Abstract
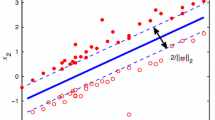
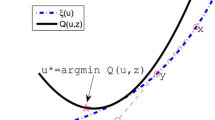
We present an algorithm for training dual soft margin support vector machines (SVMs) based on an augmented Lagrangian (AL) that uses a modification of the fast projected gradient method (FPGM) with a projection on a box set. The FPGM requires only first derivatives, which for the dual soft margin SVM means computing mainly a matrix-vector product. Therefore, AL-FPGM being computationally inexpensive may complement existing quadratic programming solvers for training large SVMs. We report numerical results for training the SVM with the AL-FPGM on data up to tens of thousands of data points from the UC Irvine Machine Learning Repository.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloom V, Griva I, Kwon B, Wolff A-R (2014) Exterior-point method for support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 25(7):1390–1393
Bottou L, Lin CJ (2007) Support vector machine solvers. In Large scale kernel machines. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp. 301–320. [Online]. Available http://www.leon.bottou.org/papers/bottou-lin-2006
Chang CC, Hsu CW, Lin CJ (2000) The analysis of decomposition methods for support vector machines. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11:1003–1008
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intell Syst Technol, vol. 2, pp. 27:1–27:27
Conn AR, Gould NIM, Toint PL (1991) A globally convergent aug- mented lagrangian algorithm for optimization with general constraints and simple bounds. SIAM J Numer Anal 28(2):545–572
Ferris MC, Munson TS (2003) Interior-point methods for massive support vector machines. SIAM J Optim 13(3):783–804
Frank A, Asuncion A (2010) UCI machine learning repository [Online]. Available: http://www.archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Gondzio J (2012) Interior point methods in machine learning. In: Sra S, Nowozin S, Wright SJ (eds) Optimization for machine learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Griva I, Polyak R (2008) 1.5-Q-superlinear convergence of an exterior-point method for constrained optimization. J Glob Optim 40(4):679–695
Guyon I, Gunn S, Ben-Hur A, Dror G (2005) Result analysis of the NIPS 2003 feature selection challenge. In: Saul LK, Weiss Y, Bottou L (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 17. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 545–552
Hestenes MR (1969) Multiplier and gradient methods. J Optim Theory Appl 4:303–320
Joachims T (1999) Making large-scale svm learning practical. In: Schlkopf B, Burges C, Smola A (eds) Advances in kernel methods: support vector learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Nesterov Y (2004) Introductory lectures on convex optimization. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Osuna E, Freund R, Girosi R (1997) An improved training algorithm for support vector machines, vol. VII. Neural networks for signal processing. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE workshop (Sept 1997)
Platt J (1998) Sequential minimial optimization: a fast alogrithm for trainning support vector machines. Microsoft Research, Tech Rep MSR-TR-98-14
Polyak RA (2013) Dual fast projected gradient method for quadratic programming. Optim Lett 7:631–645
Polyak RA (2015) Projected gradient method for non-negative least square. Contemp Math 636:167–179
Powell MJD (1969) A method for nonlinear optimization in minimization problems. In: Fletcher R (ed) Optimization. Academic Press, New York, pp 283–298
Rockafellar RT (1976) Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J Control Optim 14:887–898
Rockafellar RT (1976) Augmented lagrangians and applications of the proximal point algorithm in convex programming. Math Oper Res 1:97–116
Sra S, Nowozin S, Wright SJ (2012) Introduction: optimization and machine learning. In: Sra S, Nowozin S, Wright SJ (eds) Optimization for machine learning. MIT Press, Cambridge
Vanderbei RJ, Shanno DF (1999) An interior-point algorithm for nonconvex nonlinear programming. Comput Optim Appl 13:231–252
Vapnik VN (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bloom, V., Griva, I. & Quijada, F. Fast projected gradient method for support vector machines. Optim Eng 17, 651–662 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-016-9328-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11081-016-9328-z