Brylewski, M. Nanko, T. Maruyama and K. Przybylski, Application of Fe-16Cr ferritic alloy to interconnector for a solid oxide fuel cell. Solid State Ionics 143, 131–150 (2001).
S. Fontana, R. Amendola, S. Chevalier, P. Piccardo, G. Caboche, M. Viviani, R. Molins and M. Sennour, Metallic interconnects for SOFC: characterisation of corrosion resistance and conductivity evaluation at operating temperature of differently coated alloys. Journal of Power Sources. 171, 652–662 (2007).
T. Horita, Y. Xiong, K. Yamaji, N. Sakai and H. Yokokawa, Evaluation of Fe-Cr alloys as interconnects for reduced operation temperature SOFCs. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 150, A243–A247 (2003).
R. E. Lobnig, H. P. Schmidt, K. Hennesen and H. J. Grabke, Diffusion of cations in chromia layers grown on iron-base alloys. Oxidation of Metals 37, 81–93 (1992).
M. G. C. Cox, B. Mcenaney and V. D. Scott, Chemical diffusion model for partitioning of transition elements in oxide scales on alloys. Philosophical Magazine 26, 839–851 (1972).
H. Kurokawa, K. Kawamura and T. Maruyama, Oxidation behavior of Fe–16Cr alloy interconnect for SOFC under hydrogen potential gradient. Solid State Ionics. 168, 13–21 (2004).
H. Ebrahimifar and M. Zandrahimi, Evaluation of the parabolic rate constant during different types of oxidation tests for spinel coated Fe-17%Cr alloy. Oxidation of Metals 75, 125–141 (2010).
H. Ebrahimifar and M. Zandrahimi, Influence of oxide scale thickness on electrical conductivity of coated AISI 430 steel for use as interconnect in solid oxide fuel cells. Ionics 18, 615–624 (2012).
X. B. Chen, L. Zhang and S. P. Jiang, Chromium deposition and poisoning on (La0.6 Sr0.4-x Bax) (Co0.2 Fe0.8) O3 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.4) cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 155, B1093–B1101 (2008).
S. P. Jiang and Y. D. Zhen, Mechanism of Cr deposition and its application in the development of Cr-tolerant cathodes of solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ionics 179, 1459–1464 (2008).
J. W. Fergus, Effect of cathode and electrolyte transport properties on chromium poisoning in solid oxide fuel cells. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 32, 3664–3671 (2007).
E. Konysheva, J. Mertens, H. Penkalla, L. Singheiser and K. Hilpert, Chromium Poisoning of the Porous Composite Cathode Effect of Cathode Thickness and Current Density. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 154, B1252–B1264 (2007).
K. Ogasawara, H. Kameda, Y. Matsuzaki, T. Sakurai, T. Uehara, A. Toji, N. Sakai, K. Yamaji, T. Horita and H. Yokokawa, Chemical Stability of Ferritic Alloy Interconnect for SOFCs. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 154, B657–B663 (2007).
M. Stanislowski, J. Froitzheim, L. Niewolak, W. J. Quadakkers, K. Hilpert, T. Markus and L. Singheiser, Reduction of chromium vaporization from SOFC interconnectors by highly effective coatings. Journal of Power Sources 164, 578–589 (2007).
H. Yokokawa, T. Horita, N. Sakai, K. Yamaji, M. E. Brito, Y. P. Xiong and H. Kishimoto, Thermodynamic considerations on Cr poisoning in SOFC cathodes. Solid State Ionics 177, 3193–3198 (2006).
E. Konysheva, H. Penkalla, E. Wessel, J. Mertens, U. Seeling, L. Singheiser and K. Hilpert, Chromium Poisoning of Perovskite Cathodes by the ODS Alloy Cr5Fe1Y2O3 and the High Chromium Ferritic Steel Crofer22APU. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 153, A765–A773 (2006).
S. C. Paulson and V. I. Birss, Chromium Poisoning of LSM-YSZ SOFC Cathodes I. Detailed Study of the Distribution of Chromium Species at a Porous, Single-Phase Cathode. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 151, A1961–A1968 (2004).
Y. Matsuzaki and I. Yasuda, Dependence of SOFC Cathode Degradation by Chromium-Containing Alloy on Compositions of Electrodes and Electrolytes. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 148, A126–A131 (2001).
Y. Matsuzaki and I. Yasuda, The poisoning effect of sulfur-containing impurity gas on a SOFC anode: part I. Dependence on temperature, time, and impurity concentration. Solid State Ionics 132, 271–278 (2000).
M. Stanislowski, E. Wessel, K. Hilpert, T. Markus and L. Singheiser, Chromium vaporization from high-temperature alloys I. outer oxide layers. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 154, (4), A295–A306 (2007).
N. Sakai, T. Horita, K. Yamaji, Y. P. Xiong, H. Kishimoto, M. E. Brito and H. Yokokawa, Material transport and degradation behavior of SOFC interconnects. Solid State Ionics 177, 1933–1939 (2006).
Z. G. Yang, G. G. Xia, P. Singh and J. W. Stevenson, Electrical contacts between cathodes and metallic interconnects in solid oxide fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources 155, 246–252 (2006).
J. Zurek, E. Wessel, L. Niewolak, F. Schmitz, T.-U. Kern, L. Singheiser and W. J. Quadakkers, Anomalous temperature dependence of oxidation kinetics during steam oxidation of ferritic steels in the temperature range 550–650 & #xB0;C. Corrosion Science 46, 2301 (2004).
H. Ling, A. Petric, Electrical and Thermal Properties of Spinels, IX International Conference on Solid Oxide Fuel cells IX, (Quebec city, Canada, 2005), p. 1866.
H. Ling, MsC Thesis, High Temperature and Thermal Properties of Transition Metal Spinel Oxides, McMaster University, Canada, August 2004, p. 83.
A. Petric and H. Ling, Electrical conductivity and thermal expansion of spinels at elevated temperatures. Journal of the American Ceramic Society 90, 1515–1520 (2007).
J. L. Gonzalez-Carrasco, P. Perez, P. Adeva and J. Chao, Oxidation behaviour of an ODS NiAl-based intermetallic alloy. Intermetallics. 7, 69–78 (1999).
P.Y. Hou, K. Huang, W.T. Bakker, in Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC VI), eds. S.C. Singhal and M. Dokiya (Honolulu, Hawaii, 1999) p. 737.
N. Shaigan, D. G. Ivey and W. Chen, Metal-oxide scale interfacial imperfections andperformance of stainless steels utilized as interconnects in solid oxide fuel Cells. Journal of the Electrochemical Society 156, B765–B770 (2009).
N. Shaigan, W. Qu, D. G. Ivey and W. Chen, A review of recent progress in coatings, surface modifications and alloy developments for solid oxide fuel cell ferritic stainless steel interconnects. Journal of Power Sources. 195, 1529–1542 (2010).
A. Holta and P. Kofstada, Electrical conductivity and defect structure of Cr2O3. II. Reduced temperatures (<1000 °C). Solid State Ionics. 69, 137–143 (1994).
Acknowledgments
This research has been conducted with the cooperation of the Iran New Energies Organization. The authors would like to thank this organization for providing research funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimifar, H., Zandrahimi, M. Oxidation and Electrical Behavior of Mn-Co-Coated Crofer 22 APU Steel Produced by a Pack Cementation Method for SOFC Interconnect Applications. Oxid Met 84, 129–149 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9547-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-015-9547-2